
The following are two reaction-schemes involving magnesium. Find Compounds A to J based on the observations given are
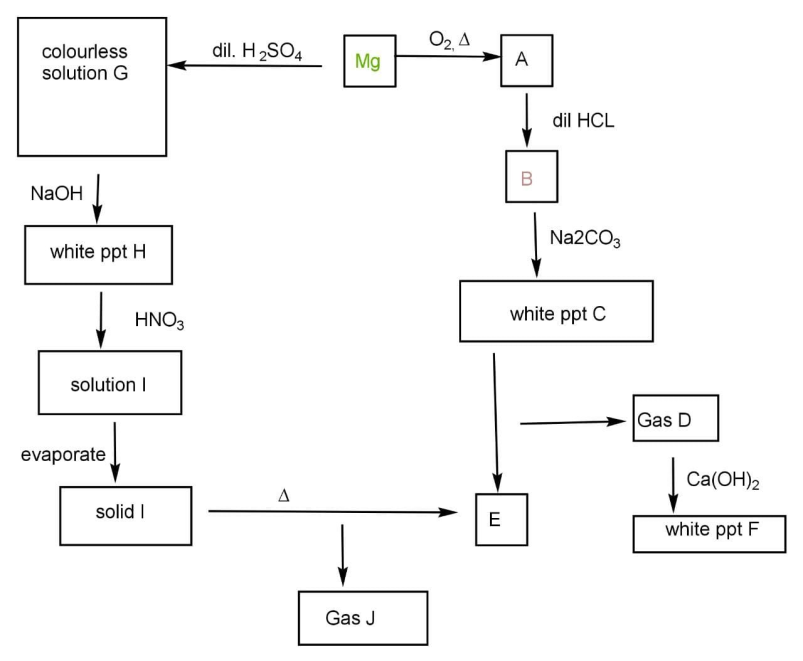
A.\[{\text{A: MgO}}\]
B.\[{\text{D: C}}{{\text{O}}_2}\]
C.\[{\text{F: CaC}}{{\text{O}}_3}\]
D.\[{\text{J: N}}{{\text{O}}_2}\]
D.All of these correct.

Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: Magnesium oxidised in the presence of oxygen. In the presence of acid displacement reaction occurs. The gas D released plays an important role in the respiration process. Magnesium hydroxide is white in colour.
Complete step by step answer:
It is a two way reaction that is the reaction the magnesium is treated with two different reagents and they ultimately form the same products.
First when magnesium is reacted with oxygen then magnesium oxide is formed. It is a very common reaction of burning of magnesium ribbon as the reaction occurs as:
\[{\text{2Mg}} + {\text{O}} \to {\text{2MgO}}\]
When magnesium oxide is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid then the displacement reaction occurs and oxygen is replaced by chlorine. The formation of magnesium chloride occurs:
\[{\text{MgO}} + {\text{2HCl}} \to {\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\]
Again magnesium chloride reacts with sodium carbonate white colour precipitate of magnesium carbonate. The white precipitate C of magnesium carbonate is:
\[{\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}} + {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} \to {\text{2NaCl}} + {\text{MgC}}{{\text{O}}_3}\]
When we heat carbonates and carbon dioxide gas is released. So heating magnesium carbonate will give us magnesium oxide the compound E and carbon dioxide gas D. the reaction occurs as:
\[{\text{MgC}}{{\text{O}}_3}\xrightarrow{\Delta }{\text{ MgO}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ }}\]
When carbon dioxide reacts with calcium hydroxide, it forms calcium carbonate, \[{\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_3}\] that id compound F and we all know the colour of calcium carbonate is white.
The product E formed is magnesium oxide. So this side of reaction we have done, now we move towards the left hand side:
Magnesium reacts with sulphuric acid to form magnesium sulphate and hydrogen gas is released.
\[{\text{Mg}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} \to {\text{4MgS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\]
The solution of magnesium sulphate is colourless. When we react with magnesium sulphate with Sodium hydroxide it forms the compound H that is magnesium hydroxide which is white in colour.
Magnesium hydroxide when treated with nitric acid forms magnesium nitrate:
\[{\text{Mg}}{\left( {{\text{OH}}} \right)_2} + 2{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_3} \to {\text{Mg}}{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_3}} \right)_2} + 2{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\]
When the solution of magnesium nitrate is heated we get solid magnesium nitrate.
Heating solid magnesium nitrate will give us nitrogen dioxide gas and magnesium oxide which is the compound E. The gas J is nitrogen dioxide:
\[{\text{Mg}}{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_3}} \right)_2}\xrightarrow{\Delta }{\text{MgO}} + {\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}\]
Hence, cycle completes and all the given options are correct.
Hence, the correct option is E.
Note:
Magnesium belongs to group number 2 of modern periodic table. Its atomic number is 12 and mass number is 24. It is a second period element. It is also known as alkaline earth metal because its oxide and hydroxide is basic in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
It is a two way reaction that is the reaction the magnesium is treated with two different reagents and they ultimately form the same products.
First when magnesium is reacted with oxygen then magnesium oxide is formed. It is a very common reaction of burning of magnesium ribbon as the reaction occurs as:
\[{\text{2Mg}} + {\text{O}} \to {\text{2MgO}}\]
When magnesium oxide is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid then the displacement reaction occurs and oxygen is replaced by chlorine. The formation of magnesium chloride occurs:
\[{\text{MgO}} + {\text{2HCl}} \to {\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\]
Again magnesium chloride reacts with sodium carbonate white colour precipitate of magnesium carbonate. The white precipitate C of magnesium carbonate is:
\[{\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}} + {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} \to {\text{2NaCl}} + {\text{MgC}}{{\text{O}}_3}\]
When we heat carbonates and carbon dioxide gas is released. So heating magnesium carbonate will give us magnesium oxide the compound E and carbon dioxide gas D. the reaction occurs as:
\[{\text{MgC}}{{\text{O}}_3}\xrightarrow{\Delta }{\text{ MgO}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ }}\]
When carbon dioxide reacts with calcium hydroxide, it forms calcium carbonate, \[{\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_3}\] that id compound F and we all know the colour of calcium carbonate is white.
The product E formed is magnesium oxide. So this side of reaction we have done, now we move towards the left hand side:
Magnesium reacts with sulphuric acid to form magnesium sulphate and hydrogen gas is released.
\[{\text{Mg}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} \to {\text{4MgS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\]
The solution of magnesium sulphate is colourless. When we react with magnesium sulphate with Sodium hydroxide it forms the compound H that is magnesium hydroxide which is white in colour.
Magnesium hydroxide when treated with nitric acid forms magnesium nitrate:
\[{\text{Mg}}{\left( {{\text{OH}}} \right)_2} + 2{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_3} \to {\text{Mg}}{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_3}} \right)_2} + 2{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\]
When the solution of magnesium nitrate is heated we get solid magnesium nitrate.
Heating solid magnesium nitrate will give us nitrogen dioxide gas and magnesium oxide which is the compound E. The gas J is nitrogen dioxide:
\[{\text{Mg}}{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_3}} \right)_2}\xrightarrow{\Delta }{\text{MgO}} + {\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}\]
Hence, cycle completes and all the given options are correct.
Hence, the correct option is E.
Note:
Magnesium belongs to group number 2 of modern periodic table. Its atomic number is 12 and mass number is 24. It is a second period element. It is also known as alkaline earth metal because its oxide and hydroxide is basic in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




