
The flow of blood in a larger artery of an anesthetized dog is diverted through a venturi meter. The wider part of the meter has a cross-sectional area equal to that of the artery $A = 8m{m^2}$. The narrower part has area $a = 4m{m^2}$. The pressure drop in the artery is $24Pa$. What is the speed of the blood in the artery? Density of blood is $1.6 \times {10^3}kg/{m^3}$
A)$13.5 \times {10^{ - 2}}m/s$
B) $12.5 \times {10^{ - 2}}m/s$
C) $26.5 \times {10^{ - 2}}m/s$
D) $32.5 \times {10^{ - 2}}m/s$
Answer
524.2k+ views
Hint: The working of the venturi meter is based on the principle of Bernoulli’s equation. Use the equation of continuity of fluid in order to find the relation between the velocities of blood at the two parts of the artery. Then use Bernoulli’s equation to find the velocity.
Bernoulli’s equation is given by the formula,
$P + \rho gH + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {V^2} = p + \rho gh + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2}$
Complete step by step solution:
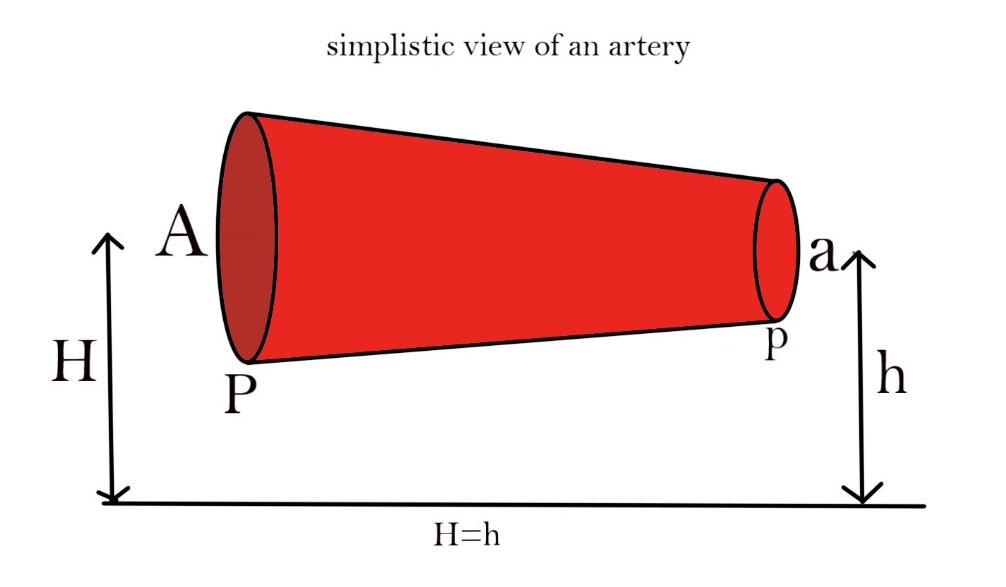
The area at the first part of artery is $A$and at the second part of the artery is $a$
Let the velocity of blood at the first part be $V$and at the second part be $v$
Law of continuity states that the volume of fluid entering in the pipe is equal to the volume of fluid leaving the pipe.
So,
By equation of continuity,
$AV = av$
$8 \times V = 4 \times v$
$2V = v$
Let it be equation 1.
Now,
Bernoulli’s equations states that,
$P + \rho gH + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {V^2} = p + \rho gh + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2}$
Where,
P is the pressure of fluid at part 1
P is the pressure of fluid at part 2
H is the height of the pipe at part 1
h is the height of pipe at part 2
but,
there is nothing given about the height of the artery so we assume $H = h$
the equation becomes
$P - p = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho ({V^2} - {v^2})$
$P - p$ is the difference in the pressure and is equal to $24Pa$ according to the question.
$\rho $is the density of blood
$24 = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 1.06 \times {10^3} \times (4{v^2} - {v^2})$
$v = 12.5 \times {10^{ - 2}}m/s$
$\therefore $ The speed of the blood in the artery is $12.5 \times {10^{ - 2}}m/s$. So, option (B) is correct.
Note:
The flow of blood in the arteries is laminar flow. This is the reason we are able to use Bernoulli’s equation for this problem. This equation is only valid in the case of laminar flow.
Bernoulli’s equation is given by the formula,
$P + \rho gH + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {V^2} = p + \rho gh + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2}$
Complete step by step solution:

The area at the first part of artery is $A$and at the second part of the artery is $a$
Let the velocity of blood at the first part be $V$and at the second part be $v$
Law of continuity states that the volume of fluid entering in the pipe is equal to the volume of fluid leaving the pipe.
So,
By equation of continuity,
$AV = av$
$8 \times V = 4 \times v$
$2V = v$
Let it be equation 1.
Now,
Bernoulli’s equations states that,
$P + \rho gH + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {V^2} = p + \rho gh + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2}$
Where,
P is the pressure of fluid at part 1
P is the pressure of fluid at part 2
H is the height of the pipe at part 1
h is the height of pipe at part 2
but,
there is nothing given about the height of the artery so we assume $H = h$
the equation becomes
$P - p = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho ({V^2} - {v^2})$
$P - p$ is the difference in the pressure and is equal to $24Pa$ according to the question.
$\rho $is the density of blood
$24 = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 1.06 \times {10^3} \times (4{v^2} - {v^2})$
$v = 12.5 \times {10^{ - 2}}m/s$
$\therefore $ The speed of the blood in the artery is $12.5 \times {10^{ - 2}}m/s$. So, option (B) is correct.
Note:
The flow of blood in the arteries is laminar flow. This is the reason we are able to use Bernoulli’s equation for this problem. This equation is only valid in the case of laminar flow.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




