
The flexibility in plants is due to a permanent tissue. This permanent tissue allows easy bending in various parts of a plant without breaking. It also provides mechanical support to plants. From the given figures, identify that tissue.

Answer
546.6k+ views
Hint: Plant body mainly consists of meristematic and permanent tissues. Meristematic cells are actively dividing cells, which occur at the tip of roots and shoots. On the other hand, permanent tissues are the ones which are formed from meristematic cells. Permanent tissue is specialised in performing major functions in the plant body. One of the types of permanent tissue is involved in providing flexibility and mechanical support to the plant.
Complete answer:
Permanent cells lose their ability to divide and perform specialised functions. There are two types of permanent tissue, namely simple and complex tissues.
Simple tissue – They possess structurally and functionally similar types of cells. Types of simple tissue –
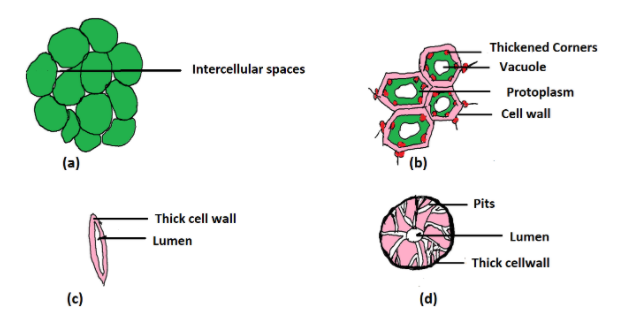
(i) Parenchyma – These are isodiametric in shape, having thin cellulosic walls. They are identified by the presence of small or inconspicuous intercellular spaces. They are mainly involved in photosynthesis, storage and secretion.
(ii) Collenchyma – These cells are oval, spherical or polygonal in shape. They have thickened cell corners due to the deposition of cellulose. They are responsible for providing flexibility and mechanical support to the young stems and leaves. They are identified by the presence of thickened corners.
(iii) Sclerenchyma – These are long, narrow cells with a cell wall made up of lignin. Cell wall may contain numerous pits. They are two types of sclerenchymatous tissue, namely fibres and sclereids. They provide mechanical support to the organs and trees during secondary stages.
Understanding the options one by one,
(A) Figure A represents parenchymatous tissue. This is identified by the presence of intercellular spaces. Thus, this cannot be the correct answer.
(B) Figure B represents collenchyma. This is identified by the presence of thickened corners. This is the correct answer, because collenchyma cells provide flexibility and mechanical strength to the young plant.
(C) Figure C represents fibres, which is a type of sclerenchyma. This is identified by the appearance of long narrow cells. Fibres also provide mechanical support but they don’t aid in flexibility. Hence, this is not the correct answer.
(D) Figure D represents sclereids, which is a type of sclerenchyma. This is identified by the presence of small pits in the cell wall. This is not the correct answer.
Hence, the correct answer is Option (B).
Note: Both collenchyma and sclerenchyma provide mechanical support. But collenchyma tissue is responsible for flexibility of the plant. The presence of collenchyma cells below the epidermis of dicot stem and leaves provide flexibility to the growing parts of the plant. Moreover, collenchyma is a living mechanical tissue, whereas sclerenchyma is dead mechanical tissue.
Complete answer:
Permanent cells lose their ability to divide and perform specialised functions. There are two types of permanent tissue, namely simple and complex tissues.
Simple tissue – They possess structurally and functionally similar types of cells. Types of simple tissue –
(i) Parenchyma – These are isodiametric in shape, having thin cellulosic walls. They are identified by the presence of small or inconspicuous intercellular spaces. They are mainly involved in photosynthesis, storage and secretion.
(ii) Collenchyma – These cells are oval, spherical or polygonal in shape. They have thickened cell corners due to the deposition of cellulose. They are responsible for providing flexibility and mechanical support to the young stems and leaves. They are identified by the presence of thickened corners.
(iii) Sclerenchyma – These are long, narrow cells with a cell wall made up of lignin. Cell wall may contain numerous pits. They are two types of sclerenchymatous tissue, namely fibres and sclereids. They provide mechanical support to the organs and trees during secondary stages.
Understanding the options one by one,
(A) Figure A represents parenchymatous tissue. This is identified by the presence of intercellular spaces. Thus, this cannot be the correct answer.
(B) Figure B represents collenchyma. This is identified by the presence of thickened corners. This is the correct answer, because collenchyma cells provide flexibility and mechanical strength to the young plant.
(C) Figure C represents fibres, which is a type of sclerenchyma. This is identified by the appearance of long narrow cells. Fibres also provide mechanical support but they don’t aid in flexibility. Hence, this is not the correct answer.
(D) Figure D represents sclereids, which is a type of sclerenchyma. This is identified by the presence of small pits in the cell wall. This is not the correct answer.
Hence, the correct answer is Option (B).
Note: Both collenchyma and sclerenchyma provide mechanical support. But collenchyma tissue is responsible for flexibility of the plant. The presence of collenchyma cells below the epidermis of dicot stem and leaves provide flexibility to the growing parts of the plant. Moreover, collenchyma is a living mechanical tissue, whereas sclerenchyma is dead mechanical tissue.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




