
The first stable product of Calvin cycle is
A. 3- phosphoglycerate
B. 1,3- diphosphoglycerate
C. Glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate
D. Ribulose-5- phosphate
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Photosynthesis is the process in which the energy rich compounds like carbohydrates are synthesized from simple inorganic compounds like carbon dioxide and water in the presence of chlorophyll and sunlight with liberation of oxygen.
Complete answer:
Photosynthesis is the absorption of light energy and its conversion into stable chemical potential. Photosynthesis shows the existence of two phases, a light phase and a dark phase. The reaction of light phase requires light and hence also called as photochemical reaction whereas reaction of the dark phase requires no light and is purely chemical reaction.
Calvin pathway occurs in all photosynthetic plants. It is a $C{O_2}$ fixation cycle in which carbon dioxide combines with ribulose−1,5−bisphosphate to produce a transient intermediate compound. This compound breaks up in the presence of water to form the two molecules of 3- phosphoglycerate or PGA. It is the first stable product of photosynthesis.
The dark phase of the Calvin Cycle, the light reactions results in the production of reducing power, which reduces NADP and in the production ATP. In the dark reaction, these agents are used to reduce $C{O_2}$. Calvin and his co-workers found that the initial product of photosynthesis were three-carbon acids, 3 phosphoglyceric acids (PGA).
The Calvin cycle reaction has three stages: fixation, reduction, and regeneration.
In the stroma, $C{O_2}$ and two other chemicals are present to initiate the Calvin cycle.
RuBisCO enzyme and RuBP molecule: RuBP has five atoms of carbon and a phosphate group on each end. RuBisCO catalyzes a reaction between $C{O_2}$ and RuBP, which forms a six-carbon compound which is converted into two three-carbon compounds. This process is called carbon fixation.
ATP and NADPH use their stored energy to convert the three-carbon compound, 3-PGA, into another three-carbon compound called G3P. This is known as reduction reaction. ADP and NAD+, resulting from the reduction reaction, return to light-dependent reactions.
One of the G3P molecules leaves the Calvin cycle and helps in formation of carbohydrate molecules. Remaining G3P molecules regenerate RuBP for which ATP is used.
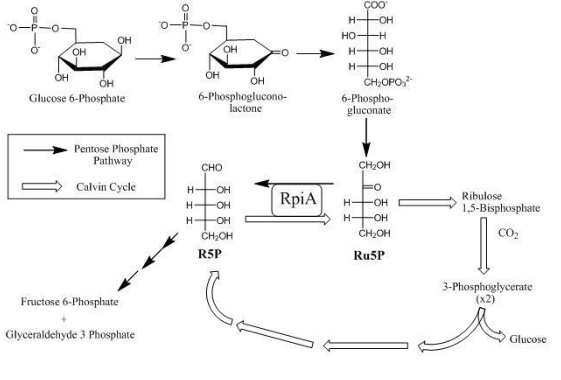
Therefore, the correct option is A, 3- phosphoglycerate.
Note: It takes six turns of the Calvin cycle to fix six carbon atoms from $C{O_2}$ . This requires energy input from 12 ATP molecules and 12 NADPH molecules in the reduction step and 6 ATP molecules in regeneration step.
In recognition of his work Calvin was awarded with the Nobel Prize in 1961.
Complete answer:
Photosynthesis is the absorption of light energy and its conversion into stable chemical potential. Photosynthesis shows the existence of two phases, a light phase and a dark phase. The reaction of light phase requires light and hence also called as photochemical reaction whereas reaction of the dark phase requires no light and is purely chemical reaction.
Calvin pathway occurs in all photosynthetic plants. It is a $C{O_2}$ fixation cycle in which carbon dioxide combines with ribulose−1,5−bisphosphate to produce a transient intermediate compound. This compound breaks up in the presence of water to form the two molecules of 3- phosphoglycerate or PGA. It is the first stable product of photosynthesis.
The dark phase of the Calvin Cycle, the light reactions results in the production of reducing power, which reduces NADP and in the production ATP. In the dark reaction, these agents are used to reduce $C{O_2}$. Calvin and his co-workers found that the initial product of photosynthesis were three-carbon acids, 3 phosphoglyceric acids (PGA).
The Calvin cycle reaction has three stages: fixation, reduction, and regeneration.
In the stroma, $C{O_2}$ and two other chemicals are present to initiate the Calvin cycle.
RuBisCO enzyme and RuBP molecule: RuBP has five atoms of carbon and a phosphate group on each end. RuBisCO catalyzes a reaction between $C{O_2}$ and RuBP, which forms a six-carbon compound which is converted into two three-carbon compounds. This process is called carbon fixation.
ATP and NADPH use their stored energy to convert the three-carbon compound, 3-PGA, into another three-carbon compound called G3P. This is known as reduction reaction. ADP and NAD+, resulting from the reduction reaction, return to light-dependent reactions.
One of the G3P molecules leaves the Calvin cycle and helps in formation of carbohydrate molecules. Remaining G3P molecules regenerate RuBP for which ATP is used.

Therefore, the correct option is A, 3- phosphoglycerate.
Note: It takes six turns of the Calvin cycle to fix six carbon atoms from $C{O_2}$ . This requires energy input from 12 ATP molecules and 12 NADPH molecules in the reduction step and 6 ATP molecules in regeneration step.
In recognition of his work Calvin was awarded with the Nobel Prize in 1961.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




