
The first member of alkyne homologous series is:
A.Ethyne
B.Ethene
C.Propyne
D.Methane
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint:
Hydrocarbons are the compounds containing carbon and hydrogen. These compounds have single, double or triple carbon-carbon bonds. Alkyne is a class of hydrocarbon compounds. Such hydrocarbons are used as a starting material in the synthesis of many other compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us see the classification of hydrocarbons;
Depending on the nature of carbon-carbon bonds present in the compound, these hydrocarbons are divided into three classes- Saturated, unsaturated and aromatic compounds.
-Saturated compounds contain carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen single bonds. Such compounds are called alkanes. Alkanes are saturated open chain hydrocarbons that have carbon-carbon single bonds. Methane $(C{H_4})$ is the first member of this family. The general formula for the alkane family is ${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}$ where $n$ is the number of carbon atoms. By using this formula, the molecular formula of any alkane can be calculated. Methane is the first member. The further members of alkane family are ethane $({C_2}{H_5})$, propane $({C_3}{H_8})$, butane $({C_4}{H_{10}})$ and so on.
-Now look at the members of the alkane family. Any two adjacent members of the family differ in the molecular formula by only $' - C{H_2}'$ group. For example, consider methane and ethane. Ethane has extra $' - C{H_2}'$ group as compared to methane. So members of such family that have the same general formula and differ by $' - C{H_2}'$ group are called as homologous members and such series is called as homologous series. Members of alkenes and alkynes family also form such homologous series.
-Unsaturated compounds have carbon-carbon double or triple bonds in them. Unsaturated compounds having carbon-carbon double bonds in their structure are called alkenes. The general molecular formula for alkenes is given as ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$ where $n$ is the number of carbon atoms. Since to have a carbon- carbon double bond, we will need at least two carbon atoms, so the first member of the alkene series has two carbon atoms. The name is derived from alkanes. The ‘-ane’ of alkane is replaced by ‘-ene’. The first member of the alkene series is ethane $({C_2}{H_4})$ and its name is derived from ethane.
-Compounds having carbon-carbon triple bonds are called alkynes. Their general molecular formula is ${C_n}{H_{2n - 2}}$ where $n$ is the number of carbon atoms. For naming alkynes, the ‘-ane’ of alkane is replaced by ‘-yne’. Again we require at least two carbon atoms to form a carbon-carbon triple bond; the first member of the alkyne series will be ethyne $({C_2}{H_2})$. The next or second member of the alkyne series is propyne $({C_3}{H_6})$ having three carbon atoms and one triple bond. The structure of ethyne is-
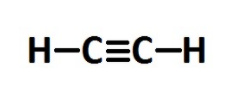
And hence option A is the correct answer.
Note: The carbon atom in alkane is $s{p^3}$ hybridized. In alkenes, the carbon atoms involved in double bonds are $s{p^2}$ hybridized and in alkenes the unsaturated carbon atoms are $sp$ hybridized. Ethyne is commonly known as acetylene. It is used for arc welding in the form of oxyacetylene gas.
Hydrocarbons are the compounds containing carbon and hydrogen. These compounds have single, double or triple carbon-carbon bonds. Alkyne is a class of hydrocarbon compounds. Such hydrocarbons are used as a starting material in the synthesis of many other compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us see the classification of hydrocarbons;
Depending on the nature of carbon-carbon bonds present in the compound, these hydrocarbons are divided into three classes- Saturated, unsaturated and aromatic compounds.
-Saturated compounds contain carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen single bonds. Such compounds are called alkanes. Alkanes are saturated open chain hydrocarbons that have carbon-carbon single bonds. Methane $(C{H_4})$ is the first member of this family. The general formula for the alkane family is ${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}$ where $n$ is the number of carbon atoms. By using this formula, the molecular formula of any alkane can be calculated. Methane is the first member. The further members of alkane family are ethane $({C_2}{H_5})$, propane $({C_3}{H_8})$, butane $({C_4}{H_{10}})$ and so on.
-Now look at the members of the alkane family. Any two adjacent members of the family differ in the molecular formula by only $' - C{H_2}'$ group. For example, consider methane and ethane. Ethane has extra $' - C{H_2}'$ group as compared to methane. So members of such family that have the same general formula and differ by $' - C{H_2}'$ group are called as homologous members and such series is called as homologous series. Members of alkenes and alkynes family also form such homologous series.
-Unsaturated compounds have carbon-carbon double or triple bonds in them. Unsaturated compounds having carbon-carbon double bonds in their structure are called alkenes. The general molecular formula for alkenes is given as ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$ where $n$ is the number of carbon atoms. Since to have a carbon- carbon double bond, we will need at least two carbon atoms, so the first member of the alkene series has two carbon atoms. The name is derived from alkanes. The ‘-ane’ of alkane is replaced by ‘-ene’. The first member of the alkene series is ethane $({C_2}{H_4})$ and its name is derived from ethane.
-Compounds having carbon-carbon triple bonds are called alkynes. Their general molecular formula is ${C_n}{H_{2n - 2}}$ where $n$ is the number of carbon atoms. For naming alkynes, the ‘-ane’ of alkane is replaced by ‘-yne’. Again we require at least two carbon atoms to form a carbon-carbon triple bond; the first member of the alkyne series will be ethyne $({C_2}{H_2})$. The next or second member of the alkyne series is propyne $({C_3}{H_6})$ having three carbon atoms and one triple bond. The structure of ethyne is-
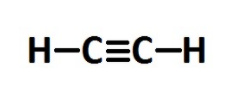
And hence option A is the correct answer.
Note: The carbon atom in alkane is $s{p^3}$ hybridized. In alkenes, the carbon atoms involved in double bonds are $s{p^2}$ hybridized and in alkenes the unsaturated carbon atoms are $sp$ hybridized. Ethyne is commonly known as acetylene. It is used for arc welding in the form of oxyacetylene gas.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




