
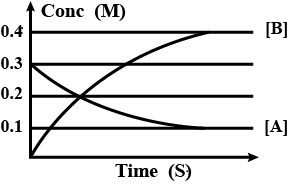
The figure shows the change in concentrations of species $A$ and $B$ as a function of time. The equilibrium constant $K_c$ for the reaction: $A(g)\rightarrow2B(g)$ is:
A. \[{K_c}>1\]
B. \[{K_c}<1\]
C. \[{K_c}=1\]
D. Data insufficient

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The equilibrium constant for a reaction can be calculated from the concentration of the product(s) and the reactant(s) at the stage when the reaction reaches the state of equilibrium, and the concentration of both product(s) and reactant(s) become constant. Time, here, does not play a role, and hence, is not considered.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given reaction, $A(g)\rightarrow2B(g)$ , there is only one reactant, $A$, and only one product, $B$. The concentration of species $A$ decreases with time as it is the reactant, and the concentration of species $B$ increases with time as it is the product.
The equilibrium constant for a reaction with only one reactant and one product is given by the formula:
$K_c = \dfrac{[Product]^x}{[Reactant]^y}$
Where $x$ represents the stoichiometric coefficient of the product;$y$ represents the stoichiometric coefficient of the reactant.To calculate the equilibrium constant, we have to consider the concentration of the species at the end of the reaction, when their concentrations become constant and show no change with time. The concentration, as mentioned, is represented on the $y-$axis as $M$. So, we will take note of the values of $M$ on the $y-$axis of the graph to determine the concentration of $A$ and $B$. From the graph, we can see that the concentration of $A$ decreases from $0.3$ to $0.2$, and then becomes constant at $0.1$. So, the concentration of $A$ at equilibrium is $0.1$. For $B$, the concentration increases from $0.1$ to $0.4$, and finally becomes constant at it. So, the concentration of $B$ at equilibrium is $0.4$. From the reaction, the stoichiometric coefficient of $B$ is known to be $2$, and that of $A$ is known to be $1$. Therefore, the equilibrium constant, $K_c$ for the given reaction can be calculated as follows:
$K_c = \dfrac{[B]^2}{[A]}$
$\Rightarrow K_c = \dfrac{[0.4]^2}{[0.1]} = 1.6$
For the given question, we have to determine whether the value of $K_c$ is greater than, less than, or equal to $1$. Since $1.6 > 1$, the value of $K_c > 1$.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: Function of time:The function of time indicates that the concentration of a reactant and the product formed by it changes with time. Time has no usage in determining the equilibrium constant of a reaction. In a first-order reaction, the rate depends on the concentration of only 1 reactant.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given reaction, $A(g)\rightarrow2B(g)$ , there is only one reactant, $A$, and only one product, $B$. The concentration of species $A$ decreases with time as it is the reactant, and the concentration of species $B$ increases with time as it is the product.
The equilibrium constant for a reaction with only one reactant and one product is given by the formula:
$K_c = \dfrac{[Product]^x}{[Reactant]^y}$
Where $x$ represents the stoichiometric coefficient of the product;$y$ represents the stoichiometric coefficient of the reactant.To calculate the equilibrium constant, we have to consider the concentration of the species at the end of the reaction, when their concentrations become constant and show no change with time. The concentration, as mentioned, is represented on the $y-$axis as $M$. So, we will take note of the values of $M$ on the $y-$axis of the graph to determine the concentration of $A$ and $B$. From the graph, we can see that the concentration of $A$ decreases from $0.3$ to $0.2$, and then becomes constant at $0.1$. So, the concentration of $A$ at equilibrium is $0.1$. For $B$, the concentration increases from $0.1$ to $0.4$, and finally becomes constant at it. So, the concentration of $B$ at equilibrium is $0.4$. From the reaction, the stoichiometric coefficient of $B$ is known to be $2$, and that of $A$ is known to be $1$. Therefore, the equilibrium constant, $K_c$ for the given reaction can be calculated as follows:
$K_c = \dfrac{[B]^2}{[A]}$
$\Rightarrow K_c = \dfrac{[0.4]^2}{[0.1]} = 1.6$
For the given question, we have to determine whether the value of $K_c$ is greater than, less than, or equal to $1$. Since $1.6 > 1$, the value of $K_c > 1$.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: Function of time:The function of time indicates that the concentration of a reactant and the product formed by it changes with time. Time has no usage in determining the equilibrium constant of a reaction. In a first-order reaction, the rate depends on the concentration of only 1 reactant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




