
The figure given below shows three velocities – substrate concentration curves for an enzyme reaction. What do the curves depict?
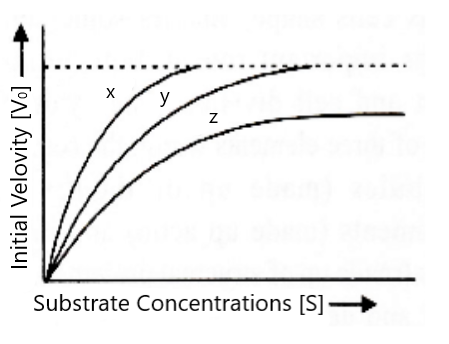
A) x- normal enzyme action, y- competitive inhibition, z- noncompetitive inhibition
B) x- enzyme with an allosteric modulator added, y-normal enzyme activity, z- competitive inhibition
C) x- enzyme with an allosteric stimulator, y- competitive inhibitor added, z- normal enzymes reaction
D) x- normal enzymes reaction, y- no competitive inhibitor added, z- allosteric inhibitor added

Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: Enzyme inhibitors are those molecules that decrease the activity of enzymes by binding to them. There are different types of enzyme inhibition like competitive, non-competitive, allosteric inhibition, etc.
Complete answer: Substrate: the chemical which is converted into a product is called the substrate. And the chemical substance which is involved in this conversion is an enzyme. The substrate binds to the active sites of the enzyme which results in the formation of an enzyme-substrate intermediate. This brings a change in the structure of the substrate and now the enzyme-substrate complex is broken off, releasing the product and enzymes (this enzyme is ready to bind with the substrate). There are many factors that affect enzyme activity, such as temperature, pH, the concentration of substrate, and inhibitor. Here, we will discuss inhibitors in detail. Inhibitors are those substances that alter the enzymatic activity. These are of the following types:
1) Competitive inhibitor: when an inhibitor closely resembles the substrate in its molecular structure and competes with the actual substrate to bind with the active site of the enzymes then it is called a competitive inhibitor. The inhibitor binds to the enzymes and decreases the enzymatic action. It does not affect the ${V_{\max }}$but increases the ${K_m}$.
2) Non-competitive inhibitor: these are those inhibitors which do not bind with the active sites of the enzyme, it binds at some other sites in enzymes called allosteric sites. And change the configuration of active sites, so it no longer could bind with the substrate. In this case, ${V_{\max }}$ is reduced but ${K_m}$ remain unchanged.
Therefore, according to this option (A) is correct. In this ‘x’ represents the normal enzymatic reaction, ‘y’ represents the same velocity as normal in case of a competitive inhibitor and ‘z’ represents the non-competitive inhibition as velocity is decreased than normal.
Note: ${V_{\max }}$ is the maximum rate of reaction achieved when the enzyme is saturated with the substrate. ${K_m}$ (Michaelis constant) represents the concentration of the substrate which helps the enzyme to reach the half of ${V_{\max }}$.
Complete answer: Substrate: the chemical which is converted into a product is called the substrate. And the chemical substance which is involved in this conversion is an enzyme. The substrate binds to the active sites of the enzyme which results in the formation of an enzyme-substrate intermediate. This brings a change in the structure of the substrate and now the enzyme-substrate complex is broken off, releasing the product and enzymes (this enzyme is ready to bind with the substrate). There are many factors that affect enzyme activity, such as temperature, pH, the concentration of substrate, and inhibitor. Here, we will discuss inhibitors in detail. Inhibitors are those substances that alter the enzymatic activity. These are of the following types:
1) Competitive inhibitor: when an inhibitor closely resembles the substrate in its molecular structure and competes with the actual substrate to bind with the active site of the enzymes then it is called a competitive inhibitor. The inhibitor binds to the enzymes and decreases the enzymatic action. It does not affect the ${V_{\max }}$but increases the ${K_m}$.
2) Non-competitive inhibitor: these are those inhibitors which do not bind with the active sites of the enzyme, it binds at some other sites in enzymes called allosteric sites. And change the configuration of active sites, so it no longer could bind with the substrate. In this case, ${V_{\max }}$ is reduced but ${K_m}$ remain unchanged.
Therefore, according to this option (A) is correct. In this ‘x’ represents the normal enzymatic reaction, ‘y’ represents the same velocity as normal in case of a competitive inhibitor and ‘z’ represents the non-competitive inhibition as velocity is decreased than normal.
Note: ${V_{\max }}$ is the maximum rate of reaction achieved when the enzyme is saturated with the substrate. ${K_m}$ (Michaelis constant) represents the concentration of the substrate which helps the enzyme to reach the half of ${V_{\max }}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




