
The figure above shows the electron energy levels, referred to the ground state (the lowest possible energy) as zero, for four different isolated atoms. Which atom can produce radiation of the shortest wavelength when atoms in the ground state are bombarded with electrons of energy W?
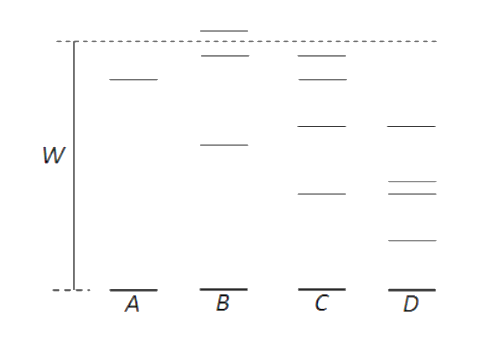
(a). A
(b). B
(c). C
(d). D

Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: For energy of energy states in atoms, it always depends on the wavelength and the frequency. Obtain the relation between energy and frequency or wavelength. Energy is directly proportional to frequency while inversely proportional to the wavelength.
Complete step by step answer:
The figure above shows the electron energy levels, referred to the ground state (the lowest possible energy) as zero, for five different isolated atoms. When atoms in the ground state are bombarded with electrons of energy W, some atoms in the ground state acquire that much energy to get excited to the highest energy level. That difference in energy level is given by the formula,
$\Delta E=\dfrac{hc}{\lambda }$
Where, $\Delta E$ is the difference in energy levels, h is the Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light and $\lambda $ is the respective wavelength.
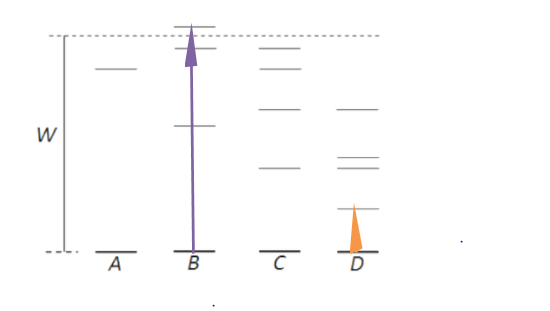
According to the above equation, energy difference is only dependent on wavelength because h and c are constants.
If atoms acquire less energy then, the atoms get excited to the lower energy state and vice versa. That atom can produce radiation which has the shortest wavelength when atoms in the ground state are bombarded with electrons of energy W.
In the above figure atom B has maximum energy difference and hence it can produce radiation of shortest wavelength. Atom D has a minimum energy difference, so it can produce radiation of the largest wavelength.
Note:
Sometimes $\Delta E$ is also written as only E. Above equation it is for the energy difference of energy states and not only the value of energy. Energy has the unit of joule as well as electron-volt. When energy is given to the atom the electrons in it jumps to higher energy levels. When the electrons come to a stable energy state, then also we get emission of radiation.
Complete step by step answer:
The figure above shows the electron energy levels, referred to the ground state (the lowest possible energy) as zero, for five different isolated atoms. When atoms in the ground state are bombarded with electrons of energy W, some atoms in the ground state acquire that much energy to get excited to the highest energy level. That difference in energy level is given by the formula,
$\Delta E=\dfrac{hc}{\lambda }$
Where, $\Delta E$ is the difference in energy levels, h is the Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light and $\lambda $ is the respective wavelength.
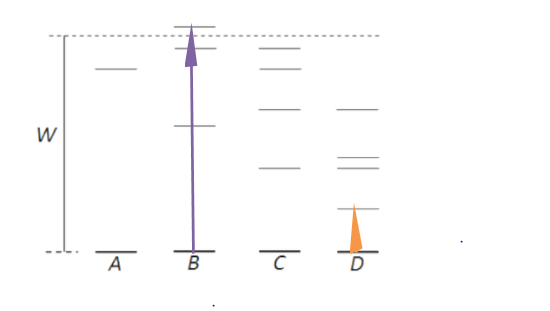
According to the above equation, energy difference is only dependent on wavelength because h and c are constants.
If atoms acquire less energy then, the atoms get excited to the lower energy state and vice versa. That atom can produce radiation which has the shortest wavelength when atoms in the ground state are bombarded with electrons of energy W.
In the above figure atom B has maximum energy difference and hence it can produce radiation of shortest wavelength. Atom D has a minimum energy difference, so it can produce radiation of the largest wavelength.
Note:
Sometimes $\Delta E$ is also written as only E. Above equation it is for the energy difference of energy states and not only the value of energy. Energy has the unit of joule as well as electron-volt. When energy is given to the atom the electrons in it jumps to higher energy levels. When the electrons come to a stable energy state, then also we get emission of radiation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




