
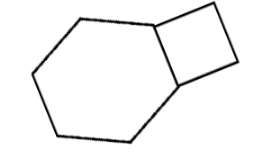
The figure above shows a regular hexagon with sides of length a and a square with sides of length a. If the area of the hexagon is $ 384\sqrt 3 $ square inches, what is the area, in square inches, of the square?
A. $ 256 $
B. $ 192 $
C. $ 64\sqrt 3 $
D. $ 16\sqrt 3 $

Answer
567k+ views
Hint: Equilateral triangles are the triangle having all the three sides and all three angles equal. Area of an equilateral triangle can be expressed by $ \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2} $ where “a” is the measure of the side of the triangle. Area of the hexagon is equal to six times the area of an equilateral triangle. Also, by substituting the value of the area in the formula, will find the measure of the side and with the help of the measure of the side, will find the area of the square.
Complete step-by-step answer:
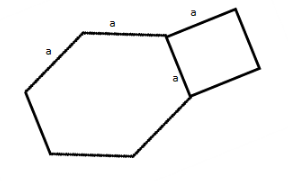
Given that the area of the hexagon is $ 384\sqrt 3 $ square inches.
Area $ = 384\sqrt 3 $ ..... (A)
Now, area of the hexagon is $ = 6 \times $ area of an equilateral triangle
Also, area of an equilateral triangle $ = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2} $
Place values in equation (A)
$ 6 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2} = 384\sqrt 3 $
Take all the terms on one side of the equation and make “a” the subject –
$ \Rightarrow {a^2} = \dfrac{{384\sqrt 3 \times 4}}{{6 \times \sqrt 3 }} $
Common multiple from the numerator and the denominator cancel each other. Therefore remove $ \sqrt 3 $ from the numerator and the denominator.
$
\Rightarrow {a^2} = \dfrac{{384 \times 4}}{6} \\
\Rightarrow {a^2} = 256 \\
$
Take square-root on both the sides of the equation.
$ \Rightarrow a = 16\,{\text{inches}} $
Now, the area of the square $ = {a^2} $
Place the values in the above equation –
Area of the square $ = {16^2} = 256{\text{ square inches}} $
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Be good in square and square-root concepts. Remember square and square-root cancel each other. Always remember the correct basic standard formula for the areas, since the solution solely depends on the formula and then simplification.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Given that the area of the hexagon is $ 384\sqrt 3 $ square inches.
Area $ = 384\sqrt 3 $ ..... (A)
Now, area of the hexagon is $ = 6 \times $ area of an equilateral triangle
Also, area of an equilateral triangle $ = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2} $
Place values in equation (A)
$ 6 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2} = 384\sqrt 3 $
Take all the terms on one side of the equation and make “a” the subject –
$ \Rightarrow {a^2} = \dfrac{{384\sqrt 3 \times 4}}{{6 \times \sqrt 3 }} $
Common multiple from the numerator and the denominator cancel each other. Therefore remove $ \sqrt 3 $ from the numerator and the denominator.
$
\Rightarrow {a^2} = \dfrac{{384 \times 4}}{6} \\
\Rightarrow {a^2} = 256 \\
$
Take square-root on both the sides of the equation.
$ \Rightarrow a = 16\,{\text{inches}} $
Now, the area of the square $ = {a^2} $
Place the values in the above equation –
Area of the square $ = {16^2} = 256{\text{ square inches}} $
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Be good in square and square-root concepts. Remember square and square-root cancel each other. Always remember the correct basic standard formula for the areas, since the solution solely depends on the formula and then simplification.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




