
The factor which initiations the intrinsic pathway of blood clotting and triggers cascade reaction is
(a) Anti-haemophilic factor
(b) Christmas factor
(c) Stuart-Power factor
(d) Hageman’s factor
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: Intrinsic pathway is when damage takes place within the walls of the blood vessels. Several factors are released by the platelets, endothelium, etc. The factor which initiates the intrinsic pathway is also known as Factor XII.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Blood coagulation or clotting is the process of conversion of an open wound to a close wound by blocking the opening with dead elements that are trapped in thread-like structures known as fibrins. Fibrins are formed from inactive fibrinogens by the enzyme thrombin. Thrombins are also formed from inactive prothrombin that is catalyzed by the enzyme thrombokinase. The enzyme thrombokinase is formed by a series of linked enzymatic reactions known as the cascade process. This cascade process occurs in two ways i.e. intrinsic pathway and the extrinsic pathway.
The initiation of the intrinsic pathway is done by Factor XII or Hageman’s factor.
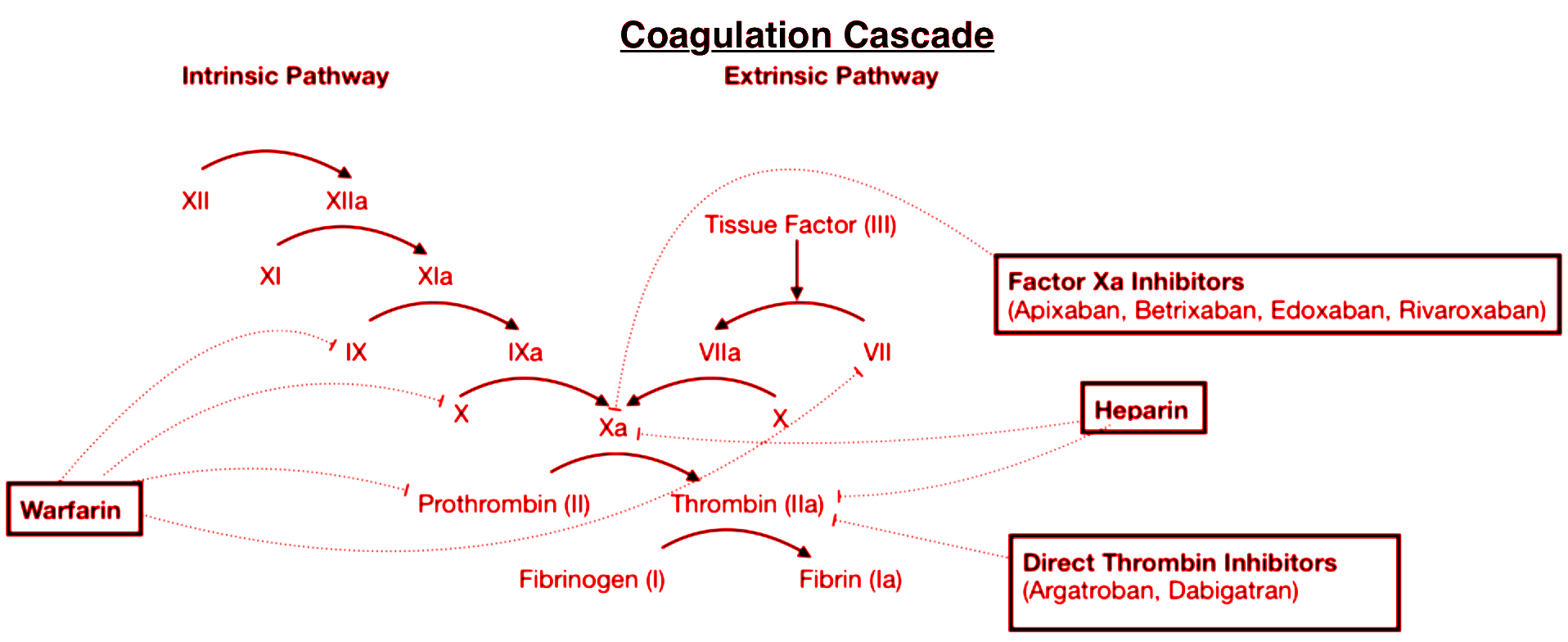
So, the correct option is ‘Hageman’s factor’.
Additional information:
Anti-hemophilic factor: This is also known as Factor VII. The deficiency of this factor leads to Haemophilia A.
Christmas factor: This is also known as Factor XI. This factor reacts with factor VII to continue the cascade reaction. Its deficiency causes Haemophilia B.
Stuart-Power factor: This is also known as Factor X. It is the first member of the common pathway of the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways.
Note: There are 13 blood clotting factors present in our body. Calcium ions are essential for the clotting of blood. Platelets are also called thrombocytes. These are produced from megakaryocytes present in the bone marrow. Clotting factors that are released from the damaged tissue lead to the initiation of the extrinsic pathway.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Blood coagulation or clotting is the process of conversion of an open wound to a close wound by blocking the opening with dead elements that are trapped in thread-like structures known as fibrins. Fibrins are formed from inactive fibrinogens by the enzyme thrombin. Thrombins are also formed from inactive prothrombin that is catalyzed by the enzyme thrombokinase. The enzyme thrombokinase is formed by a series of linked enzymatic reactions known as the cascade process. This cascade process occurs in two ways i.e. intrinsic pathway and the extrinsic pathway.
The initiation of the intrinsic pathway is done by Factor XII or Hageman’s factor.

So, the correct option is ‘Hageman’s factor’.
Additional information:
Anti-hemophilic factor: This is also known as Factor VII. The deficiency of this factor leads to Haemophilia A.
Christmas factor: This is also known as Factor XI. This factor reacts with factor VII to continue the cascade reaction. Its deficiency causes Haemophilia B.
Stuart-Power factor: This is also known as Factor X. It is the first member of the common pathway of the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways.
Note: There are 13 blood clotting factors present in our body. Calcium ions are essential for the clotting of blood. Platelets are also called thrombocytes. These are produced from megakaryocytes present in the bone marrow. Clotting factors that are released from the damaged tissue lead to the initiation of the extrinsic pathway.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




