
The external bisectors of $\angle B$ and $\angle C$meet at O . If $\angle A$ is equal to ${50^ \circ }$ ,then the magnitude of $\angle BOC$ is
a.${140^ \circ }$
b.${105^ \circ }$
c.${65^ \circ }$
d.${60^ \circ }$
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: Considering the angles $\angle A$,$\angle B$ and $\angle C$to be the exterior angles of the triangle ABC and using the property the sum of the exterior angles of any closed figure is ${360^ \circ }$we get that $\angle B + \angle C = {230^ \circ }$ and then considering the triangle BOC and using the property the sum of the angles of a triangle is ${180^ \circ }$ we get the required angle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let's consider a triangle ABC
And let $\angle A$,$\angle B$ and $\angle C$be the exterior angles of the triangle
And the bisectors of $\angle B$ and $\angle C$meet at O
Now we are given $\angle A$ is equal to ${50^ \circ }$ and this mentions the interior angle
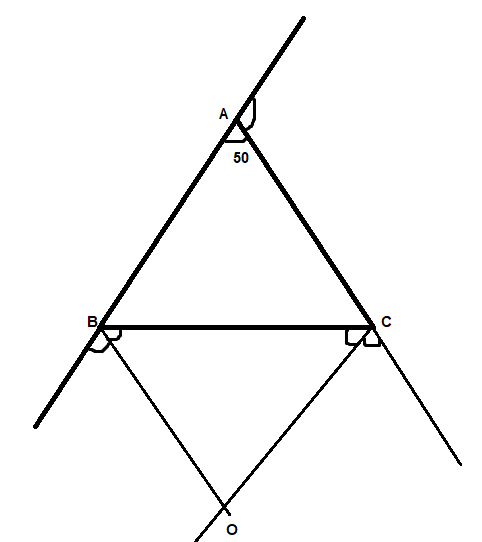
Hence the exterior angle is given by subtracting it from ${180^ \circ }$ as the angle formed by straight line is ${180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow \angle A = 180 - 50 = {130^ \circ }$
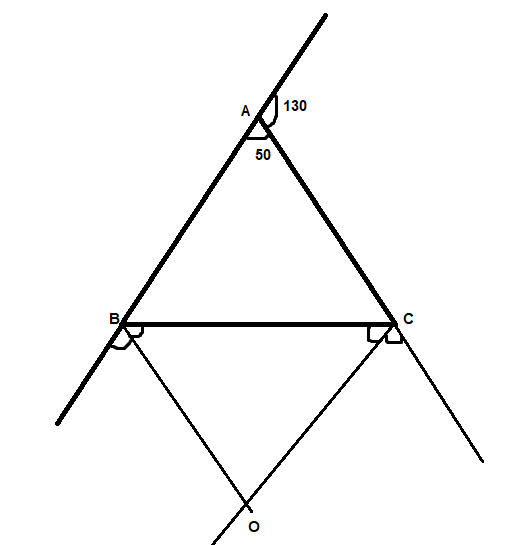
We know that the sum of the exterior angles of any closed figure is ${360^ \circ }$
$
\Rightarrow \angle A + \angle B + \angle C = {360^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow {130^ \circ } + \angle B + \angle C = {360^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \angle B + \angle C = {360^ \circ } - {130^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \angle B + \angle C = {230^ \circ } \\
$
Now lets consider the triangle BOC
Since $\angle B$ is bisected we get $\angle OBC = \dfrac{{\angle B}}{2}$
Same way , Since $\angle C$ is bisected we get $\angle OCB = \dfrac{{\angle C}}{2}$
We know that the sum of the angles of the triangle is ${180^ \circ }$
$
\Rightarrow \angle OBC + \angle OCB + \angle BOC = {180^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\angle B}}{2} + \dfrac{{\angle C}}{2} + \angle BOC = {180^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\angle B + \angle C}}{2} + \angle BOC = {180^ \circ } \\
$
We know that $\angle B + \angle C = {230^ \circ }$
Using that we get
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{230}^ \circ }}}{2} + \angle BOC = {180^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow {115^ \circ } + \angle BOC = {180^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \angle BOC = {180^ \circ } - {115^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \angle BOC = {65^ \circ } \\
$
Hence we get the required angle
The correct option is c
Note: The sum of the length of two sides of a triangle is always greater than the length of the third side.
A triangle with vertices P, Q, and R is denoted as $\vartriangle PQR$ .
The area of a triangle is equal to half of the product of its base and height.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let's consider a triangle ABC
And let $\angle A$,$\angle B$ and $\angle C$be the exterior angles of the triangle
And the bisectors of $\angle B$ and $\angle C$meet at O
Now we are given $\angle A$ is equal to ${50^ \circ }$ and this mentions the interior angle

Hence the exterior angle is given by subtracting it from ${180^ \circ }$ as the angle formed by straight line is ${180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow \angle A = 180 - 50 = {130^ \circ }$

We know that the sum of the exterior angles of any closed figure is ${360^ \circ }$
$
\Rightarrow \angle A + \angle B + \angle C = {360^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow {130^ \circ } + \angle B + \angle C = {360^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \angle B + \angle C = {360^ \circ } - {130^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \angle B + \angle C = {230^ \circ } \\
$
Now lets consider the triangle BOC
Since $\angle B$ is bisected we get $\angle OBC = \dfrac{{\angle B}}{2}$
Same way , Since $\angle C$ is bisected we get $\angle OCB = \dfrac{{\angle C}}{2}$
We know that the sum of the angles of the triangle is ${180^ \circ }$
$
\Rightarrow \angle OBC + \angle OCB + \angle BOC = {180^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\angle B}}{2} + \dfrac{{\angle C}}{2} + \angle BOC = {180^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\angle B + \angle C}}{2} + \angle BOC = {180^ \circ } \\
$
We know that $\angle B + \angle C = {230^ \circ }$
Using that we get
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{230}^ \circ }}}{2} + \angle BOC = {180^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow {115^ \circ } + \angle BOC = {180^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \angle BOC = {180^ \circ } - {115^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \angle BOC = {65^ \circ } \\
$
Hence we get the required angle
The correct option is c
Note: The sum of the length of two sides of a triangle is always greater than the length of the third side.
A triangle with vertices P, Q, and R is denoted as $\vartriangle PQR$ .
The area of a triangle is equal to half of the product of its base and height.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




