
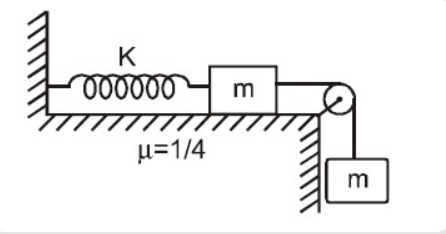
The extension in the spring when the masses come to momentary rest for the first time is
$ \left( A \right)1.5m \\
\left( B \right)6m \\
\left( C \right)3m \\
\left( D \right)none of these \\ $

Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint :In order to solve this question, we are going to use the work energy theorem .We know that the masses stop when the total work done on them is zero. This can be found by taking the potential energy due to the height of suspended mass, the kinetic energy and the spring energy, their sum is equated to zero.
The potential energy of a box of mass $ m $ sliding on surface with coefficient of friction $ \mu $ with displacement $ x $ is $ \mu mgx $
Potential energy for mass suspended at height $ h $
$ E = mgh $
Energy for the spring with extension $ x $ and spring constant $ k $ is
$ E = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2} $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
According to the Work energy theorem, the total work done on a system is equal to the difference of its initial and final energies
Applying the theorem in this situation, we get
$ W = mgx - \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2} - \mu mgx = 0 $
Here, the extension $ x $ in the spring is the displacement on the surface and the height of the suspended mass also
Solving the equation, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2} = mgx\left( {1 - \mu } \right) \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2mg}}{k}\left( {1 - \mu } \right) \\ $
Now, the values of all these constants are known, so putting those in the above equation, we get
$\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2mg}}{k}\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{4}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2mg}}{k} \times \dfrac{3}{4} = \dfrac{{3mg}}{{2k}} \\ $
Putting the rest values in it
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{3 \times 2 \times 10}}{{2 \times 20}} = 1.5 $
Therefore, the extension in the spring when the masses come to momentary rest for the first time is
$ 1.5m $ , option $ \left( A \right) $ .
Note :
The extension to which the spring is stretched displaces the mass on the surfaces to exactly that value only and the mass that is suspended in the air leading to a change in the potential energy to be $ mgx $ . When the work done will be zero or the initial and the final energies are equal, the masses come to rest.
The potential energy of a box of mass $ m $ sliding on surface with coefficient of friction $ \mu $ with displacement $ x $ is $ \mu mgx $
Potential energy for mass suspended at height $ h $
$ E = mgh $
Energy for the spring with extension $ x $ and spring constant $ k $ is
$ E = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2} $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
According to the Work energy theorem, the total work done on a system is equal to the difference of its initial and final energies
Applying the theorem in this situation, we get
$ W = mgx - \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2} - \mu mgx = 0 $
Here, the extension $ x $ in the spring is the displacement on the surface and the height of the suspended mass also
Solving the equation, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2} = mgx\left( {1 - \mu } \right) \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2mg}}{k}\left( {1 - \mu } \right) \\ $
Now, the values of all these constants are known, so putting those in the above equation, we get
$\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2mg}}{k}\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{4}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2mg}}{k} \times \dfrac{3}{4} = \dfrac{{3mg}}{{2k}} \\ $
Putting the rest values in it
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{3 \times 2 \times 10}}{{2 \times 20}} = 1.5 $
Therefore, the extension in the spring when the masses come to momentary rest for the first time is
$ 1.5m $ , option $ \left( A \right) $ .
Note :
The extension to which the spring is stretched displaces the mass on the surfaces to exactly that value only and the mass that is suspended in the air leading to a change in the potential energy to be $ mgx $ . When the work done will be zero or the initial and the final energies are equal, the masses come to rest.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




