
The equation of the perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining $A\left( {2,3} \right)$ and $B\left( {6, - 5} \right)$ is:
(A) $x - y = - 1$
(B) $x - 2y = 3$
(C) $x + y = 3$
(D) $x - 2y = 6$
Answer
503.1k+ views
Hint: In the given problem, we are required to find the equation of the perpendicular bisector of the line formed by the join of the given two points. We first find the slope of the line formed by joining the given points. Then, we find the slope of the required line. We will find out the midpoint of the two given points using the midpoint formula and then use the slope point to form a straight line in order to get to the equation of the required line.
Complete step-by-step answer:
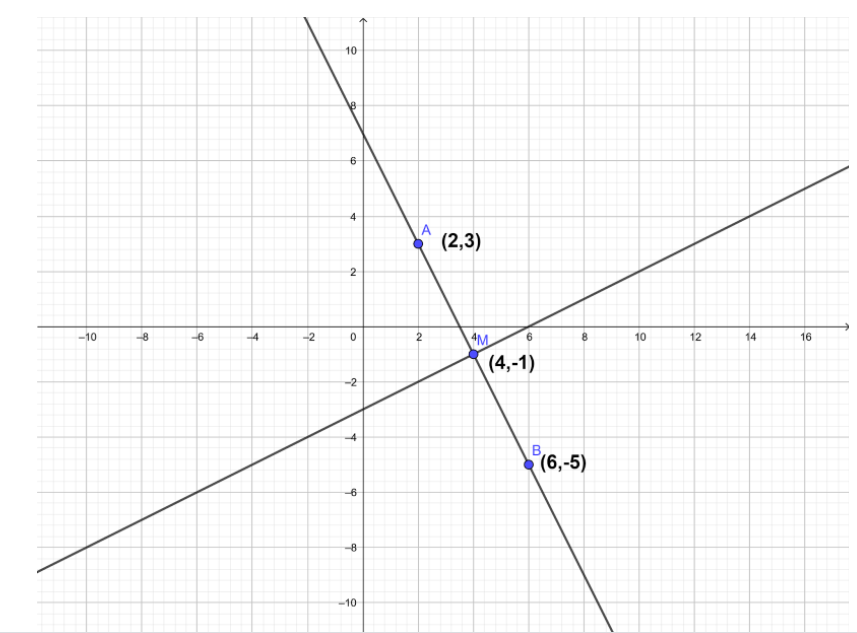
So, we are given the points $A\left( {2,3} \right)$ and $B\left( {6, - 5} \right)$. Now, by joining these two points, we get a line whose slope can be calculated using the formula $\left( {\dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}} \right)$.
Let us consider ${x_1} = 2$, ${y_1} = 3$, ${x_2} = 6$ and ${y_2} = - 5$.
So, we get the slope of the line as $\left( {\dfrac{{ - 5 - 3}}{{6 - 2}}} \right) = \dfrac{{ - 8}}{4} = - 2$.
So, we get the slope of the line formed by joining these two points $A\left( {2,3} \right)$ and $B\left( {6, - 5} \right)$ as $ - 2$.
Now, we know that the perpendicular bisector is a line that is perpendicular to the given line and passes through the midpoint of the line joining the two given points.
We also know that the product of the slopes of two perpendicular lines is always $ - 1$. Since the slope of the line formed by joining the two given points is $ - 2$, so the slope of the perpendicular bisector is $\dfrac{1}{2}$ because $\left( { - 2} \right) \times \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = - 1$.
Now, we find the midpoint of the line joining the two endpoints $A\left( {2,3} \right)$ and $B\left( {6, - 5} \right)$ using the midpoint formula $\left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$.
So, we get the midpoint as $M = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$.
Now, substituting the values of coordinates of the endpoint, we get,
$ \Rightarrow M = \left( {\dfrac{{2 + 6}}{2},\dfrac{{3 + \left( { - 5} \right)}}{2}} \right)$
Now, simplifying the expression and carrying out the calculations, we get,
$ \Rightarrow M = \left( {4, - 1} \right)$
So, we get the slope of the required line as $\dfrac{1}{2}$ and the coordinates of the point lying on the line as $\left( {4, - 1} \right)$.
We know the slope point form of the line, where we can find the equation of a straight line given the slope of the line and the point lying on it. The slope point form of the line can be represented as: $\left( {y - {y_3}} \right) = m\left( {x - {x_3}} \right)$ where $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ is the point lying on the line given to us and m is the slope of the required straight line.
Consider ${x_3} = 4$and ${y_3} = - 1$ as the midpoint is $\left( {4, - 1} \right)$.
Therefore, required equation of line is as follows:
$\left( {y - \left( { - 1} \right)} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {x - 4} \right)$
On opening the brackets and simplifying further, we get,
$ \Rightarrow y + 1 = \dfrac{{x - 4}}{2}$
Now, cross multiplying the terms of the equation, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2y + 2 = x - 4$
Taking all the variables to the left side of the equation and all constant on right side of equation, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2 + 4 = x - 2y$
Simplifying the equation, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x - 2y = 6$
Hence, the equation of the required straight line is: $x - 2y = 6$. So, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note: The given problem requires us to have thorough knowledge of the concepts of coordinate geometry. We must know the midpoint formula for solving the given question. We should remember the slope point form of a straight line to get the required answer. One must know that the product of the slopes of two perpendicular lines is one.
Complete step-by-step answer:
So, we are given the points $A\left( {2,3} \right)$ and $B\left( {6, - 5} \right)$. Now, by joining these two points, we get a line whose slope can be calculated using the formula $\left( {\dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}} \right)$.
Let us consider ${x_1} = 2$, ${y_1} = 3$, ${x_2} = 6$ and ${y_2} = - 5$.
So, we get the slope of the line as $\left( {\dfrac{{ - 5 - 3}}{{6 - 2}}} \right) = \dfrac{{ - 8}}{4} = - 2$.
So, we get the slope of the line formed by joining these two points $A\left( {2,3} \right)$ and $B\left( {6, - 5} \right)$ as $ - 2$.
Now, we know that the perpendicular bisector is a line that is perpendicular to the given line and passes through the midpoint of the line joining the two given points.
We also know that the product of the slopes of two perpendicular lines is always $ - 1$. Since the slope of the line formed by joining the two given points is $ - 2$, so the slope of the perpendicular bisector is $\dfrac{1}{2}$ because $\left( { - 2} \right) \times \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = - 1$.
Now, we find the midpoint of the line joining the two endpoints $A\left( {2,3} \right)$ and $B\left( {6, - 5} \right)$ using the midpoint formula $\left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$.
So, we get the midpoint as $M = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$.
Now, substituting the values of coordinates of the endpoint, we get,
$ \Rightarrow M = \left( {\dfrac{{2 + 6}}{2},\dfrac{{3 + \left( { - 5} \right)}}{2}} \right)$
Now, simplifying the expression and carrying out the calculations, we get,
$ \Rightarrow M = \left( {4, - 1} \right)$
So, we get the slope of the required line as $\dfrac{1}{2}$ and the coordinates of the point lying on the line as $\left( {4, - 1} \right)$.
We know the slope point form of the line, where we can find the equation of a straight line given the slope of the line and the point lying on it. The slope point form of the line can be represented as: $\left( {y - {y_3}} \right) = m\left( {x - {x_3}} \right)$ where $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ is the point lying on the line given to us and m is the slope of the required straight line.

Consider ${x_3} = 4$and ${y_3} = - 1$ as the midpoint is $\left( {4, - 1} \right)$.
Therefore, required equation of line is as follows:
$\left( {y - \left( { - 1} \right)} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {x - 4} \right)$
On opening the brackets and simplifying further, we get,
$ \Rightarrow y + 1 = \dfrac{{x - 4}}{2}$
Now, cross multiplying the terms of the equation, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2y + 2 = x - 4$
Taking all the variables to the left side of the equation and all constant on right side of equation, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2 + 4 = x - 2y$
Simplifying the equation, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x - 2y = 6$
Hence, the equation of the required straight line is: $x - 2y = 6$. So, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note: The given problem requires us to have thorough knowledge of the concepts of coordinate geometry. We must know the midpoint formula for solving the given question. We should remember the slope point form of a straight line to get the required answer. One must know that the product of the slopes of two perpendicular lines is one.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




