
The equation of the circle, which is the mirror image of the circle,${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x = 0$ in the line y = 3 – x is:
A.${x^2} + {y^2} - 6x - 8y + 24 = 0$
B.${x^2} + {y^2} - 8x - 6y + 24 = 0$
C.${x^2} + {y^2} - 4x - 6y + 12 = 0$
D.${x^2} + {y^2} - 6x - 4y + 12 = 0$
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: We will process by drawing a diagram and applying geometry, for that, we need to find the values of radius and centre of the original circle so as to get the same for the image circle and obtain its equation.
The image formed will be exactly opposite, in the same line and plane, and will have the same radius but not the centre with respect to the original circle.
General equation of a circle:
${(x - h)^2} + {(y - k)^2} = {r^2}$
Where h and k are centre and r is radius of the circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given equation of circle is ${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x = 0$
Calculating centre and radius:
${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x$ can be written as ${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 1 + 1$ [solving by completing the square]
$({x^2} - 2x + 1) + {y^2} - 1 = 0$
${(x - 1)^2} + {(y - 0)^2} = 1$
Comparing it with general equation of circle, we get:
Centre as (1, 0) and radius as 1.
Let the centre of image circle be ( x , y )
Then the diagram according to the question, can be given as:
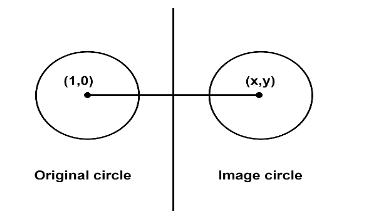
The radius of both the circles is the same (in image the size of the circle will remain same and so does the radius).
Now,
y = 3 – x can be written as x + y – 3
The image of (1, 0) with line is given by:
$\dfrac{{x - {x_1}}}{l} = \dfrac{{y - {y_1}}}{m} = \dfrac{{ - 2(xl + gm + n)}}{{{l^2} + {m^2}}}$
Here, we have
\[{x_1} = 1\] \[l = 1\] \[{y_1} = 0\] \[m = 1\] \[n = - 3\]
Where x and y are the centres of the image circle.
Substituting the values, we get:
$\dfrac{{x - 1}}{1} = \dfrac{{y - 0}}{1} = \dfrac{{ - 2(1 + 0 - 3)}}{{1 + 1}}$
$x = 3$,$y = 2$
Therefore centre of image circle (x,y) is (3,2)
From the general equation of circle, we get the equation of image circle:
${(x - 3)^2} + {(y - 2)^2} = 1$
${x^2} + 9 - 6x + {y^2} + 4 - 4y = 1$ [Simplifying]
${x^2} + {y^2} - 6x - 4y + 12$
Therefore, equation of mirror image of circle \[{x^2} + {y^2} - 2x = 0\] with the line y = 3 – x is ${x^2} + {y^2} - 6x - 4y + 12 = 0$ and the correct option is D).
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: General equation of a circle can also be
${x^2} + {y^2} + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0$
For this, the centres are (-g , -f) and radius is $\sqrt {{g^2} + {f^2} - c} $
We use either of them according to the question.
Line is generally given as: $y = mx + c$
For this question, the line was y = 3 – x so the values of m and c are:
m=-1 and c=3
The image formed will be exactly opposite, in the same line and plane, and will have the same radius but not the centre with respect to the original circle.
General equation of a circle:
${(x - h)^2} + {(y - k)^2} = {r^2}$
Where h and k are centre and r is radius of the circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given equation of circle is ${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x = 0$
Calculating centre and radius:
${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x$ can be written as ${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 1 + 1$ [solving by completing the square]
$({x^2} - 2x + 1) + {y^2} - 1 = 0$
${(x - 1)^2} + {(y - 0)^2} = 1$
Comparing it with general equation of circle, we get:
Centre as (1, 0) and radius as 1.
Let the centre of image circle be ( x , y )
Then the diagram according to the question, can be given as:

The radius of both the circles is the same (in image the size of the circle will remain same and so does the radius).
Now,
y = 3 – x can be written as x + y – 3
The image of (1, 0) with line is given by:
$\dfrac{{x - {x_1}}}{l} = \dfrac{{y - {y_1}}}{m} = \dfrac{{ - 2(xl + gm + n)}}{{{l^2} + {m^2}}}$
Here, we have
\[{x_1} = 1\] \[l = 1\] \[{y_1} = 0\] \[m = 1\] \[n = - 3\]
Where x and y are the centres of the image circle.
Substituting the values, we get:
$\dfrac{{x - 1}}{1} = \dfrac{{y - 0}}{1} = \dfrac{{ - 2(1 + 0 - 3)}}{{1 + 1}}$
$x = 3$,$y = 2$
Therefore centre of image circle (x,y) is (3,2)
From the general equation of circle, we get the equation of image circle:
${(x - 3)^2} + {(y - 2)^2} = 1$
${x^2} + 9 - 6x + {y^2} + 4 - 4y = 1$ [Simplifying]
${x^2} + {y^2} - 6x - 4y + 12$
Therefore, equation of mirror image of circle \[{x^2} + {y^2} - 2x = 0\] with the line y = 3 – x is ${x^2} + {y^2} - 6x - 4y + 12 = 0$ and the correct option is D).
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: General equation of a circle can also be
${x^2} + {y^2} + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0$
For this, the centres are (-g , -f) and radius is $\sqrt {{g^2} + {f^2} - c} $
We use either of them according to the question.
Line is generally given as: $y = mx + c$
For this question, the line was y = 3 – x so the values of m and c are:
m=-1 and c=3
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




