
The ellipse $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{25}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{16}=1$ and the hyperbola $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{25}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{16}=1$, have in common
A. centre only
B. centre, foci and directrices
C. centre, foci and vertices
D. centre and vertices only
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: We first define the general equation of ellipse and hyperbola and their different parts. We then equate that with the given equations. Using the values, we find out the common characteristics of those two conics.
Complete step by step answer:
We have been given two conics, one of ellipse and one hyperbola.
We first define the general equation of ellipse and its different parts.
General equation of ellipse is $\dfrac{{{\left( x-\alpha \right)}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{\left( y-\beta \right)}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$. The eccentricity of the ellipse is \[e=\sqrt{1-\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}\].
The centre will be $\left( \alpha ,\beta \right)$. Coordinates of vertices are $\left( \alpha \pm a,\beta \right)$. Coordinates of foci are $\left( \alpha \pm ae,\beta \right)$. Equations of the directrices are $x=\alpha \pm \dfrac{a}{e}$.
Now for our given equation $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{25}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{16}=1$. Equating we get $\alpha =0,\beta =0,a=5,b=4$.
The eccentricity of the ellipse is \[e=\sqrt{1-\dfrac{{{4}^{2}}}{{{5}^{2}}}}=\dfrac{3}{5}\].
The centre will be $\left( 0,0 \right)$. Coordinates of vertices are $\left( \pm 5,0 \right)$. Coordinates of foci are $\left( \pm 3,0 \right)$. Equations of the directrices are $x=\pm \dfrac{25}{3}$.
We now define the general equation of hyperbola and its different parts.
General equation of ellipse is $\dfrac{{{\left( x-\alpha \right)}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{\left( y-\beta \right)}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$. The eccentricity of the ellipse is \[e=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}\].
The centre will be $\left( \alpha ,\beta \right)$. Coordinates of vertices are $\left( \alpha \pm a,\beta \right)$. Coordinates of foci are $\left( \alpha \pm ae,\beta \right)$. Equations of the directrices are $x=\alpha \pm \dfrac{a}{e}$.
Now for our given equation $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{25}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{16}=1$. Equating we get $\alpha =0,\beta =0,a=5,b=4$.
The eccentricity of the ellipse is \[e=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{4}^{2}}}{{{5}^{2}}}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{41}}{5}\].
The centre will be $\left( 0,0 \right)$. Coordinates of vertices are $\left( \pm 5,0 \right)$. Coordinates of foci are $\left( \pm \sqrt{41},0 \right)$. Equations of the directrices are $x=\pm \dfrac{25}{\sqrt{41}}$.
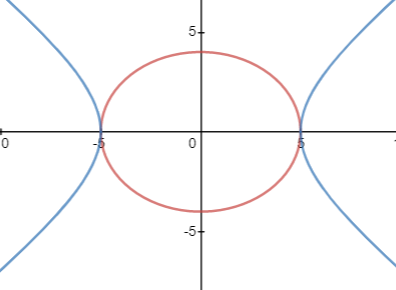
So, we can see for the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{25}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{16}=1$ and the hyperbola $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{25}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{16}=1$, they have their centre and vertices in common.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The changes happened because of the value of the eccentricity. It has been used in cases of Coordinates of foci and equations of the directrices which are $\left( \alpha \pm ae,\beta \right)$ and $x=\alpha \pm \dfrac{a}{e}$ respectively.
Complete step by step answer:
We have been given two conics, one of ellipse and one hyperbola.
We first define the general equation of ellipse and its different parts.
General equation of ellipse is $\dfrac{{{\left( x-\alpha \right)}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{\left( y-\beta \right)}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$. The eccentricity of the ellipse is \[e=\sqrt{1-\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}\].
The centre will be $\left( \alpha ,\beta \right)$. Coordinates of vertices are $\left( \alpha \pm a,\beta \right)$. Coordinates of foci are $\left( \alpha \pm ae,\beta \right)$. Equations of the directrices are $x=\alpha \pm \dfrac{a}{e}$.
Now for our given equation $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{25}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{16}=1$. Equating we get $\alpha =0,\beta =0,a=5,b=4$.
The eccentricity of the ellipse is \[e=\sqrt{1-\dfrac{{{4}^{2}}}{{{5}^{2}}}}=\dfrac{3}{5}\].
The centre will be $\left( 0,0 \right)$. Coordinates of vertices are $\left( \pm 5,0 \right)$. Coordinates of foci are $\left( \pm 3,0 \right)$. Equations of the directrices are $x=\pm \dfrac{25}{3}$.
We now define the general equation of hyperbola and its different parts.
General equation of ellipse is $\dfrac{{{\left( x-\alpha \right)}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{\left( y-\beta \right)}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$. The eccentricity of the ellipse is \[e=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}\].
The centre will be $\left( \alpha ,\beta \right)$. Coordinates of vertices are $\left( \alpha \pm a,\beta \right)$. Coordinates of foci are $\left( \alpha \pm ae,\beta \right)$. Equations of the directrices are $x=\alpha \pm \dfrac{a}{e}$.
Now for our given equation $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{25}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{16}=1$. Equating we get $\alpha =0,\beta =0,a=5,b=4$.
The eccentricity of the ellipse is \[e=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{4}^{2}}}{{{5}^{2}}}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{41}}{5}\].
The centre will be $\left( 0,0 \right)$. Coordinates of vertices are $\left( \pm 5,0 \right)$. Coordinates of foci are $\left( \pm \sqrt{41},0 \right)$. Equations of the directrices are $x=\pm \dfrac{25}{\sqrt{41}}$.

So, we can see for the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{25}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{16}=1$ and the hyperbola $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{25}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{16}=1$, they have their centre and vertices in common.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The changes happened because of the value of the eccentricity. It has been used in cases of Coordinates of foci and equations of the directrices which are $\left( \alpha \pm ae,\beta \right)$ and $x=\alpha \pm \dfrac{a}{e}$ respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




