
The elevator E has a mass of $ 3000kg $ when fully loaded and is connected as shown to a counterweight $ W $ of mass $ 1000kg $. Determine the power in kilowatts delivered by the motor
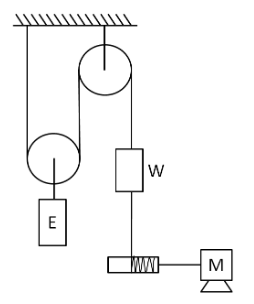
(i) When the elevator is moving down at a constant speed of $ 3m/s $,
(ii) When it has an upward velocity of $ 3m/s $ and a deceleration of $ 0.5m/{s^2} $.

Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we need to find out the force applied by the motor in each case and also its velocity. For this we have to consider the free body diagram of each of the weight and the elevator. Finally applying the formula for the power will give the required answer.
Formula used: The formula which is used to solve this question is given by,
$ P = Fv\cos {{\theta }} $, here $ P $ is the power, $ F $ is the force, $ v $ is the velocity and $ {{\theta }} $ is the angle between the force and the velocity vectors.
Complete step by step answer
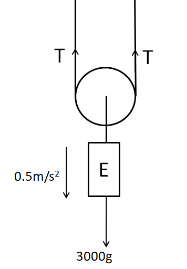
Let the tension in the string, which is common in both the pulleys, be $ T $, as shown below.
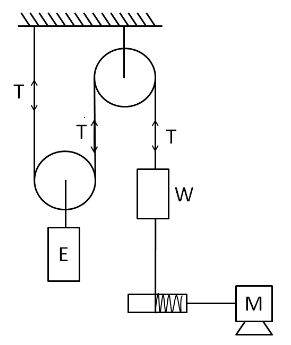
Now, for determining the power supplied by the motor, we have to find out the velocity of the motor. As the elevator is moving downwards in both the cases, so we let the velocity of the elevator be $ v $ downwards, as shown in the below figure.
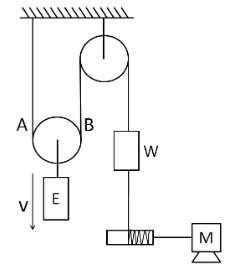
Let the velocity of the left string $ A $ be $ {v_A} $ and that of the right string B be $ {v_B} $.
Since the string A is connected to the fixed end, so its velocity must be zero.
$ \therefore {v_A} = 0 $
Now, applying writing constraint relation for the elevator, we get
$ {v_A} + {v_B} = 2v $
$ \Rightarrow 0 + {v_B} = 2v $
So the velocity of the B string becomes
$ {v_B} = 2v $ …………………...(1)
Now, since the motor is connected to the string B through the block B, so its velocity is equal to the string B. Therefore the velocity of the motor is
$ {v_M} = 2v $ …………………...(2)
We consider the free body diagram of the elevator E as shown below.
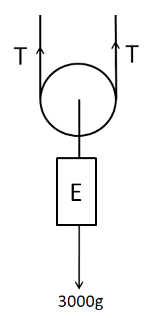
As the elevator is moving at a constant speed, so its acceleration is zero. This means that the elevator should be in equilibrium. Therefore from the above figure we have
$ T + T = 3000g $
$ \Rightarrow 2T = 3000g $
Substituting $ g = 10m/{s^2} $ we get
$ 2T = 30000 $
Dividing both sides by $ 2 $
$ T = 15000N $ …………………...(4)
Now we consider the free body diagram of the counterweight W.
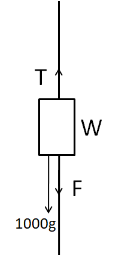
Here $ F $ is the force applied by the motor. As the block is moving with a constant velocity, so it is in equilibrium. So we have
$ T = F + 1000g $
$ \Rightarrow T = F + 10000 $
From (4)
$ 15000 = F + 10000 $
$ \Rightarrow F = 5000N $
According to the question, the velocity of the elevator is
$ v = 3m/s $
From (2) the velocity of the motor is
$ {v_M} = 2 \times 3 = 6m/s $
We know that the power is given by
$ P = Fv\cos {{\theta }} $
As the force and the velocity are opposite directions, so $ {{\theta = }}{180^ \circ } $. Therefore the power is
$ P = 5000 \times 6 \times \cos {180^ \circ } $
$ \Rightarrow P = - 30000{\text{W}} = - 30{\text{kW}} $
This time, the elevator is moving upwards with a velocity of $ 3m/s $. So from (3) the velocity of the motor becomes
$ {v_M} = 2 \times 3 = 6m/s $ …………………...(4)
Also, the elevator has a deceleration of $ 0.5m/{s^2} $. Since the elevator is moving upwards, the acceleration must be downwards. Now we consider the free body diagram of the elevator.
From Newton’s second law of motion we have
$ 3000g - \left( {T + T} \right) = 3000 \times 0.5 $
$ \Rightarrow 30000 - 2T = 1500 $
On rearranging, we get
$ 2T = 30000 - 1500 $
$ \Rightarrow T = 14250N $ …………………...(5)
Differentiating both sides of (1) we get
$ \dfrac{{d{v_B}}}{{dt}} = 2\dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}} $
As the acceleration of the elevator is $ 0.5m/{s^2} $ upwards, so we have $ \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}} = 0.5m/{s^2} $. Substituting this above, we get
$ \dfrac{{d{v_B}}}{{dt}} = 1m/{s^2} $
So the acceleration of the string B is $ 1m/{s^2} $ downwards. As the weight W is directly connected to this string, so its acceleration is $ 1m/{s^2} $ upwards.
Now we consider the FBD of the weight W.
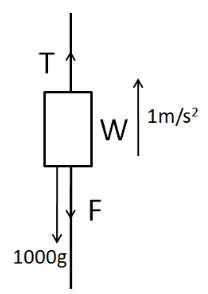
From Newton’s second law of motion we have
$ T - F - 1000g = 1000 \times 1 $
$ \Rightarrow T - F - 10000 = 1000 $
From (5)
$ 14250 - F - 10000 = 1000 $
$ \Rightarrow F = 3250N $
Now, from the power formula we have
$ P = Fv\cos {{\theta }} $
As the force and the velocity are in the same direction so $ {{\theta = }}{0^ \circ } $. So we have
$ P = 3250 \times 6\cos {0^ \circ } $
$ \Rightarrow P = 19500{\text{W}} = 19.5{\text{kW}} $.
Note
While calculating the power, we must not ignore the signs. For that we need to consider the angle between the force and the velocity vector.
Formula used: The formula which is used to solve this question is given by,
$ P = Fv\cos {{\theta }} $, here $ P $ is the power, $ F $ is the force, $ v $ is the velocity and $ {{\theta }} $ is the angle between the force and the velocity vectors.
Complete step by step answer
Let the tension in the string, which is common in both the pulleys, be $ T $, as shown below.

Now, for determining the power supplied by the motor, we have to find out the velocity of the motor. As the elevator is moving downwards in both the cases, so we let the velocity of the elevator be $ v $ downwards, as shown in the below figure.

Let the velocity of the left string $ A $ be $ {v_A} $ and that of the right string B be $ {v_B} $.
Since the string A is connected to the fixed end, so its velocity must be zero.
$ \therefore {v_A} = 0 $
Now, applying writing constraint relation for the elevator, we get
$ {v_A} + {v_B} = 2v $
$ \Rightarrow 0 + {v_B} = 2v $
So the velocity of the B string becomes
$ {v_B} = 2v $ …………………...(1)
Now, since the motor is connected to the string B through the block B, so its velocity is equal to the string B. Therefore the velocity of the motor is
$ {v_M} = 2v $ …………………...(2)
We consider the free body diagram of the elevator E as shown below.

As the elevator is moving at a constant speed, so its acceleration is zero. This means that the elevator should be in equilibrium. Therefore from the above figure we have
$ T + T = 3000g $
$ \Rightarrow 2T = 3000g $
Substituting $ g = 10m/{s^2} $ we get
$ 2T = 30000 $
Dividing both sides by $ 2 $
$ T = 15000N $ …………………...(4)
Now we consider the free body diagram of the counterweight W.

Here $ F $ is the force applied by the motor. As the block is moving with a constant velocity, so it is in equilibrium. So we have
$ T = F + 1000g $
$ \Rightarrow T = F + 10000 $
From (4)
$ 15000 = F + 10000 $
$ \Rightarrow F = 5000N $
According to the question, the velocity of the elevator is
$ v = 3m/s $
From (2) the velocity of the motor is
$ {v_M} = 2 \times 3 = 6m/s $
We know that the power is given by
$ P = Fv\cos {{\theta }} $
As the force and the velocity are opposite directions, so $ {{\theta = }}{180^ \circ } $. Therefore the power is
$ P = 5000 \times 6 \times \cos {180^ \circ } $
$ \Rightarrow P = - 30000{\text{W}} = - 30{\text{kW}} $
This time, the elevator is moving upwards with a velocity of $ 3m/s $. So from (3) the velocity of the motor becomes
$ {v_M} = 2 \times 3 = 6m/s $ …………………...(4)
Also, the elevator has a deceleration of $ 0.5m/{s^2} $. Since the elevator is moving upwards, the acceleration must be downwards. Now we consider the free body diagram of the elevator.

From Newton’s second law of motion we have
$ 3000g - \left( {T + T} \right) = 3000 \times 0.5 $
$ \Rightarrow 30000 - 2T = 1500 $
On rearranging, we get
$ 2T = 30000 - 1500 $
$ \Rightarrow T = 14250N $ …………………...(5)
Differentiating both sides of (1) we get
$ \dfrac{{d{v_B}}}{{dt}} = 2\dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}} $
As the acceleration of the elevator is $ 0.5m/{s^2} $ upwards, so we have $ \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}} = 0.5m/{s^2} $. Substituting this above, we get
$ \dfrac{{d{v_B}}}{{dt}} = 1m/{s^2} $
So the acceleration of the string B is $ 1m/{s^2} $ downwards. As the weight W is directly connected to this string, so its acceleration is $ 1m/{s^2} $ upwards.
Now we consider the FBD of the weight W.

From Newton’s second law of motion we have
$ T - F - 1000g = 1000 \times 1 $
$ \Rightarrow T - F - 10000 = 1000 $
From (5)
$ 14250 - F - 10000 = 1000 $
$ \Rightarrow F = 3250N $
Now, from the power formula we have
$ P = Fv\cos {{\theta }} $
As the force and the velocity are in the same direction so $ {{\theta = }}{0^ \circ } $. So we have
$ P = 3250 \times 6\cos {0^ \circ } $
$ \Rightarrow P = 19500{\text{W}} = 19.5{\text{kW}} $.
Note
While calculating the power, we must not ignore the signs. For that we need to consider the angle between the force and the velocity vector.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




