
The element crystallizes in a body centred cubic lattice and the edge of unit cell is 0.351 nm. The density is 0.533 \[\text{g/c}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\]. What is the atomic weight?
(a) 12.0
(b) 6.94
(c) 9.01
(d) 10.8
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: Answer to this question can be approached by defining a body centred cubic lattice first and then relating packing dfraction, density and mass of a cube which are given by several formulas.
Complete answer:
In the classes of chemistry, we have come across the concepts of physical chemistry and also some part of inorganic chemistry which tells about the arrangements of atoms in a space and their detailed structure such as in the form of primitive cell, unit cells, body centred cubic, face centred cubic etc.
Let us see this concept in detail so that we can derive the correct answer.
This is the structure of a body-centred unit cell-
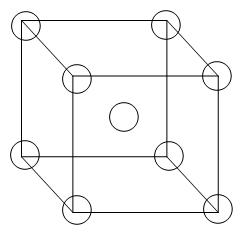
From the diagram we can see that 8 atoms are arranged in all the corners of the cube and there is 1 atom in the centre of the unit cell. Therefore, the contribution per unit cell will be
For primitive – 8 atoms are arranged in all the corners of the cube, therefore, the contribution per unit cell will be 1 atom, \[8\text{x}\dfrac{1}{8}=1\] atom or molecule.
Total contribution = 1 atom (primitive) + 1 atom (body centred) = 2
Now, let us write the formula for density of a unit cell.
Density (d) = \[\dfrac{\text{Z x M}}{{{\text{a}}^{\text{3}}}\text{ x }{{\text{N}}_{\text{A}}}}\] , where,
Z = atom per unit cell = 2 (in case of Body Centred cubic lattice)
M = Mass / weight (unknown)
a = length of edge = 0.351 nm
\[{{\text{N}}_{\text{A}}}\]= Avogadro’s constant = \[\text{6}\text{.022 x 1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{23}}}\]
From this formula, we can calculate atomic weight as-
\[\text{M = }\dfrac{\text{d x }{{\text{a}}^{\text{3}}}\text{ x }{{\text{N}}_{\text{A}}}}{\text{Z}}\]
\[\text{M = }\dfrac{\text{0}\text{.533 x (3}\text{.51 x 1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{-8}}}{{\text{)}}^{\text{3}}}\text{ x 6}\text{.022 x 1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{23}}}}{2}\]
M = 6.94
Therefore, the answer is – option (b) – the atomic weight of the element is 6.94 g.
Note:
Do not be confused with the body centred and face centred cube where the difference lies only in the part that in BCC there is one additional atom in the centre of each cube and in FCC there is one additional atom in each of the six faces of a cube.
Complete answer:
In the classes of chemistry, we have come across the concepts of physical chemistry and also some part of inorganic chemistry which tells about the arrangements of atoms in a space and their detailed structure such as in the form of primitive cell, unit cells, body centred cubic, face centred cubic etc.
Let us see this concept in detail so that we can derive the correct answer.
This is the structure of a body-centred unit cell-

From the diagram we can see that 8 atoms are arranged in all the corners of the cube and there is 1 atom in the centre of the unit cell. Therefore, the contribution per unit cell will be
For primitive – 8 atoms are arranged in all the corners of the cube, therefore, the contribution per unit cell will be 1 atom, \[8\text{x}\dfrac{1}{8}=1\] atom or molecule.
Total contribution = 1 atom (primitive) + 1 atom (body centred) = 2
Now, let us write the formula for density of a unit cell.
Density (d) = \[\dfrac{\text{Z x M}}{{{\text{a}}^{\text{3}}}\text{ x }{{\text{N}}_{\text{A}}}}\] , where,
Z = atom per unit cell = 2 (in case of Body Centred cubic lattice)
M = Mass / weight (unknown)
a = length of edge = 0.351 nm
\[{{\text{N}}_{\text{A}}}\]= Avogadro’s constant = \[\text{6}\text{.022 x 1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{23}}}\]
From this formula, we can calculate atomic weight as-
\[\text{M = }\dfrac{\text{d x }{{\text{a}}^{\text{3}}}\text{ x }{{\text{N}}_{\text{A}}}}{\text{Z}}\]
\[\text{M = }\dfrac{\text{0}\text{.533 x (3}\text{.51 x 1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{-8}}}{{\text{)}}^{\text{3}}}\text{ x 6}\text{.022 x 1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{23}}}}{2}\]
M = 6.94
Therefore, the answer is – option (b) – the atomic weight of the element is 6.94 g.
Note:
Do not be confused with the body centred and face centred cube where the difference lies only in the part that in BCC there is one additional atom in the centre of each cube and in FCC there is one additional atom in each of the six faces of a cube.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




