
The electronegativity difference between N and F is greater than N and H, yet the dipole moment of \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] (1.5 D) is greater than of \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\] (0.2 D). This is because:
A) In \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] as well as \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\], the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the opposite direction.
B) In \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] the atomic dipole and bond are in the opposite direction, whereas in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\] these are in the same direction.
C) In \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] as well as in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\] the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction.
D) In \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction, whereas in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\] these are in the opposite direction.
Answer
549.6k+ views
Hint: Polarity is the ability of the charge separation. The measure of the polarity of the chemical bond is known as dipole moment and it is represented as \[\mu \].
The chemical formula of the dipole moment is given as follows:
\[\mu = \delta \times d\]
Here, the dipole moment is represented as \[\mu \], the charge on the species is \[\delta \], and the distance between the partial charges is \[d\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom or element to pull the electron density of another species toward itself.
In the periodic table from the left to right in the period electronegativity increases and hence, halogen possesses the highest value of electronegativity in the period. In the case of the group from top to bottom electronegativity decreases.
Here, two compounds given are \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] and \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\] their structures are as follows:
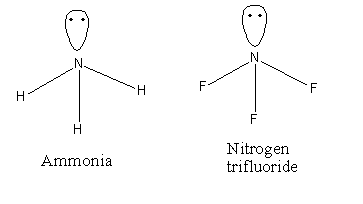
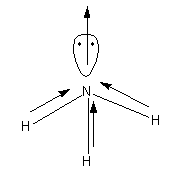
In the case of the \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] dipole moment direction of the dipole moment among the N and lone pair is toward the pole pair and in between the N and H is toward the N atom. Thus, the direction of atomic as well as the bond dipole moment is the same. Hence, the resultant dipole moment is greater. The direction of the dipole moments in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] is shown as follows:
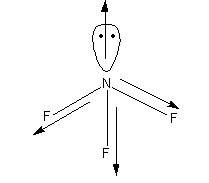
In the case of \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\], the N-F bond is more polar because of the more electronegativity difference between the F and N atoms than the N-H bond in the \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\].
Here, the dipole direction of the dipole moment among the N and lone pair is toward the pole pair, and in between the N and F is toward the F atom. Thus, the direction of atomic and bond dipole moment is opposite. Hence, the resultant dipole moment is lower. The direction of the dipole moments in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\] is shown as follows:
Here, option(A) in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] as well as \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\], the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the opposite direction is incorrect.
Now, option(B) in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] the atomic dipole and bond are in the opposite direction, whereas in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\] these are in the same direction is incorrect.
Option(C) in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] as well as in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\] the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction is incorrect.
Now, option(D) in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction, whereas in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\] these are in the opposite direction is the correct answer to the given question.
Hence the correct answer is option ‘D’.
Note:
i) In the case of the compounds, the resultant dipole moment depends on the bond dipole moment and atomic dipole moment.
ii) If the direction of both atomic dipole moment and bond dipole moment is the same then the resultant dipole moment of the compound is increased.
iii) If the direction of the atomic dipole moment and bond dipole moment is opposite then the resultant dipole moment of the compound decreases.
The chemical formula of the dipole moment is given as follows:
\[\mu = \delta \times d\]
Here, the dipole moment is represented as \[\mu \], the charge on the species is \[\delta \], and the distance between the partial charges is \[d\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom or element to pull the electron density of another species toward itself.
In the periodic table from the left to right in the period electronegativity increases and hence, halogen possesses the highest value of electronegativity in the period. In the case of the group from top to bottom electronegativity decreases.
Here, two compounds given are \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] and \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\] their structures are as follows:

In the case of the \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] dipole moment direction of the dipole moment among the N and lone pair is toward the pole pair and in between the N and H is toward the N atom. Thus, the direction of atomic as well as the bond dipole moment is the same. Hence, the resultant dipole moment is greater. The direction of the dipole moments in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] is shown as follows:

In the case of \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\], the N-F bond is more polar because of the more electronegativity difference between the F and N atoms than the N-H bond in the \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\].
Here, the dipole direction of the dipole moment among the N and lone pair is toward the pole pair, and in between the N and F is toward the F atom. Thus, the direction of atomic and bond dipole moment is opposite. Hence, the resultant dipole moment is lower. The direction of the dipole moments in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\] is shown as follows:

Here, option(A) in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] as well as \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\], the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the opposite direction is incorrect.
Now, option(B) in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] the atomic dipole and bond are in the opposite direction, whereas in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\] these are in the same direction is incorrect.
Option(C) in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] as well as in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\] the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction is incorrect.
Now, option(D) in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction, whereas in \[{\text{N}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\] these are in the opposite direction is the correct answer to the given question.
Hence the correct answer is option ‘D’.
Note:
i) In the case of the compounds, the resultant dipole moment depends on the bond dipole moment and atomic dipole moment.
ii) If the direction of both atomic dipole moment and bond dipole moment is the same then the resultant dipole moment of the compound is increased.
iii) If the direction of the atomic dipole moment and bond dipole moment is opposite then the resultant dipole moment of the compound decreases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




