
What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has formula $CO_2$?
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: The molecule of carbon dioxide is arranged in a way that the two oxygen atoms are bonded on either side with carbon atoms by double bonds. Which means each oxygen form 2 bonds with $C$. Carbon shares its 4 electrons, 2 with one oxygen atom and 2 with 2nd oxygen atom.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question we have to draw the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide. So, first of all what is electron dot structure and how to draw this structure. We write atoms by using their chemical symbol. Lines or dots are drawn between atoms that show bond between two atoms. Remaining electrons form lone pairs and are represented by two dots, which are drawn next to the atoms.
For the Lewis structure of carbon dioxide, at first we write the symbols of the atom that are $C$ and $O$. $C$ in the middle with $O$ on both sides. As we know there are 6 electrons in the outer shell of $O$ atom and 4 electrons in the outer shell of $C$.
So, at first, we will make two bonds of carbon with each $O$ atom, by these bonding, each oxygen will share one electron with carbon and vice versa.
So, carbon has 6 electrons and each oxygen has 7 electrons but we need 8 electrons in the outer shell of each atom so that the molecule becomes stable. For this we'll make two more bonds of carbon, one with each oxygen.
By this way each oxygen and carbon will have 8 electrons in their outer shell. Now the remaining electrons of oxygen, which isn't involved in bonding will be drawn as a lone pair.
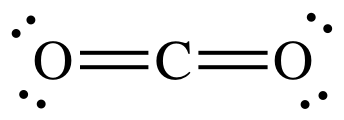
Note:
Covalent bonds are indicated as dashes and lone pairs of electrons are shown as pairs of dots. In carbon dioxide, each oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons remaining. So, the covalent bonds between the oxygen and carbon atoms each use two electrons from the oxygen atom and two from the carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question we have to draw the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide. So, first of all what is electron dot structure and how to draw this structure. We write atoms by using their chemical symbol. Lines or dots are drawn between atoms that show bond between two atoms. Remaining electrons form lone pairs and are represented by two dots, which are drawn next to the atoms.
For the Lewis structure of carbon dioxide, at first we write the symbols of the atom that are $C$ and $O$. $C$ in the middle with $O$ on both sides. As we know there are 6 electrons in the outer shell of $O$ atom and 4 electrons in the outer shell of $C$.
So, at first, we will make two bonds of carbon with each $O$ atom, by these bonding, each oxygen will share one electron with carbon and vice versa.
So, carbon has 6 electrons and each oxygen has 7 electrons but we need 8 electrons in the outer shell of each atom so that the molecule becomes stable. For this we'll make two more bonds of carbon, one with each oxygen.
By this way each oxygen and carbon will have 8 electrons in their outer shell. Now the remaining electrons of oxygen, which isn't involved in bonding will be drawn as a lone pair.
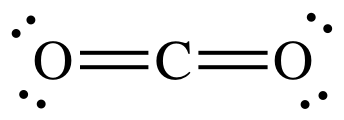
Note:
Covalent bonds are indicated as dashes and lone pairs of electrons are shown as pairs of dots. In carbon dioxide, each oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons remaining. So, the covalent bonds between the oxygen and carbon atoms each use two electrons from the oxygen atom and two from the carbon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




