
The electron dot structure for $B{{F}_{3}}$ is:
(A)-
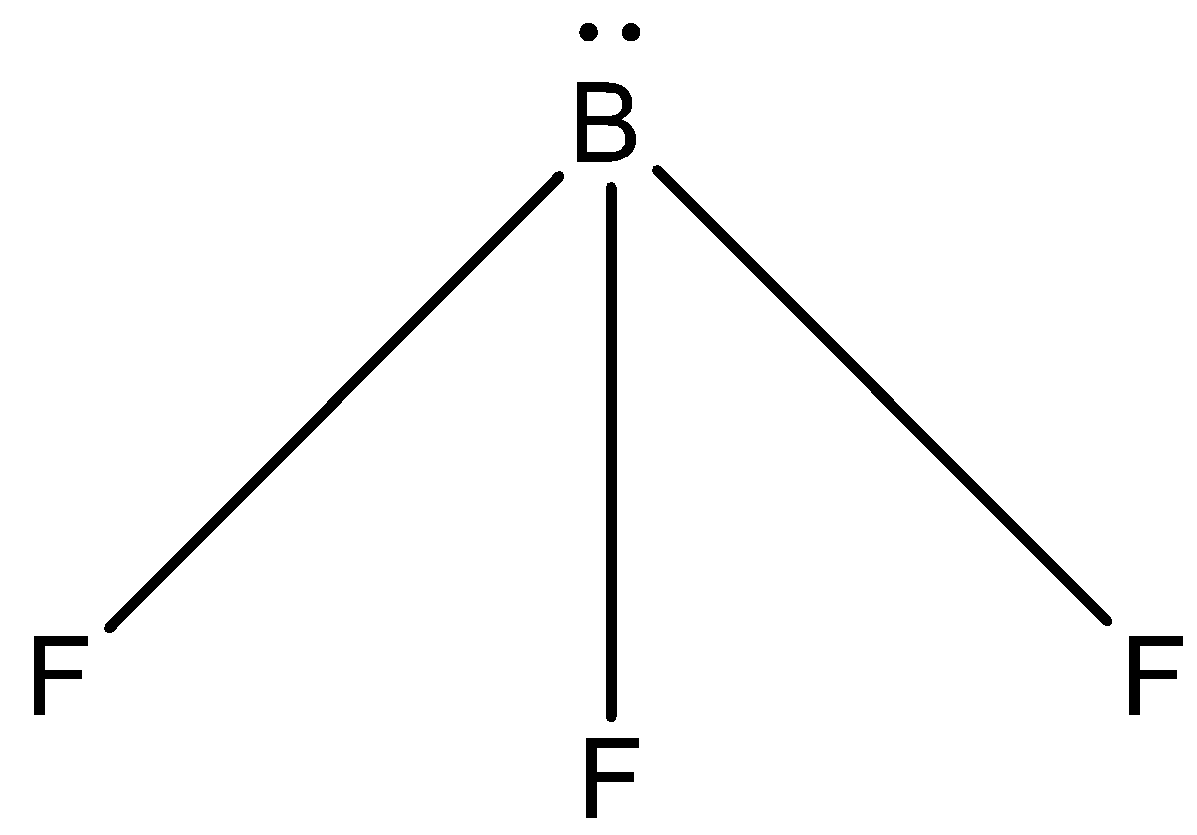
(B)-
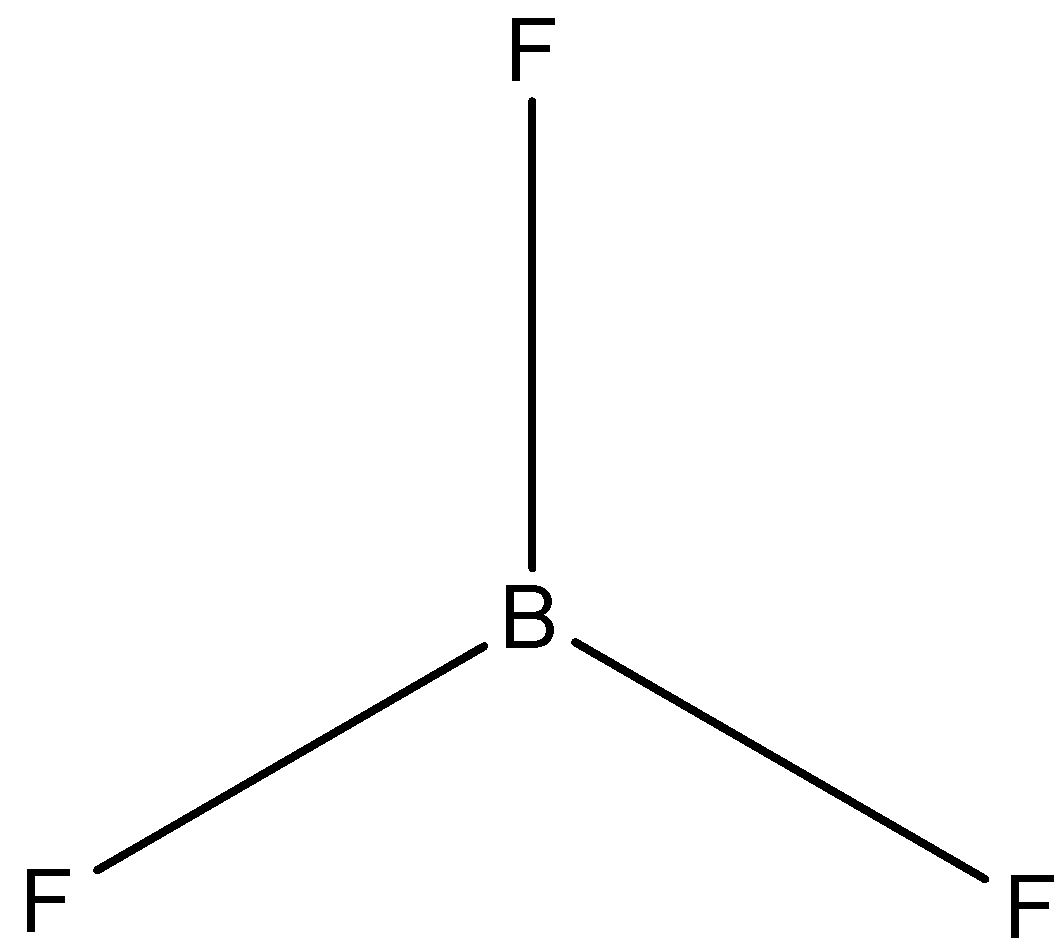
(C)-
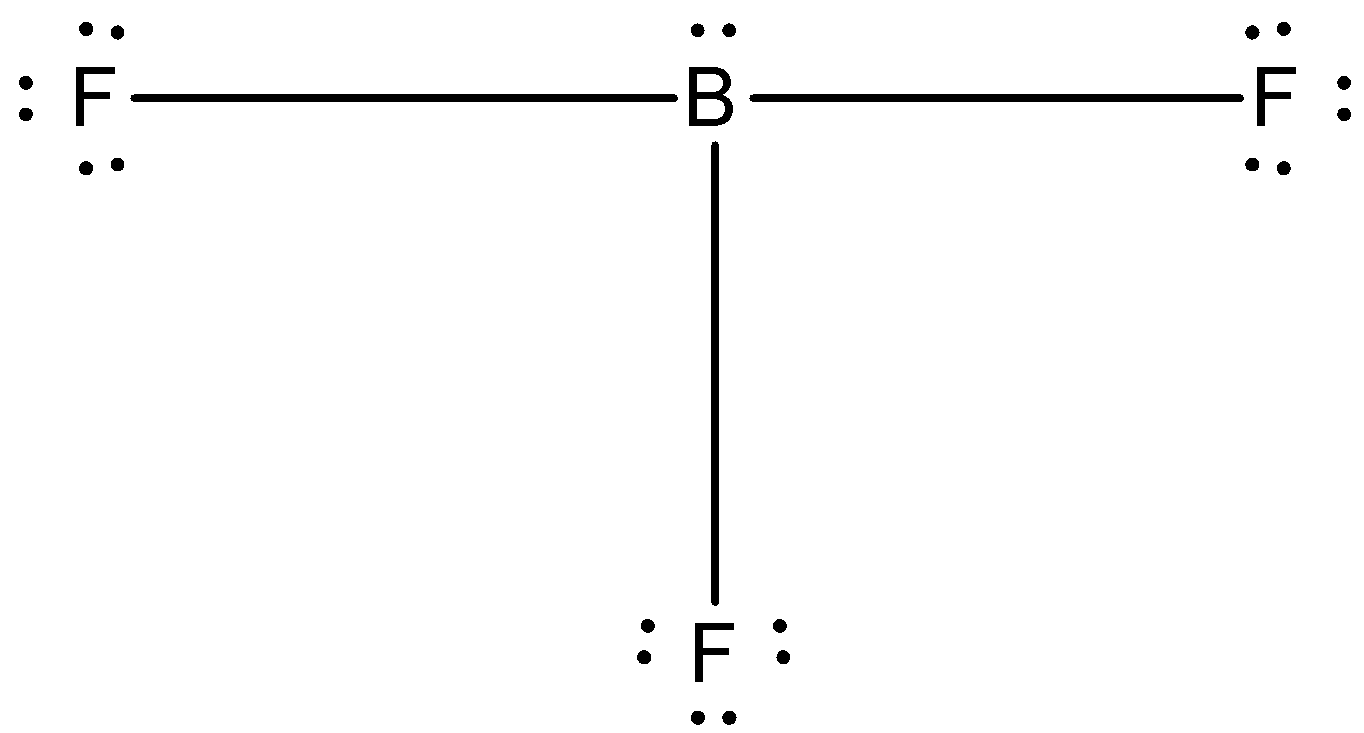
(D)-
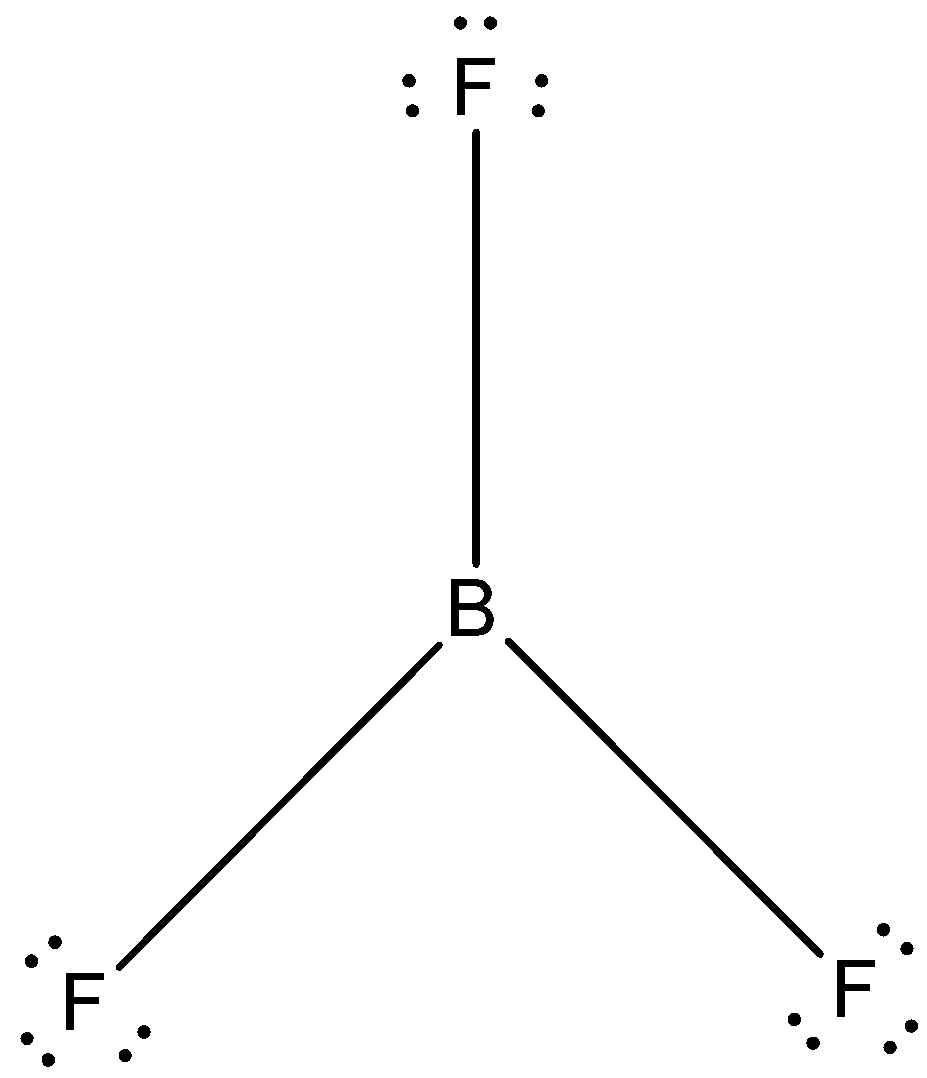




Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: Write the electronic configuration of boron atom in its ground state. Now three electrons will be used for formation of chemical bonds with incoming fluorine atoms. Now find out the hybridization of boron atoms considering the bonds and lone pairs if present. This will help to find the structure of the compound.
Complete step by step answer:
- Boron trifluoride is an organic compound with the formula $\text{B}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}$. It is a pungent colourless toxic gas which forms white fumes in moist air. It is very good Lewis acid as it has a vacant orbital that can accommodate a lone pair of electrons.
- We will write the electronic configuration of boron atoms.
E.C = $\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{1}}}$
Boron has 3 electrons in its valence shell. These electrons are used up in bond formation with the incoming fluorine ions. Boron has no lone pair of electrons.
- Let us determine its hybridisation.
Number of bond pairs = 3
Number of lone pairs = 0
The hybridisation becomes $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ .
$B{{F}_{3}}$ is a planar compound with hybridisation $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ and has a trigonal planar shape.
- The Lewis dot structure of boron trifluoride is given below:
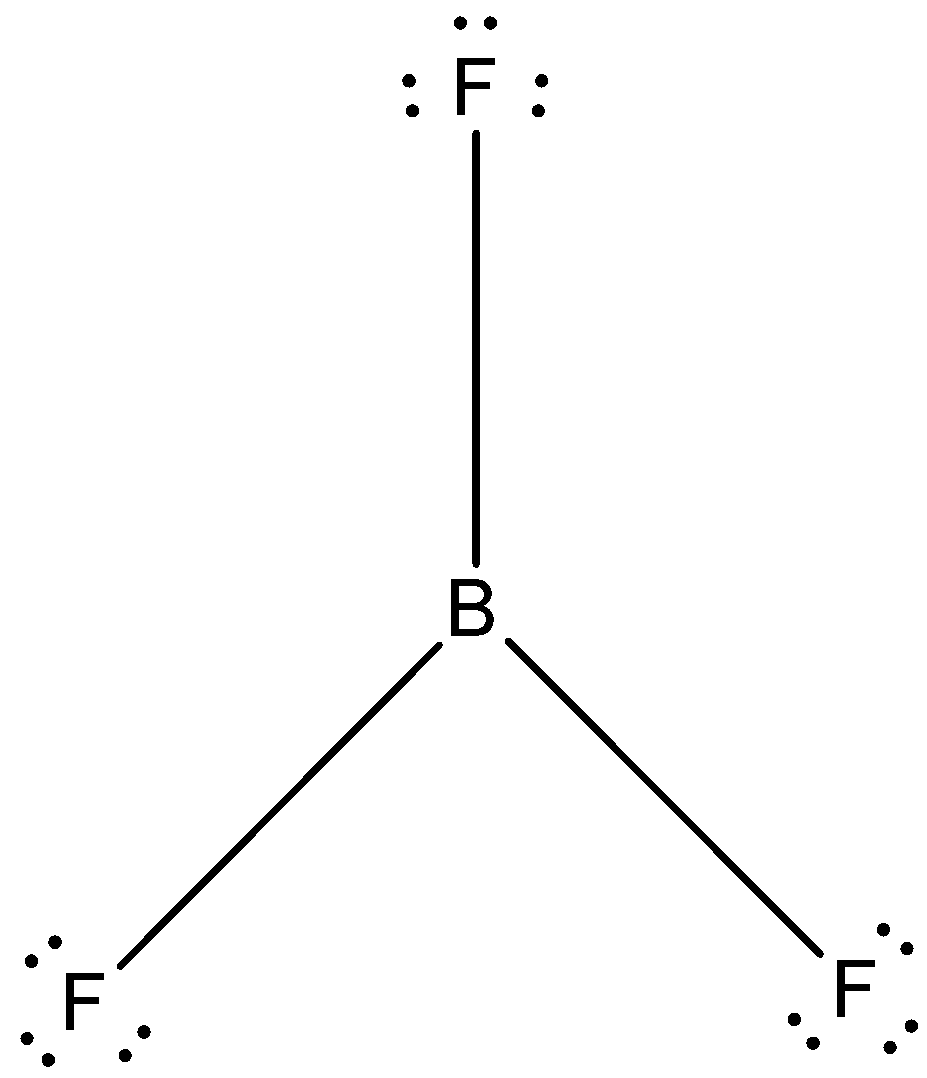
The correct answer is option “D” .
Note: Fluorine has 3 lone pairs of electrons in its valence shell. We know that boron has a vacant orbital in boron trifluoride. Due to this there is formation of a synergic bond between one fluorine atom and central boron atom. This is called back bonding and is very prevalent in boron trifluoride.
Complete step by step answer:
- Boron trifluoride is an organic compound with the formula $\text{B}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}$. It is a pungent colourless toxic gas which forms white fumes in moist air. It is very good Lewis acid as it has a vacant orbital that can accommodate a lone pair of electrons.
- We will write the electronic configuration of boron atoms.
E.C = $\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{1}}}$
Boron has 3 electrons in its valence shell. These electrons are used up in bond formation with the incoming fluorine ions. Boron has no lone pair of electrons.
- Let us determine its hybridisation.
Number of bond pairs = 3
Number of lone pairs = 0
The hybridisation becomes $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ .
$B{{F}_{3}}$ is a planar compound with hybridisation $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ and has a trigonal planar shape.
- The Lewis dot structure of boron trifluoride is given below:

The correct answer is option “D” .
Note: Fluorine has 3 lone pairs of electrons in its valence shell. We know that boron has a vacant orbital in boron trifluoride. Due to this there is formation of a synergic bond between one fluorine atom and central boron atom. This is called back bonding and is very prevalent in boron trifluoride.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




