
The effective capacitances between the points P and Q of the arrangements shown in the figure is

a) $\dfrac{1}{2} \mu $F
b) $1 \mu$ F
c) $2\mu$ F
d) $1.33 \mu$ F

Answer
534k+ views
Hint: In series connected capacitors, charge is the same of all capacitors. So, total voltage is equal to the sum of individual voltages across capacitors. In parallel connected capacitors, charge is the same of all capacitors. So, total charge is equal to the sum of individual charges across capacitors.
Formula Used:
For two capacitors in series, we will use-
$C_{eq} = \dfrac{C_{1} \times C_{2}}{ C_{1} + C_{2} }$
C: -Capacitance
For two capacitors in parallel, we will use-
$C_{eq} = C_{1} + C_{2} $
Complete answer:
We have given a circuit containing capacitors. So, we need to find the equivalent capacitor. The point T wire has zero current so, we can remove this and the two capacitors between T and Q are parallel to each other so we just add on two capacitors.
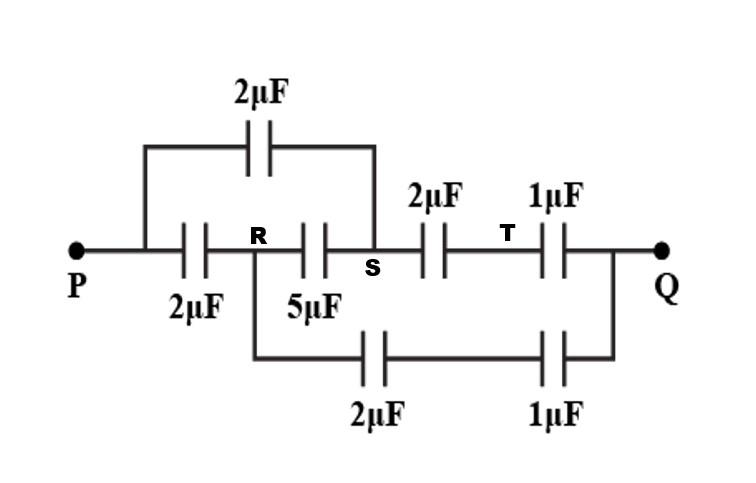
Now we will make an equivalent circuit.
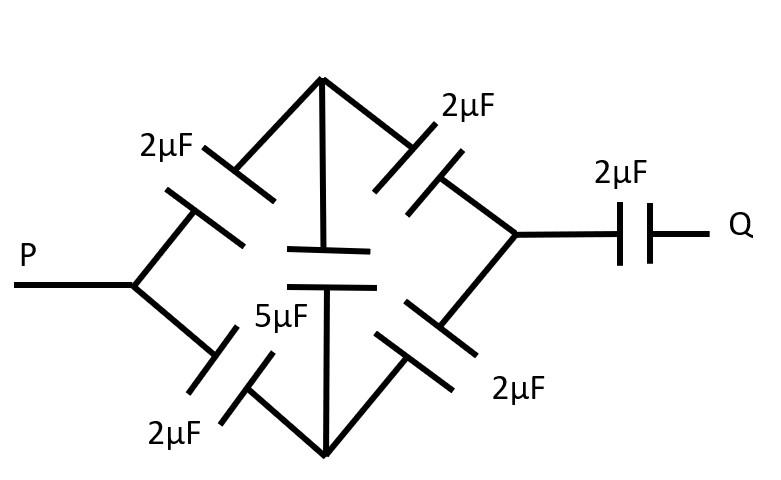
As we see in the above diagram, we can see the Wheatstone bridge is formed, so we can remove the $5\mu$ F capacitor.

Two sets of $2 \mu$ F capacitors are in series so,
$C_{eq} = \dfrac{2\times 2}{ 2 + 2 } = 1 \mu$F
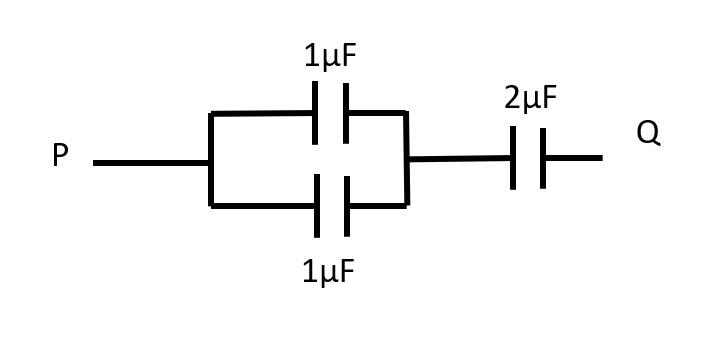
Two $1 \mu$ F capacitors are in parallel. So,
$C_{eq} = 1 +1 = 2 \mu $F
Now, simplified circuit between point P and Q is-
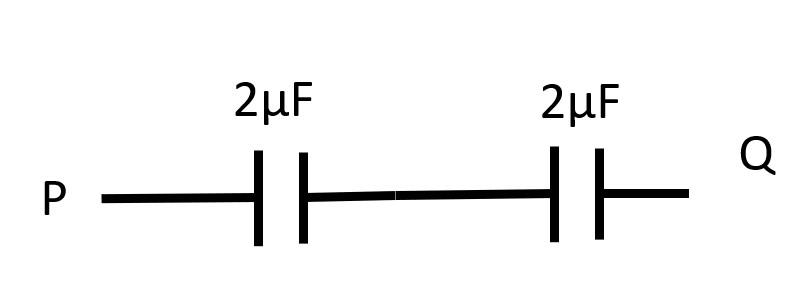
Now, two $2 \mu$ F capacitors are in series.
So, equivalent resistance between P and Q is
$C_{eq} = \dfrac{2\times 2}{ 2 + 2 } = 1 \mu$F
Option (b) is correct.
Additional Information:
In series, each capacitor has an identical charge flow from the battery. +Q charge proceeds from the positive terminal of the battery to the left primary capacitor plate, and it attracts –Q charge on the right plate, or we can say, -Q charge moves from the battery to the right plate, and it attracts +Q on the left plate.
Note:
Capacitors can be connected in two ways, either in series or in parallel. The voltage is the same on the capacitors connecting in parallel. The charge is identical on the capacitors connecting in series. In a parallel circuit, the overall capacitor is always less than any branch capacitor.
Formula Used:
For two capacitors in series, we will use-
$C_{eq} = \dfrac{C_{1} \times C_{2}}{ C_{1} + C_{2} }$
C: -Capacitance
For two capacitors in parallel, we will use-
$C_{eq} = C_{1} + C_{2} $
Complete answer:
We have given a circuit containing capacitors. So, we need to find the equivalent capacitor. The point T wire has zero current so, we can remove this and the two capacitors between T and Q are parallel to each other so we just add on two capacitors.

Now we will make an equivalent circuit.

As we see in the above diagram, we can see the Wheatstone bridge is formed, so we can remove the $5\mu$ F capacitor.

Two sets of $2 \mu$ F capacitors are in series so,
$C_{eq} = \dfrac{2\times 2}{ 2 + 2 } = 1 \mu$F

Two $1 \mu$ F capacitors are in parallel. So,
$C_{eq} = 1 +1 = 2 \mu $F
Now, simplified circuit between point P and Q is-

Now, two $2 \mu$ F capacitors are in series.
So, equivalent resistance between P and Q is
$C_{eq} = \dfrac{2\times 2}{ 2 + 2 } = 1 \mu$F
Option (b) is correct.
Additional Information:
In series, each capacitor has an identical charge flow from the battery. +Q charge proceeds from the positive terminal of the battery to the left primary capacitor plate, and it attracts –Q charge on the right plate, or we can say, -Q charge moves from the battery to the right plate, and it attracts +Q on the left plate.
Note:
Capacitors can be connected in two ways, either in series or in parallel. The voltage is the same on the capacitors connecting in parallel. The charge is identical on the capacitors connecting in series. In a parallel circuit, the overall capacitor is always less than any branch capacitor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




