
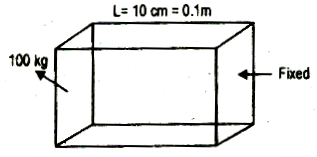
The edge of an aluminum cube is \[10cm\] long. One face of the cube is fixed to a vertical wall. A mass of \[100kg\] is then attached to the opposite facet of the cube. The shear modulus of aluminum is \[25Gpa\]. What is the vertical deflection of this face?
Answer
506.1k+ views
Hint: Lateral strain is also known as transverse strain. The ratio of the change in diameter of a circular bar of a material to its diameter due to deformation in the longitudinal direction is called lateral strain. We know that the shear modulus is defined as the ratio of Tangential stress to the shearing strain. And similarly, we know that the shearing strain is defined as the ratio of Lateral strain to the side of the cube. By applying these formulae we can find out the vertical deflection of this face.
Formula used:
Shearing Strain \[ = \] Tangential Stress / Shear modulus
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{F}{{A\eta }}\], Where \[F = \]Tangential Stress, \[\eta = \]Shear modulus, \[A = \] Area of each face
Lateral Strain \[ = \] Shearing Strain\[ \times \] Side of the cube
Complete step-by-step solution:
Here, side of the cube, \[L = 10cm = 0.1m\]
Area of each face \[A = {\left( {0.1} \right)^2} = 0.01{m^2}\]
The tangential force acting on the face, \[F = 100kg = 100 \times 9.8 = 980N\]
Shear modulus, \[\eta \]\[ = \]Tangential stress / Shearing strain
Shearing strain = Tangential stress / Shear modulus
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{F}{{A\eta }} = \dfrac{{980}}{{0.01 \times 25 \times {{10}^9}}}\]
\[ = 3.92 \times {10^{ - 6}}\]
Now, The lateral strain/side of the cube = shearing strain
Lateral strain = Shearing strain \[ \times \]side of the cube
\[ = 3.92 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 0.1\]
\[ = 3.92 \times {10^{ - 7}}m\]
Hence, the vertical deflection of this face is \[3.92 \times {10^{ - 7}}m\].
Note:The force acting on a moving body in the direction of the tangent to the curved path of the body is called the Tangential force.
A material can resist transverse deformations and is a valid index of elastic behavior only for small deformations, after which the material can return to its original configuration is defined as the shear modulus.
The vertical distance between a point from the unreformed axis of a structure and the same point which lies on the deformed axis is called the vertical deflection.
Formula used:
Shearing Strain \[ = \] Tangential Stress / Shear modulus
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{F}{{A\eta }}\], Where \[F = \]Tangential Stress, \[\eta = \]Shear modulus, \[A = \] Area of each face
Lateral Strain \[ = \] Shearing Strain\[ \times \] Side of the cube
Complete step-by-step solution:
Here, side of the cube, \[L = 10cm = 0.1m\]
Area of each face \[A = {\left( {0.1} \right)^2} = 0.01{m^2}\]
The tangential force acting on the face, \[F = 100kg = 100 \times 9.8 = 980N\]

Shear modulus, \[\eta \]\[ = \]Tangential stress / Shearing strain
Shearing strain = Tangential stress / Shear modulus
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{F}{{A\eta }} = \dfrac{{980}}{{0.01 \times 25 \times {{10}^9}}}\]
\[ = 3.92 \times {10^{ - 6}}\]
Now, The lateral strain/side of the cube = shearing strain
Lateral strain = Shearing strain \[ \times \]side of the cube
\[ = 3.92 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 0.1\]
\[ = 3.92 \times {10^{ - 7}}m\]
Hence, the vertical deflection of this face is \[3.92 \times {10^{ - 7}}m\].
Note:The force acting on a moving body in the direction of the tangent to the curved path of the body is called the Tangential force.
A material can resist transverse deformations and is a valid index of elastic behavior only for small deformations, after which the material can return to its original configuration is defined as the shear modulus.
The vertical distance between a point from the unreformed axis of a structure and the same point which lies on the deformed axis is called the vertical deflection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




