
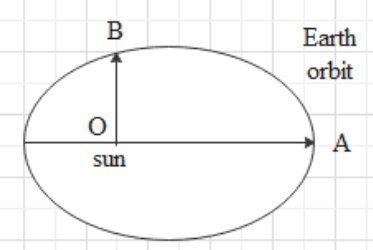
The earth moves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit as shown in the given figure. The ratio $\dfrac{OA}{OB}=x$ . The ratio of the speed of the earth at B to that at A is nearly:
(A). $\sqrt{x}$
(B). x
(C). $x\sqrt{x}$
(D). ${{x}^{2}}$

Answer
603.3k+ views
Hint: Try to understand the motion of earth around the sun and learn about how gravitational effects this motion. Try to understand where we can use the conservation laws. Here we are applying the law of conservation of momentum. So, try to study about it.
Complete step by step answer:
The earth is moving around the sun in an elliptical orbit.
Given, the ration of the distance from the sun to earth in two positions A and B is
$\dfrac{OA}{OB}=x$
Now, we need to find the ratio of velocities of earth at the two points.
The earth and the sun are connected by the gravitational force.
To find the ratio of velocities at the two points we can use the law of conservation of angular momentum, because in this system external torque is zero.
From the laws of conservation of angular momentum,
Angular momentum of earth at point B is equal to the angular momentum of earth at point A.
$\begin{align}
& m{{v}_{B}}{{r}_{B}}=m{{v}_{A}}{{r}_{A}} \\
& {{v}_{B}}{{r}_{B}}={{v}_{A}}{{r}_{A}} \\
& \dfrac{{{v}_{B}}}{{{v}_{A}}}=\dfrac{{{r}_{A}}}{{{r}_{B}}} \\
& \dfrac{{{v}_{B}}}{{{v}_{A}}}=\dfrac{OA}{OB} \\
& \dfrac{{{v}_{B}}}{{{v}_{A}}}=x \\
\end{align}$
So, the ratio of velocity of earth at point B to the point A is x.
The correct option is (B).
Note: The earth orbits the sun in an elliptical orbit. The external torque on the earth in its orbit is zero. It is because the gravitational force on the earth is towards the sun and the direction of position vector is also along the direction of earth to sun. Since, torque is defined as the cross product of the force and position vector and the force and position vectors are parallel here, the total external torque on earth is also zero.
Complete step by step answer:
The earth is moving around the sun in an elliptical orbit.
Given, the ration of the distance from the sun to earth in two positions A and B is
$\dfrac{OA}{OB}=x$
Now, we need to find the ratio of velocities of earth at the two points.
The earth and the sun are connected by the gravitational force.
To find the ratio of velocities at the two points we can use the law of conservation of angular momentum, because in this system external torque is zero.
From the laws of conservation of angular momentum,
Angular momentum of earth at point B is equal to the angular momentum of earth at point A.
$\begin{align}
& m{{v}_{B}}{{r}_{B}}=m{{v}_{A}}{{r}_{A}} \\
& {{v}_{B}}{{r}_{B}}={{v}_{A}}{{r}_{A}} \\
& \dfrac{{{v}_{B}}}{{{v}_{A}}}=\dfrac{{{r}_{A}}}{{{r}_{B}}} \\
& \dfrac{{{v}_{B}}}{{{v}_{A}}}=\dfrac{OA}{OB} \\
& \dfrac{{{v}_{B}}}{{{v}_{A}}}=x \\
\end{align}$
So, the ratio of velocity of earth at point B to the point A is x.
The correct option is (B).
Note: The earth orbits the sun in an elliptical orbit. The external torque on the earth in its orbit is zero. It is because the gravitational force on the earth is towards the sun and the direction of position vector is also along the direction of earth to sun. Since, torque is defined as the cross product of the force and position vector and the force and position vectors are parallel here, the total external torque on earth is also zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




