
The d-orbitals involved in \[s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}\] or \[{{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridization of the central metal ion are:
(this question has multiple correct options)
a.) \[{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}\]
b.) \[{{d}_{xy}}\]
c.) \[{{d}_{yz}}\]
d.) \[{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}\]
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: From the given hybridization we can say that the geometry of the compound has octahedral. So, to solve this question, consider the splitting of d-orbitals in an octahedral complex, when approached by a ligand.
Complete step by step solution:
When any negatively charged species or ligand approaches a metal, the energy of the orbitals increases. This leads to the splitting of orbitals as –
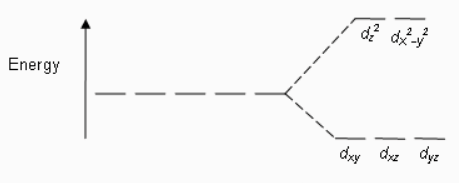
In octahedral complexes, the splitting of orbitals always takes place in this manner.
The electron first goes to the lower energy orbital, i.e. \[{{d}_{xy}}\].\[{{d}_{yz}}\],\[{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}\]and then to the higher energy orbital, i.e., \[{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}\]and \[{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}\]. Therefore, bonding electrons go to the high energy orbitals which decide the hybridization of the compound.
In case of \[s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}\] hybridization, nd (outermost) orbitals are involved. The compound is therefore also known as outer-orbital complex.
In case of \[{{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridization, (n-1)d (next to outermost) orbitals are involved. The compound is therefore also known as inner-orbital complex.
Therefore, the answer is – option (a) and option (d).
Additional information: In short, if inner d-orbital is used for bonding, the hybridization will be \[{{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}\]. Similarly, if outer d-orbital is used, the hybridization will be \[s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}\].
Note: Irrespective of the differences between \[s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}\] and \[{{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}\], there are certain similarities, such as –
Both hybridization results in octahedral geometry.
Both have six hybrid orbitals.
There is an angle of 90 degrees between hybrid orbitals.
Complete step by step solution:
When any negatively charged species or ligand approaches a metal, the energy of the orbitals increases. This leads to the splitting of orbitals as –

In octahedral complexes, the splitting of orbitals always takes place in this manner.
The electron first goes to the lower energy orbital, i.e. \[{{d}_{xy}}\].\[{{d}_{yz}}\],\[{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}\]and then to the higher energy orbital, i.e., \[{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}\]and \[{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}\]. Therefore, bonding electrons go to the high energy orbitals which decide the hybridization of the compound.
In case of \[s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}\] hybridization, nd (outermost) orbitals are involved. The compound is therefore also known as outer-orbital complex.
In case of \[{{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridization, (n-1)d (next to outermost) orbitals are involved. The compound is therefore also known as inner-orbital complex.
Therefore, the answer is – option (a) and option (d).
Additional information: In short, if inner d-orbital is used for bonding, the hybridization will be \[{{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}\]. Similarly, if outer d-orbital is used, the hybridization will be \[s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}\].
Note: Irrespective of the differences between \[s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}\] and \[{{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}\], there are certain similarities, such as –
Both hybridization results in octahedral geometry.
Both have six hybrid orbitals.
There is an angle of 90 degrees between hybrid orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




