
The distance between a node and an anti-node is
A. \[2\lambda \]
B. \[\lambda \]
C. \[\dfrac{\lambda }{2}\]
D. \[\dfrac{\lambda }{4}\]
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: From definition we know that an antinode and a node is \[\dfrac{1}{2}\]the distance between \[2\]consecutive nodes. Then we solve it using the formula \[\lambda = 2(2 \times \]Distance between a node and an antinode\[)\].
Complete step by step solution:
Here,
From the definition we know that,
The wavelength of a wave is defined as having twice the distance between two consecutive nodes and antinodes.
Now,
The distance between an antinode and a node is \[\dfrac{1}{2}\] the distance between \[2\] consecutive nodes.
Therefore,
\[\lambda = 2(2 \times \] Distance between a node and an antinode\[)\]
Hence,
The required distance is \[\dfrac{\lambda }{4}\]
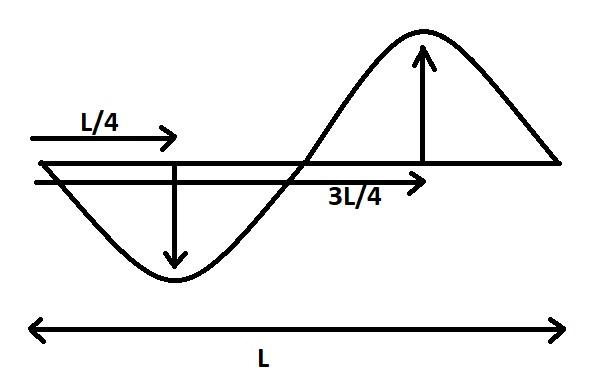
Note: From definition we know that an antinode is the place where the wave’s maximum amplitude is generated by positive interference of the incoming and reflected waves. A node, by comparison, is the position where destructive interference reduces the amplitude of the wave to zero.
Complete step by step solution:
Here,
From the definition we know that,
The wavelength of a wave is defined as having twice the distance between two consecutive nodes and antinodes.
Now,
The distance between an antinode and a node is \[\dfrac{1}{2}\] the distance between \[2\] consecutive nodes.
Therefore,
\[\lambda = 2(2 \times \] Distance between a node and an antinode\[)\]
Hence,
The required distance is \[\dfrac{\lambda }{4}\]

Note: From definition we know that an antinode is the place where the wave’s maximum amplitude is generated by positive interference of the incoming and reflected waves. A node, by comparison, is the position where destructive interference reduces the amplitude of the wave to zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




