
The displacement time graph for two particles A and B are straight lines inclined at angles of ${30^0}{\text{ and 6}}{{\text{0}}^0}$ with the time axis. The ratio of the velocities of ${V_A}:{V_B}$ is
$
(a){\text{ 1:2}} \\
(b){\text{ 1:}}\sqrt 3 \\
(c){\text{ }}\sqrt 3 {\text{:1}} \\
(d){\text{ 1:3}} \\
$
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: In this question use the concept that the velocity is the rate of change of the displacement with respect to the time and this is nothing but the slope of the straight lines about the tan of the inclination for a displacement time graph. Use this concept to get the velocities for the particles A and B respectively and then find the ratio. This will help to approach the problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
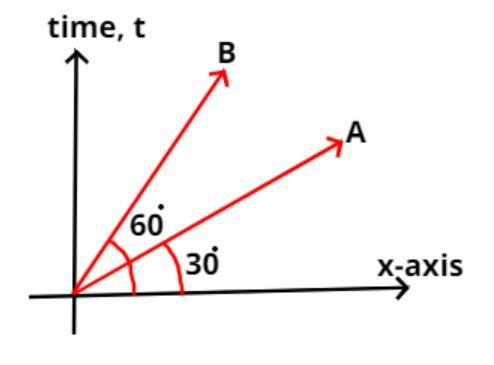
As we all know that the velocity is the rate of change of the displacement with respect to the time and this is nothing both the slope of the straight lines about the tan of the inclination.
Now it is given that the particle A is inclined at an angle ${30^o}$
So the velocity of the particle A is
$ \Rightarrow {V_A} = $ Slope of x – t graph = $\dfrac{{d{x_A}}}{{dt}} = \tan {30^o}$..................... (1)
Now it is given that the particle B is inclined at an angle ${60^o}$
So the velocity of the particle B is
$ \Rightarrow {V_B} = $ Slope of x – t graph = $\dfrac{{d{x_B}}}{{dt}} = \tan {60^o}$.................. (2)
Now we have to find out the ratio of the velocities ${V_A}$ and ${V_B}$.
So divide equation (1) by equation (2) we have,
Therefore, $\dfrac{{{V_A}}}{{{V_B}}} = \dfrac{{\tan {{30}^o}}}{{\tan {{60}^o}}}$
Now as we know that $\tan {30^o} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ and $\tan {60^o} = \sqrt 3 $
Now substitute these values in the above equation we have,
Therefore, $\dfrac{{{V_A}}}{{{V_B}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Now simplify this equation we have,
Therefore, $\dfrac{{{V_A}}}{{{V_B}}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 \times \sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{1}{3}$
So this is the required ratio of the velocities of particles A and B.
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (D) is the correct answer.
Note – The slope of a straight line is defined as the angle it makes with the positive direction of the x-axis in anticlockwise sense. Since $v = \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}$ thus the slope has a relationship with the velocity. Now as acceleration that is $a = \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}$ so the slope of a velocity-time curve will give the value of acceleration.
Complete step-by-step answer:

As we all know that the velocity is the rate of change of the displacement with respect to the time and this is nothing both the slope of the straight lines about the tan of the inclination.
Now it is given that the particle A is inclined at an angle ${30^o}$
So the velocity of the particle A is
$ \Rightarrow {V_A} = $ Slope of x – t graph = $\dfrac{{d{x_A}}}{{dt}} = \tan {30^o}$..................... (1)
Now it is given that the particle B is inclined at an angle ${60^o}$
So the velocity of the particle B is
$ \Rightarrow {V_B} = $ Slope of x – t graph = $\dfrac{{d{x_B}}}{{dt}} = \tan {60^o}$.................. (2)
Now we have to find out the ratio of the velocities ${V_A}$ and ${V_B}$.
So divide equation (1) by equation (2) we have,
Therefore, $\dfrac{{{V_A}}}{{{V_B}}} = \dfrac{{\tan {{30}^o}}}{{\tan {{60}^o}}}$
Now as we know that $\tan {30^o} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ and $\tan {60^o} = \sqrt 3 $
Now substitute these values in the above equation we have,
Therefore, $\dfrac{{{V_A}}}{{{V_B}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Now simplify this equation we have,
Therefore, $\dfrac{{{V_A}}}{{{V_B}}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 \times \sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{1}{3}$
So this is the required ratio of the velocities of particles A and B.
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (D) is the correct answer.
Note – The slope of a straight line is defined as the angle it makes with the positive direction of the x-axis in anticlockwise sense. Since $v = \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}$ thus the slope has a relationship with the velocity. Now as acceleration that is $a = \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}$ so the slope of a velocity-time curve will give the value of acceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




