
The direction $\left( \theta \right)$ of $\overrightarrow{E}$ at point P due to uniformly charged finite rod will be
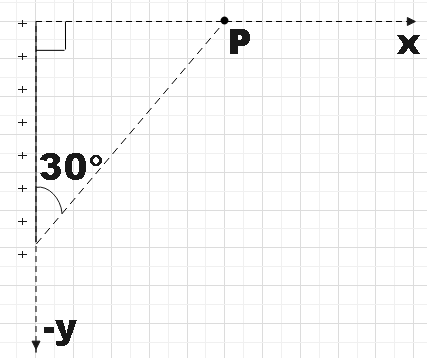
A. at angle $30{}^\circ $ from x-axis
B. $45{}^\circ $ from x-axis
C. $60{}^\circ $ from x-axis
D. none of these

Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint: As a first step find the angle subtended by the finite rod at the point P by using the property of angle sum of triangles. Then, you could assume the net charge to be concentrated at the centre most point of the rod. Then, knowing how the electric field would be directed for a positively charged rod and simple geometry you could solve the question.
Complete answer:
In the question, we are given a finite rod which is positively charged. We are given one of the angles in the triangle to be$30{}^\circ $. Now, from angle sum property of triangles we have,
$90+30+x=180$
Where, x is the angle subtended by the finite rod at the point marked P.
$x=60{}^\circ $
Now, we could recall that the electric field direction is given from positive to negative and so the electric field will be directed outward at point P.
Now, let us assume that the charge is concentrated at the midpoint of the given finite rod. So, we know from basic geometry that the line bisecting the finite rod will bisect the angle subtended at the point P.
In the above figure we see that the electric field line the angle x which is the angle subtended by the finite rod at point P. So, we could write that,
$x=2\theta =60{}^\circ $
$\therefore \theta =30{}^\circ $
Hence, we found that the direction $\left( \theta \right)$ of $\overrightarrow{E}$ at point P due to uniformly charged finite rod will be at angle $30{}^\circ $ from x-axis.
Option A is correct.
Note:
We have solved the above question by simply having a strong grasp on basic geometry and also based on some quite obvious assumptions. Very similar to assuming the centre of mass at the geometric centre of certain objects we have here assumed the net charge to be concentrated at the centre of the finite rod given.
Complete answer:
In the question, we are given a finite rod which is positively charged. We are given one of the angles in the triangle to be$30{}^\circ $. Now, from angle sum property of triangles we have,
$90+30+x=180$
Where, x is the angle subtended by the finite rod at the point marked P.
$x=60{}^\circ $
Now, we could recall that the electric field direction is given from positive to negative and so the electric field will be directed outward at point P.
Now, let us assume that the charge is concentrated at the midpoint of the given finite rod. So, we know from basic geometry that the line bisecting the finite rod will bisect the angle subtended at the point P.
In the above figure we see that the electric field line the angle x which is the angle subtended by the finite rod at point P. So, we could write that,
$x=2\theta =60{}^\circ $
$\therefore \theta =30{}^\circ $
Hence, we found that the direction $\left( \theta \right)$ of $\overrightarrow{E}$ at point P due to uniformly charged finite rod will be at angle $30{}^\circ $ from x-axis.
Option A is correct.
Note:
We have solved the above question by simply having a strong grasp on basic geometry and also based on some quite obvious assumptions. Very similar to assuming the centre of mass at the geometric centre of certain objects we have here assumed the net charge to be concentrated at the centre of the finite rod given.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




