
The dipole moments of \[CC{{l}_{4}}\], \[CHC{{l}_{3}}\] and \[C{{H}_{4}}\]
A. \[C{{H}_{4}}\]= \[CC{{l}_{4}}\]<\[CHC{{l}_{3}}\]
B. \[CC{{l}_{4}}\]<\[C{{H}_{4}}\]<\[CHC{{l}_{3}}\]
C. \[C{{H}_{4}}\]<\[CC{{l}_{4}}\]<\[CHC{{l}_{3}}\]
D. \[CHC{{l}_{3}}\]<\[C{{H}_{4}}\]=\[CC{{l}_{4}}\]
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: Dipole moment is the separation of two charges by a distance. When one atom is more electronegative than the other, it tries to pull the shared electrons towards itself.
Hence, greater the electronegativity of one atom than the other, greater will be the length and more dipole moment.
Complete step by step answer:
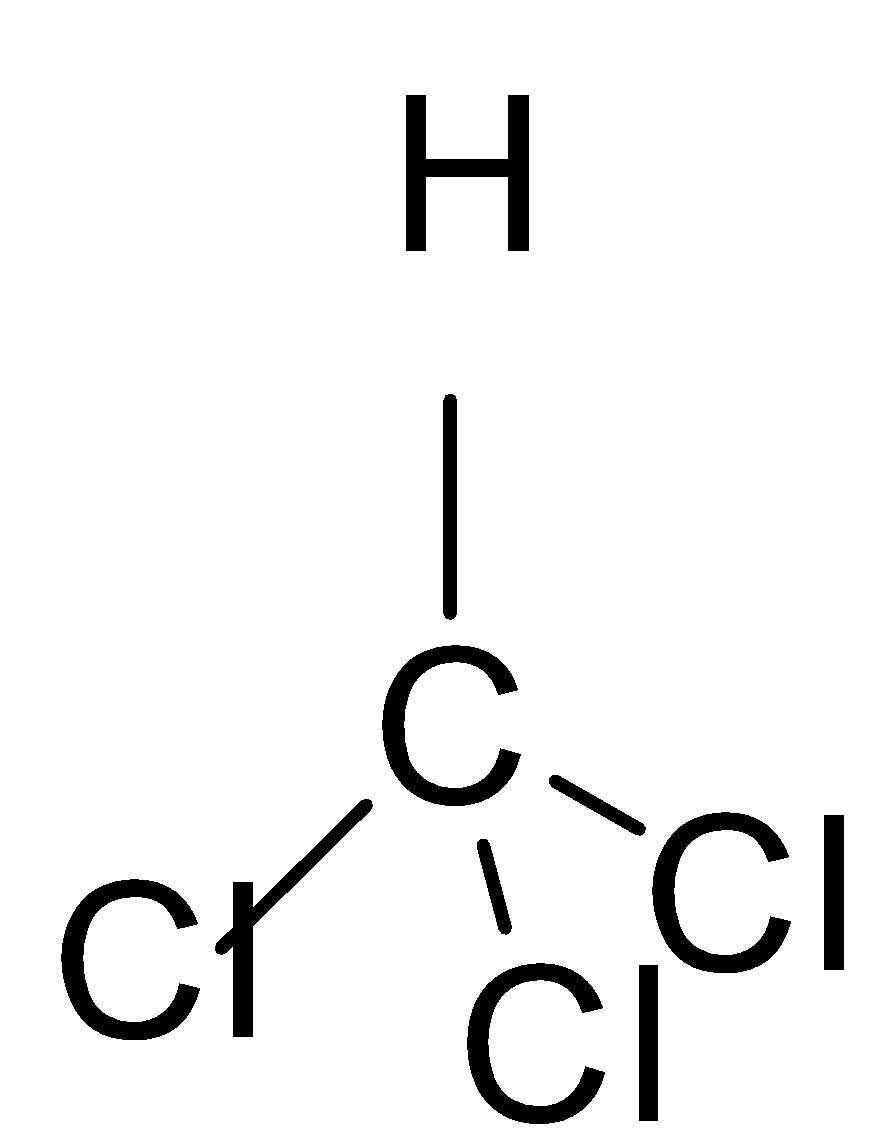
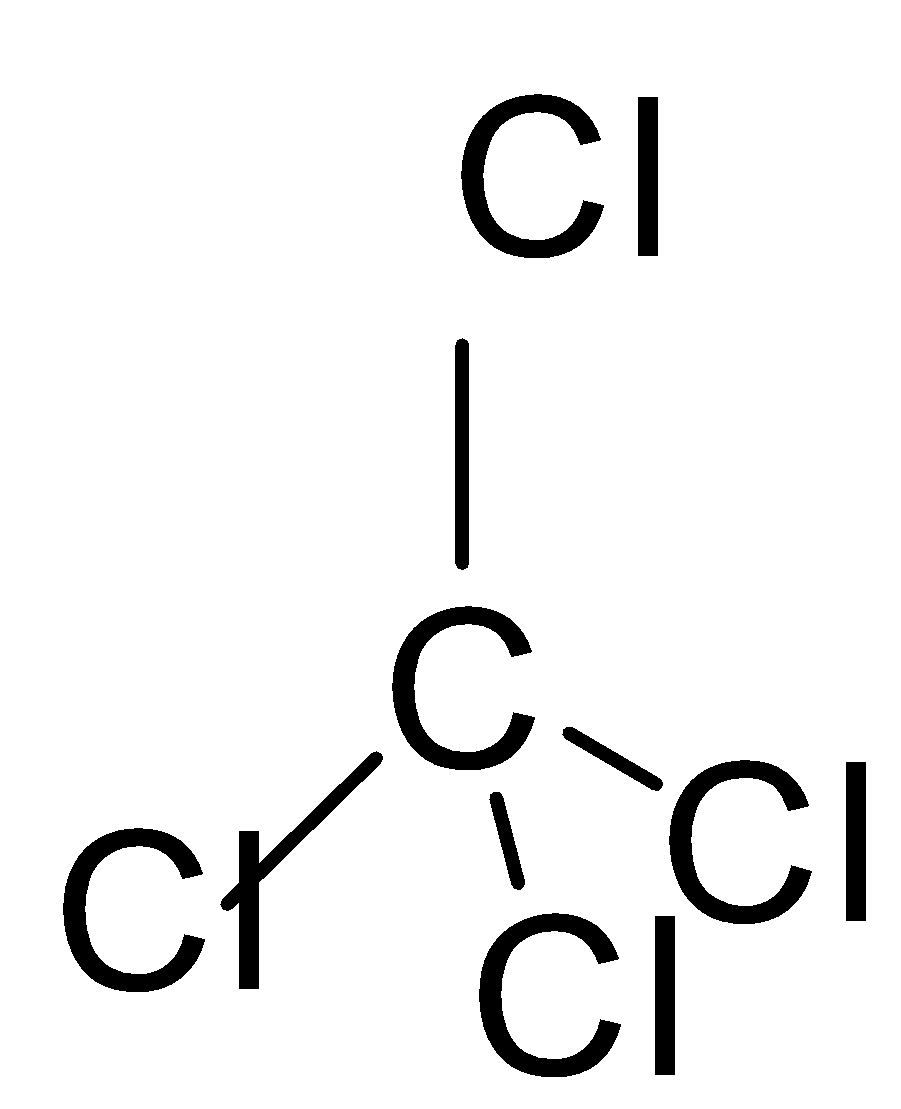
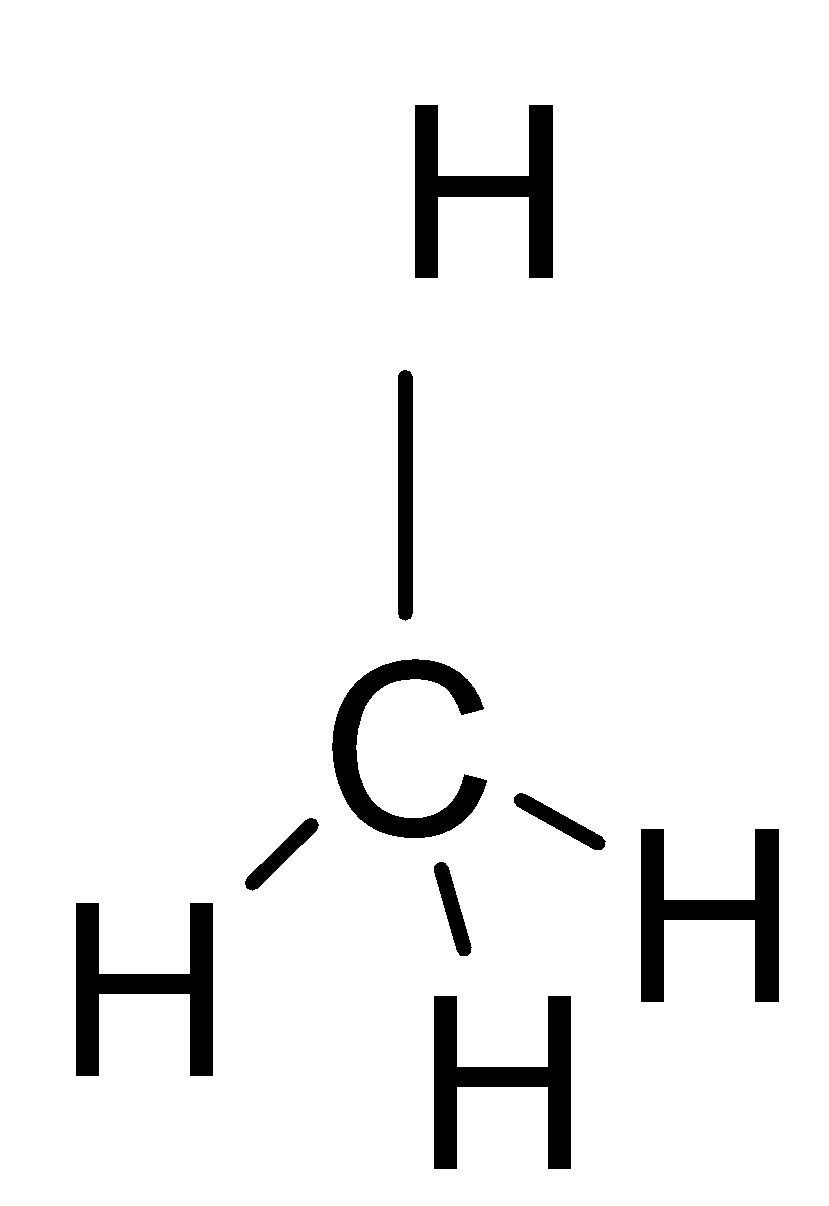
If we look at the structures of these molecules and try to find the solution, we can easily work out the solution to this question. The first thing to be noticed is that these structures have tetrahedral geometry.
In the first molecule which is chloroform we all know that chlorine is more electronegative than the Carbon and hydrogen due to which it tries to draw all the electrons towards it and its dipole moment is non-zero \[\mu \ne 0\].
In the second molecule, if we look at the structure, we will see that all the surrounding atoms are chlorine which makes this dipole moment non zero which is not true because if you look at the shape it is very symmetrical which is the prime reason that the dipole moment of this molecule is zero \[\mu =0\]
The third molecule is Methane which is a gas but it too has a zero-dipole moment \[\mu =0\], because it also has a very perfect tetrahedral structure and symmetry leads to this reason.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Dipole moment does not only depend on the electronegativity of the element or polarity of the bond but also depends upon the symmetry of the molecule as then the net dipole of that molecule becomes zero due to the charge distribution which takes place evenly.
Hence, greater the electronegativity of one atom than the other, greater will be the length and more dipole moment.
Complete step by step answer:



If we look at the structures of these molecules and try to find the solution, we can easily work out the solution to this question. The first thing to be noticed is that these structures have tetrahedral geometry.
In the first molecule which is chloroform we all know that chlorine is more electronegative than the Carbon and hydrogen due to which it tries to draw all the electrons towards it and its dipole moment is non-zero \[\mu \ne 0\].
In the second molecule, if we look at the structure, we will see that all the surrounding atoms are chlorine which makes this dipole moment non zero which is not true because if you look at the shape it is very symmetrical which is the prime reason that the dipole moment of this molecule is zero \[\mu =0\]
The third molecule is Methane which is a gas but it too has a zero-dipole moment \[\mu =0\], because it also has a very perfect tetrahedral structure and symmetry leads to this reason.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Dipole moment does not only depend on the electronegativity of the element or polarity of the bond but also depends upon the symmetry of the molecule as then the net dipole of that molecule becomes zero due to the charge distribution which takes place evenly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




