
The diagrams below show the regions of equipotentials. A positive charge is moved from $A$ to $B$ in each diagram.
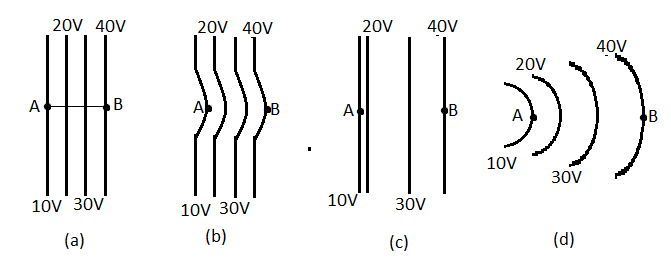
A) Maximum work is required to move $q$ in figure (b)
B) Maximum work is required to move $q$ in figure (c)
C) In all the cases the work done is the same
D) Minimum work is required to move $q$ in figure (a)

Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: The external work required to move a charge in an electric field depends only upon the change in the electric potential of the charge and not the path taken by the charge. Equipotentials are the boundaries or regions where a charge will have the same electric potential.
Formula used:
$W=q\Delta V$
Complete step by step answer:
The magnitude of work done by an external agent while moving a charge from point $A$ to point $B$ depends upon the difference of the electric potential of the points.
The magnitude of work done $W$ by an external agent to move a charge $q$ through the potential difference $\Delta V$ is given by
$W=q\Delta V$ --(1)
As we see in the figure, in all cases the charge is moved from point $A$ which has a potential of $10V$ to point $B$ which has a potential of $40V$. Hence, the change in the electric potential in all these cases is the same, that is, $40V-10V=30V$.
Hence, since the change in potential $\Delta V$ is the same in all cases, using (1), we can say that the work done in all the cases will be the same.
Hence, the correct option is C) In all the cases the work done is the same.
Note: The work done in moving a charge is dependent on the difference in the electric potential of the final and initial points as explained above. This is because the electrostatic forces are conservative forces, that is, the work done by them only depends upon the initial and final positions and not the path taken by the body. This is similar to the force of gravity and the work done by gravity (change in gravitational potential energy) which only depends upon the initial and final positions of the body and not the path taken to reach the final position from the initial position.
Formula used:
$W=q\Delta V$
Complete step by step answer:
The magnitude of work done by an external agent while moving a charge from point $A$ to point $B$ depends upon the difference of the electric potential of the points.
The magnitude of work done $W$ by an external agent to move a charge $q$ through the potential difference $\Delta V$ is given by
$W=q\Delta V$ --(1)
As we see in the figure, in all cases the charge is moved from point $A$ which has a potential of $10V$ to point $B$ which has a potential of $40V$. Hence, the change in the electric potential in all these cases is the same, that is, $40V-10V=30V$.
Hence, since the change in potential $\Delta V$ is the same in all cases, using (1), we can say that the work done in all the cases will be the same.
Hence, the correct option is C) In all the cases the work done is the same.
Note: The work done in moving a charge is dependent on the difference in the electric potential of the final and initial points as explained above. This is because the electrostatic forces are conservative forces, that is, the work done by them only depends upon the initial and final positions and not the path taken by the body. This is similar to the force of gravity and the work done by gravity (change in gravitational potential energy) which only depends upon the initial and final positions of the body and not the path taken to reach the final position from the initial position.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




