
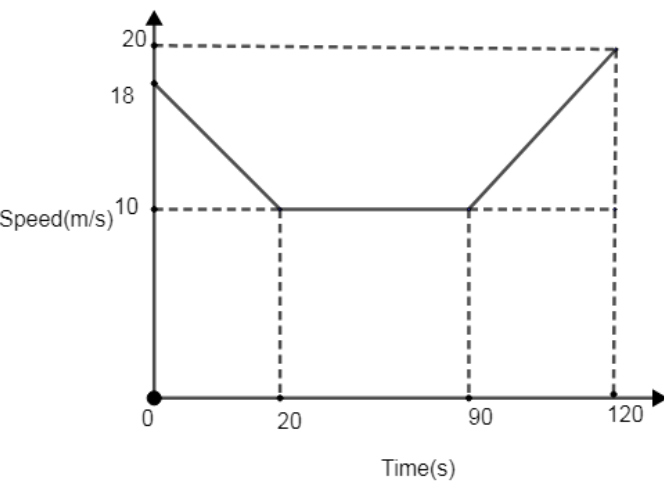
The diagram shows the speed-time graph for 120 seconds of a car journey.
(a) Calculate the deceleration of the car during the first 20 seconds.
(b) Calculate the total distance traveled by car during the 120 seconds.
(c) Calculate the average speed for this 120-second journey.

Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: Divide the above journey of the car into 3 parts. The first part from 0 – 20 seconds, the second part from 20 – 90 seconds, and the third part from 90 – 120 seconds. For part (a), observe the graph from 0 – 20 seconds and apply the formula: -
\[a=\dfrac{v-u}{t}\], where ‘a’ is acceleration, ‘v’ is velocity at t = 20s and ‘u’ is velocity at t = 0s. ‘t’ is the time interval of 20 seconds. For part (b), calculate the area under the speed-time graph to find the total distance. For part (c), divide the distance obtained in part (b) with t = 120s.
Complete step-by-step solution
(a) We have to calculate the deceleration of the car during the first 20 seconds.
The term ‘deceleration’ means negative acceleration.
Applying the formula: - \[a=\dfrac{v-u}{t}\], where a = acceleration, v = velocity at t = 20s, u = velocity at t = 0s and t = time interval of 20s, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{10-18}{20}=\dfrac{-8}{20} \\
& \Rightarrow a=-0.4m{{s}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Since, ‘a’ is negative, therefore deceleration = \[-0.4m{{s}^{-2}}\].
(b) Here, we have to find the total distance traveled by car during the 120 seconds. Therefore, Total distance traveled = Area under the speed-time graph.

\[\Rightarrow \] Total distance travelled
= Area of trapezium ABEDC + Area of rectangle CDGF +Area of trapezium FGIH
Applying the formula of area of trapezium = \[\dfrac{1}{2}\times \] [Sum of parallel sides] \[\times \] height
We have, total distance travelled
\[\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left[ 18+10 \right]\times 20+70\times 10+\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left[ 20+10 \right]\times 30 \\
& =280+700+450 \\
\end{align}\]
= 1430m
Therefore, total distance travelled = 1430m.
(c) Here, we have to find the average speed during the 120 seconds journey.
Applying the formula for average speed = $\dfrac{\text{Total distance}}{\text{Total time}}$
We get, Average speed = \[\dfrac{1430}{120}\].
\[\Rightarrow \] Average speed \[\approx 11.92m{{s}^{-1}}\].
Hence, average speed during the 120s journey is nearly \[11.92m{{s}^{-1}}\].
Note: One may note that we have divided the journey into 3 parts because then it will be easy for us to calculate the area of the speed-time graph which is the total distance traveled. We can also calculate the area in different ways like by forming two triangles and a rectangle. The other method can include the method of integration which is used for complex curves, so we do not need such an integration method here.
\[a=\dfrac{v-u}{t}\], where ‘a’ is acceleration, ‘v’ is velocity at t = 20s and ‘u’ is velocity at t = 0s. ‘t’ is the time interval of 20 seconds. For part (b), calculate the area under the speed-time graph to find the total distance. For part (c), divide the distance obtained in part (b) with t = 120s.
Complete step-by-step solution
(a) We have to calculate the deceleration of the car during the first 20 seconds.
The term ‘deceleration’ means negative acceleration.
Applying the formula: - \[a=\dfrac{v-u}{t}\], where a = acceleration, v = velocity at t = 20s, u = velocity at t = 0s and t = time interval of 20s, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{10-18}{20}=\dfrac{-8}{20} \\
& \Rightarrow a=-0.4m{{s}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Since, ‘a’ is negative, therefore deceleration = \[-0.4m{{s}^{-2}}\].
(b) Here, we have to find the total distance traveled by car during the 120 seconds. Therefore, Total distance traveled = Area under the speed-time graph.

\[\Rightarrow \] Total distance travelled
= Area of trapezium ABEDC + Area of rectangle CDGF +Area of trapezium FGIH
Applying the formula of area of trapezium = \[\dfrac{1}{2}\times \] [Sum of parallel sides] \[\times \] height
We have, total distance travelled
\[\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left[ 18+10 \right]\times 20+70\times 10+\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left[ 20+10 \right]\times 30 \\
& =280+700+450 \\
\end{align}\]
= 1430m
Therefore, total distance travelled = 1430m.
(c) Here, we have to find the average speed during the 120 seconds journey.
Applying the formula for average speed = $\dfrac{\text{Total distance}}{\text{Total time}}$
We get, Average speed = \[\dfrac{1430}{120}\].
\[\Rightarrow \] Average speed \[\approx 11.92m{{s}^{-1}}\].
Hence, average speed during the 120s journey is nearly \[11.92m{{s}^{-1}}\].
Note: One may note that we have divided the journey into 3 parts because then it will be easy for us to calculate the area of the speed-time graph which is the total distance traveled. We can also calculate the area in different ways like by forming two triangles and a rectangle. The other method can include the method of integration which is used for complex curves, so we do not need such an integration method here.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





