
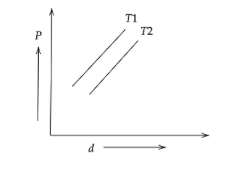
The diagram shows the graph of pressure vs density for given mass of an ideal gas at two temperatures ${T_1}$ and ${T_2}$
A) ${T_1} > {T_2}$
B) ${T_1} = {T_2}$
C) ${T_1} < {T_2}$
D) Any of the three are possible

Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint:The internal energy of the gas is measured by multiplying the total number of gas molecules with the average kinetic energy of each molecule. This means that the density is inversely proportional to temperature. To address this statement, the basic laws are used for unit volume.
Useful formula:
Ideal Gas Law in term of density
$PM = dRT$
Where,
$d$ - density of gas
$P$ - Pressure
$R$- Gas Constant
$T$-Temperature
$M$- Molar Mass
Complete step by step process:
Given by,
An ideal gas at two temperatures ${T_1}$ and ${T_2}$
As we know the ideal gas formula,
$PM = dRT$
The above diagram,
The slope of the straight line ${T_1}$ is greater than that of ${T_2}$.
pressure of a given gas is inversely proportional to its volume provided the temperature remains constant
$PV = nRT$
Therefore,
$P = wRT/MV$
Rearranging the above equation,
$P = dRT/M$
The $rms$ speed of the gas is given by $3{P_p}$.
It means gas $rms$ of ${T_1}$ molecules are higher than ${T_2}$ molecules.
Therefore, $P\alpha d - T$
So, ${T_1} > {T_2}$.
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Note: The number of molecules in a gas is very high and the average separation between them is greater than the size of the gas molecules. The molecules of different gases are different. The measurement of heat is temperature. The molecules of different gases are different. Density is the indicator of how tightly an object is packaged or the ratio of the object's mass to its length.
Useful formula:
Ideal Gas Law in term of density
$PM = dRT$
Where,
$d$ - density of gas
$P$ - Pressure
$R$- Gas Constant
$T$-Temperature
$M$- Molar Mass
Complete step by step process:
Given by,
An ideal gas at two temperatures ${T_1}$ and ${T_2}$
As we know the ideal gas formula,
$PM = dRT$
The above diagram,
The slope of the straight line ${T_1}$ is greater than that of ${T_2}$.
pressure of a given gas is inversely proportional to its volume provided the temperature remains constant
$PV = nRT$
Therefore,
$P = wRT/MV$
Rearranging the above equation,
$P = dRT/M$
The $rms$ speed of the gas is given by $3{P_p}$.
It means gas $rms$ of ${T_1}$ molecules are higher than ${T_2}$ molecules.
Therefore, $P\alpha d - T$
So, ${T_1} > {T_2}$.
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Note: The number of molecules in a gas is very high and the average separation between them is greater than the size of the gas molecules. The molecules of different gases are different. The measurement of heat is temperature. The molecules of different gases are different. Density is the indicator of how tightly an object is packaged or the ratio of the object's mass to its length.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




