
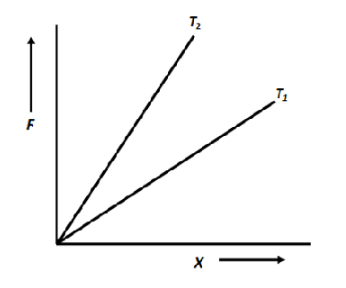
The diagram shows the change \[x\] in the length of a thin uniform wire caused by the application of stress \[F\] at two different temperatures \[{T_1}\] and \[{T_2}\]. The variations shown suggest that:
A. \[{T_1} > {T_2}\]
B. \[{T_1} < {T_2}\]
C. \[{T_1} = {T_2}\]
D. None of these

Answer
558k+ views
Hint: The thin uniform wire changes its length because of the property of elasticity and due to its restoring force. The stress \[F\] and the change in length \[x\] are temperature dependent.
The modulus of elasticity decreases with increase in temperature. Therefore, greater the modulus of elasticity, lesser should be the temperature. Also, elasticity is the slope of stress versus the change in length of the wire.
Formula Used:
The modulus of elasticity is given by: \[\mu = \dfrac{\sigma }{\varepsilon }\]
where, \[\sigma \] is the stress and \[\varepsilon \]is the strain on the body.
The stress is given by: \[\sigma = \dfrac{F}{a}\]
where, \[F\]is the force and \[a\]is the area.
Complete step by step solution:
The property of materials by virtue of which they regain their original shape and size on removal of deforming forces is called elasticity. The restoring force per unit area is called stress. It can be denoted as \[\sigma \].
Suppose the restoring force set up within the body is
\[F\]. And the surface area is \[a\], then the stress is given by \[\sigma = \dfrac{F}{a}\].
Hooke's law is defined as follows “Within elastic limits, the strain \[\varepsilon \]is proportional to stress
\[\sigma \]. Thus,
\[\
\sigma \propto \varepsilon \\
or \\
\sigma = \mu \varepsilon \\
\ \]\[ \to (1)\]
where \[\mu \]is a constant, called the modulus of elasticity.
Elasticity is the slope of stress versus the change in length of the wire. The slope of line \[{T_2}\] is greater than slope of line \[{T_1}\]. Therefore, the elasticity is greater at temperature \[{T_2}\] as compared to that at temperature\[{T_1}\]. The modulus of elasticity decreases with increase in temperature. Therefore, greater the modulus of elasticity, lesser should be the temperature. Thus, temperature \[{T_1}\] is greater than temperature \[{T_2}\]. That is, \[{T_1} > {T_2}\].
Hence, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note: Modulus of elasticity may also be defined as the ratio of stress upon strain. It depends on the nature of material as well as that of deformation. According to equation (1), the modulus of elasticity can also be written as \[\mu = \dfrac{\sigma }{\varepsilon }\]. It is the ratio of stress with strain. Strain is defined as the change in length per unit original length of the body. In the problem given, the quantity \[x\] is actually the strain on the body.
The modulus of elasticity decreases with increase in temperature. Therefore, greater the modulus of elasticity, lesser should be the temperature. Also, elasticity is the slope of stress versus the change in length of the wire.
Formula Used:
The modulus of elasticity is given by: \[\mu = \dfrac{\sigma }{\varepsilon }\]
where, \[\sigma \] is the stress and \[\varepsilon \]is the strain on the body.
The stress is given by: \[\sigma = \dfrac{F}{a}\]
where, \[F\]is the force and \[a\]is the area.
Complete step by step solution:
The property of materials by virtue of which they regain their original shape and size on removal of deforming forces is called elasticity. The restoring force per unit area is called stress. It can be denoted as \[\sigma \].
Suppose the restoring force set up within the body is
\[F\]. And the surface area is \[a\], then the stress is given by \[\sigma = \dfrac{F}{a}\].
Hooke's law is defined as follows “Within elastic limits, the strain \[\varepsilon \]is proportional to stress
\[\sigma \]. Thus,
\[\
\sigma \propto \varepsilon \\
or \\
\sigma = \mu \varepsilon \\
\ \]\[ \to (1)\]
where \[\mu \]is a constant, called the modulus of elasticity.
Elasticity is the slope of stress versus the change in length of the wire. The slope of line \[{T_2}\] is greater than slope of line \[{T_1}\]. Therefore, the elasticity is greater at temperature \[{T_2}\] as compared to that at temperature\[{T_1}\]. The modulus of elasticity decreases with increase in temperature. Therefore, greater the modulus of elasticity, lesser should be the temperature. Thus, temperature \[{T_1}\] is greater than temperature \[{T_2}\]. That is, \[{T_1} > {T_2}\].
Hence, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note: Modulus of elasticity may also be defined as the ratio of stress upon strain. It depends on the nature of material as well as that of deformation. According to equation (1), the modulus of elasticity can also be written as \[\mu = \dfrac{\sigma }{\varepsilon }\]. It is the ratio of stress with strain. Strain is defined as the change in length per unit original length of the body. In the problem given, the quantity \[x\] is actually the strain on the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




