
The diagram shows apparatus for plating a spoon with silver. Which statement is not correct?
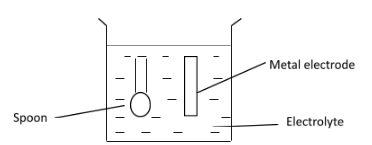
(A) Silver would stick to the spoon because it is a very reactive metal.
(B) The electrolyte would be a silver salt dissolved in water
(C) The metal electrode would be made from silver
(D) The spoon would be connected to the negative terminal of the power supply

Answer
546.9k+ views
Hint :Electroplating refers to the process in which a metal coating is applied on another metal piece via an electro-deposition process. In the process of electroplating, the metal which is deposited becomes a part of the existing product with the coating due to the transfer of electrons from anode to cathode.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The most commonly used metals for coating are nickel, gold, silver, copper, tin etc. In the process of silver plating, the metal to be plated is coated with silver. In this case, the metal is a steel spoon. The steel spoon to be coated with silver is the cathode of the electrolytic cell. The anode of the electrolytic cell is made of a silver metal and the electrolyte used for electroplating silver on spoon must contain silver ions $ \left( {{\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^{\text{ + }}}} \right) $ , for example, silver nitrate $ \left( {{\text{AgN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}} \right) $ or silver cyanide $ \left( {{\text{AgCN}}} \right) $ dissolved in water. When electric current is passed throughout the electrolytic cell, positively charged silver ions $ \left( {{\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^{\text{ + }}}} \right) $ will migrate from the electrolyte towards the negative cathode (which is spoon in this case). Here, the silver ions are neutralized by electrons and they will stick to the spoon as silver metal $ \left( {{\text{Ag}}} \right) $ . On the other hand, the anode bar made of silver metal will give up electrons and form silver ions $ \left( {{\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^{\text{ + }}}} \right) $ .
At silver metal anode, $ {\text{Ag}} \to {\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}} $
And at the spoon cathode, $ {\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}} \to {\text{Ag}} $
Therefore, the silver anode bar gradually dissolves to give silver ions into the solution. As a result, silver metal is transferred from the anode to the spoon cathode and the process keeps going on until the spoon cathode becomes thick with silver coating. So, statement A is not correct as silver being a very reactive metal is not the reason why it sticks to the spoon.
B is correct because the electrolyte used in silver plating must be a silver salt in water as already discussed. C is correct as the anode bar is made of silver metal as already discussed. D is correct as the spoon is made from the cathode which is connected to the negative terminal of the battery.
Note :
In the process of silver electroplating, the object which is to be electroplated with silver is made the cathode of the electrolytic cell. Silver electroplating has many applications. It is used in dinnerware, in jewelry, in telecom. Most importantly, it is used in electrical connectors.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The most commonly used metals for coating are nickel, gold, silver, copper, tin etc. In the process of silver plating, the metal to be plated is coated with silver. In this case, the metal is a steel spoon. The steel spoon to be coated with silver is the cathode of the electrolytic cell. The anode of the electrolytic cell is made of a silver metal and the electrolyte used for electroplating silver on spoon must contain silver ions $ \left( {{\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^{\text{ + }}}} \right) $ , for example, silver nitrate $ \left( {{\text{AgN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}} \right) $ or silver cyanide $ \left( {{\text{AgCN}}} \right) $ dissolved in water. When electric current is passed throughout the electrolytic cell, positively charged silver ions $ \left( {{\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^{\text{ + }}}} \right) $ will migrate from the electrolyte towards the negative cathode (which is spoon in this case). Here, the silver ions are neutralized by electrons and they will stick to the spoon as silver metal $ \left( {{\text{Ag}}} \right) $ . On the other hand, the anode bar made of silver metal will give up electrons and form silver ions $ \left( {{\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^{\text{ + }}}} \right) $ .
At silver metal anode, $ {\text{Ag}} \to {\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}} $
And at the spoon cathode, $ {\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}} \to {\text{Ag}} $
Therefore, the silver anode bar gradually dissolves to give silver ions into the solution. As a result, silver metal is transferred from the anode to the spoon cathode and the process keeps going on until the spoon cathode becomes thick with silver coating. So, statement A is not correct as silver being a very reactive metal is not the reason why it sticks to the spoon.
B is correct because the electrolyte used in silver plating must be a silver salt in water as already discussed. C is correct as the anode bar is made of silver metal as already discussed. D is correct as the spoon is made from the cathode which is connected to the negative terminal of the battery.
Note :
In the process of silver electroplating, the object which is to be electroplated with silver is made the cathode of the electrolytic cell. Silver electroplating has many applications. It is used in dinnerware, in jewelry, in telecom. Most importantly, it is used in electrical connectors.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




