
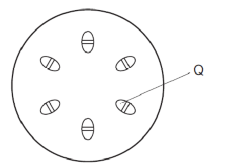
The diagram shows a cross-section through a plant stem. Q shows the part that is stained red when the stem is placed in water containing a red dye. What is found at Q?
A. Guard cells
B. Palisade cells
C. Phloem
D. Xylem

Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: It is a vascular tissue made up of complex permanent tissues. It conducts water and minerals in plants. It also provides rigidity to the plant body.
Complete answer:
Q is a xylem. The physical phenomenon of water in an exceedingly plant stem takes place through the vascular tissue, i.e. xylem. Hence, the vascular tissue appeared as red-stained cells within the cross-section. Xylem is a specialised tissue of plants that transports water and nutrients from the plant-soil interface to stems and leaves and provides mechanical support and storage. The water‐conducting performance of vascular tissue is one amongst the key identifying options of tube plants. The xylem is composed of four different types of cells that work together as a unit. They are tracheids, vessels, xylem fibres and xylem parenchyma. Tracheids, vessels and xylem fibres are dead cells that have lignified thick walls, whereas parenchyma is living that has thin walls and are involved in the storage process. The xylem is always present on the inner side of the stem.
i. Guard cells are regulated pores referred to as a stoma or stroma. It provides a passage to the photosynthetic gas (carbon dioxide uptake and dioxygen unleash) and transpirational release of water in terrestrial plants.
ii. The palisade cell is found within the leaves of higher plants. Their purpose is to change the chemical processes to be administered with efficiency and that they have many diversifications.
Palisade cells are units that soak up daylight and synthesize carbohydrates (photosynthesis literally). They are typically rectangular, differentiating them from spongy mesophyll cells that are circular like forms.
iii. Phloem is the plant tissue accountable for the transport of sugars from supply tissues (ex. Photosynthetic leaf cells) to sink tissues (ex. non-photosynthetic root cells or developing flowers). Different molecules like proteins and mRNAs also are transported throughout the plant via this vascular tissue.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note: Xylem conjointly contains 2 different cell types: parenchyma and fibers. Xylem is found:
i. In tube bundles, a gift in non-woody plants and non-woody elements of woody plants.
ii. In secondary vascular tissue, ordered down by a plant tissue known as the tube cambium in woody plants.
iii. As a part of a stellar arrangement not divided into bundles, as in several ferns.
Complete answer:
Q is a xylem. The physical phenomenon of water in an exceedingly plant stem takes place through the vascular tissue, i.e. xylem. Hence, the vascular tissue appeared as red-stained cells within the cross-section. Xylem is a specialised tissue of plants that transports water and nutrients from the plant-soil interface to stems and leaves and provides mechanical support and storage. The water‐conducting performance of vascular tissue is one amongst the key identifying options of tube plants. The xylem is composed of four different types of cells that work together as a unit. They are tracheids, vessels, xylem fibres and xylem parenchyma. Tracheids, vessels and xylem fibres are dead cells that have lignified thick walls, whereas parenchyma is living that has thin walls and are involved in the storage process. The xylem is always present on the inner side of the stem.
i. Guard cells are regulated pores referred to as a stoma or stroma. It provides a passage to the photosynthetic gas (carbon dioxide uptake and dioxygen unleash) and transpirational release of water in terrestrial plants.
ii. The palisade cell is found within the leaves of higher plants. Their purpose is to change the chemical processes to be administered with efficiency and that they have many diversifications.
Palisade cells are units that soak up daylight and synthesize carbohydrates (photosynthesis literally). They are typically rectangular, differentiating them from spongy mesophyll cells that are circular like forms.
iii. Phloem is the plant tissue accountable for the transport of sugars from supply tissues (ex. Photosynthetic leaf cells) to sink tissues (ex. non-photosynthetic root cells or developing flowers). Different molecules like proteins and mRNAs also are transported throughout the plant via this vascular tissue.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note: Xylem conjointly contains 2 different cell types: parenchyma and fibers. Xylem is found:
i. In tube bundles, a gift in non-woody plants and non-woody elements of woody plants.
ii. In secondary vascular tissue, ordered down by a plant tissue known as the tube cambium in woody plants.
iii. As a part of a stellar arrangement not divided into bundles, as in several ferns.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




