
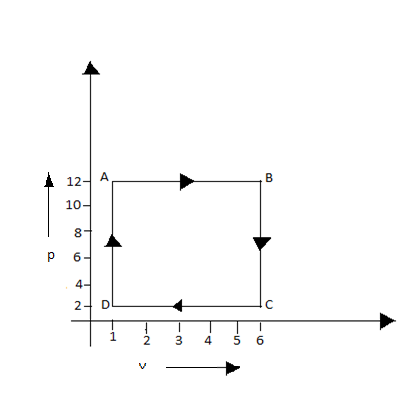
The diagram shown is a P-V graph of thermodynamic behavior of an ideal gas. Find out from this graph (I) work done in the process A $ \to $B, B$ \to $ C, C$ \to $D and D$ \to $A. (II) Work done in the complete cycle A$ \to $B$ \to $C$ \to $D$ \to $A.



Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Work done is defined by the product of pressure exerted and change in volume. Therefore the work done is given as: W = P$\Delta V$
Where, p is pressure and $\Delta V$ is change in volume ( ${V_{final}} - {V_{initial}}$).
Complete step by step answer:
The work done is given by W = P$\Delta V$. Here understanding sign convention is very important to solve problems like this.
- If the process is expansion the work done by gas will give negative sign convention.
W = - P$\Delta V$
-If the process is contraction the work done on gas will give a positive sign convention.
W = + P$\Delta V$
Let's solve the problem
(i) - Work done in process A $ \to $B, from the graph we can make out that pressure is constant in this process. Always when pressure is constant there will be change in volume. Therefore the process is expansion.
W = - P$\Delta V$
= - ($12 \times {10^5}$)($5 \times {10^{ - 3}}$)
= -6000J
- Work done in process B$ \to $ C, from the graph we can make out that volume remains constant so the work done in this process is 0.
- Work done in process C$ \to $D, from the graph we can make out that pressure is constant and there is a change in volume. Here the process carried out is contraction.
W = + P$\Delta V$
= + ($2 \times {10^5}$)($5 \times {10^{ - 3}}$)
= 1000J
- Work done process D$ \to $A, from the graph we can make sure that the volume is kept constant. Thus the work done is zero.
(ii) the work done in complete cycle = sum of work done in process A $ \to $B, B$ \to $ C, C$ \to $D and D$ \to $A
= 6000J + 0J + 1000J + 0J
= 7000J
Thus the work done in complete cycle is 7000J
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: If the process is expansion the work done is by gas so the sign convention is negative as, when work is done by the gas some energy is let out. If the process is contraction the work done is on gas so the sign convention is positive as, when work is done on the system there will be addition of energy to the system.
Where, p is pressure and $\Delta V$ is change in volume ( ${V_{final}} - {V_{initial}}$).
Complete step by step answer:
The work done is given by W = P$\Delta V$. Here understanding sign convention is very important to solve problems like this.
- If the process is expansion the work done by gas will give negative sign convention.
W = - P$\Delta V$
-If the process is contraction the work done on gas will give a positive sign convention.
W = + P$\Delta V$
Let's solve the problem
(i) - Work done in process A $ \to $B, from the graph we can make out that pressure is constant in this process. Always when pressure is constant there will be change in volume. Therefore the process is expansion.
W = - P$\Delta V$
= - ($12 \times {10^5}$)($5 \times {10^{ - 3}}$)
= -6000J
- Work done in process B$ \to $ C, from the graph we can make out that volume remains constant so the work done in this process is 0.
- Work done in process C$ \to $D, from the graph we can make out that pressure is constant and there is a change in volume. Here the process carried out is contraction.
W = + P$\Delta V$
= + ($2 \times {10^5}$)($5 \times {10^{ - 3}}$)
= 1000J
- Work done process D$ \to $A, from the graph we can make sure that the volume is kept constant. Thus the work done is zero.
(ii) the work done in complete cycle = sum of work done in process A $ \to $B, B$ \to $ C, C$ \to $D and D$ \to $A
= 6000J + 0J + 1000J + 0J
= 7000J
Thus the work done in complete cycle is 7000J
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: If the process is expansion the work done is by gas so the sign convention is negative as, when work is done by the gas some energy is let out. If the process is contraction the work done is on gas so the sign convention is positive as, when work is done on the system there will be addition of energy to the system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




