
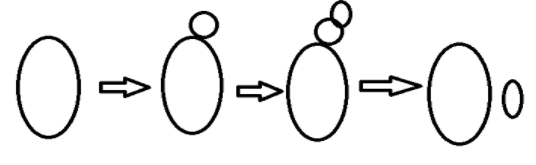
The diagram given shows a special method of reproduction in organisms. Which of the following organisms also reproduces in the same way?
A) Amoeba
B) Hydra
C) Paramecium
D) Euglena

Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: Asexual reproduction takes place in simple organisms. The diagram given shows an asexual method of reproduction that is similar to that takes place in the yeast. In this method, a bud or an outgrowth develops which on maturation breaks and lives as an independent individual.
Complete answer:
Asexual reproduction is the type of reproduction in which the fusion of gametes does not take place. This type of reproduction takes place in bacteria, archaebacteria, fungi, many plants etc. The types of asexual reproduction are budding, binary fission, fragmentation, regeneration, vegetative propagation etc.
The given figure represents the type of asexual reproduction called budding. In this type of reproduction, an outgrowth or the bud develops from the organism. This bud after fully grown detaches itself from the parent and live as an individual organism. This type of reproduction is seen in fungi like yeast and hydra. The hydra has regenerative cells which on repeated cell division develops into a bud which detaches on full maturation.
Amoeba- Amoeba is a unicellular organism that divides by binary fission. Each amoebae cells yield two daughter cells.
The paramecium-The division is carried out by the process of binary fission. The nucleus splits by the process of mitosis.
Euglena- The division in Euglena takes place by the process of binary fission. The nucleus splits by the process of mitosis followed by the division of the cytoplasm.
Therefore the correct answer is option ‘B’.
Note: Asexual reproduction does not involve fusion of gametes. It takes place both in multicellular and unicellular organisms. Jellyfish, sea anemones, corals reproduce through budding.
Complete answer:
Asexual reproduction is the type of reproduction in which the fusion of gametes does not take place. This type of reproduction takes place in bacteria, archaebacteria, fungi, many plants etc. The types of asexual reproduction are budding, binary fission, fragmentation, regeneration, vegetative propagation etc.
The given figure represents the type of asexual reproduction called budding. In this type of reproduction, an outgrowth or the bud develops from the organism. This bud after fully grown detaches itself from the parent and live as an individual organism. This type of reproduction is seen in fungi like yeast and hydra. The hydra has regenerative cells which on repeated cell division develops into a bud which detaches on full maturation.
Amoeba- Amoeba is a unicellular organism that divides by binary fission. Each amoebae cells yield two daughter cells.
The paramecium-The division is carried out by the process of binary fission. The nucleus splits by the process of mitosis.
Euglena- The division in Euglena takes place by the process of binary fission. The nucleus splits by the process of mitosis followed by the division of the cytoplasm.
Therefore the correct answer is option ‘B’.
Note: Asexual reproduction does not involve fusion of gametes. It takes place both in multicellular and unicellular organisms. Jellyfish, sea anemones, corals reproduce through budding.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




