
The diagram given below represents a section of the human heart. Which parts of the heart are in the diastolic phase? Give a reason to support your answer.


Answer
508.8k+ views
Hint: In the given image, 1 is the artery and 2 is the vein. Both the artery and vein plays a significant role in the transfer of blood in and out of the heart.
Complete answer:
Ventricles are in the diastolic phase in this image. When the heart beats for one time (complete one cardiac cycle) it completes two phases, which are the diastolic phase and systolic phase. The diastolic phase shows the period where the ventricles are relaxed. In this time flow of blood is from the left and right atrium to the left and right ventricle.
The blood travels via atrioventricular valves which separates the atria from the ventricles. The right atrium gets carbon dioxide-rich blood from the body by superior and inferior vena cava. The left atrium gets oxygen-rich blood from the lungs by the pulmonary veins. The diastolic phase ends by both the atria contracting and adding extra blood into the ventricles.
Hence, In the given image, 1 is the pulmonary artery and 2 is the pulmonary vein.
Note:
-Systolic phase is the time when the contraction of the ventricles takes place and pushes the blood into the aorta and pulmonary artery.
-The cardiac cycle is of 7 parts which are P wave (atrial deposition) then second phase, the third phase, and fourth phases are of systolic phase and fifth phase, sixth phase, and seventh phase are of diastolic phase which repeats with P wave.
-Sound of heartbeat is represented by the Lubb and Dub sound. Lubb sound is formed by the closing of atrioventricular valves and the closing of semilunar valves at the root of the pulmonary artery and aorta produces Dub sound.
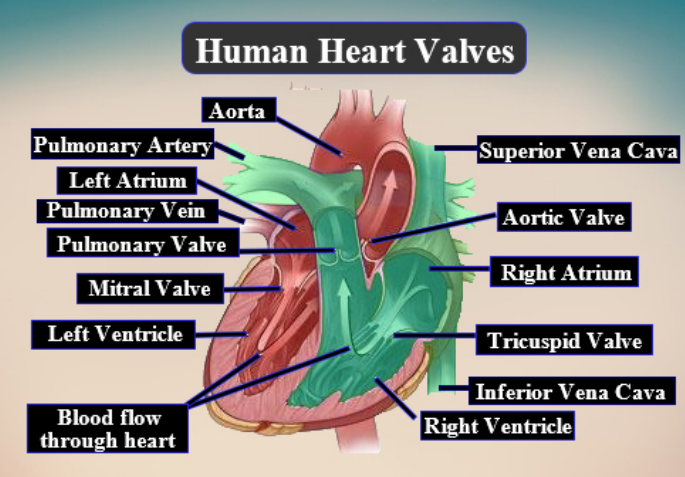
Complete answer:
Ventricles are in the diastolic phase in this image. When the heart beats for one time (complete one cardiac cycle) it completes two phases, which are the diastolic phase and systolic phase. The diastolic phase shows the period where the ventricles are relaxed. In this time flow of blood is from the left and right atrium to the left and right ventricle.
The blood travels via atrioventricular valves which separates the atria from the ventricles. The right atrium gets carbon dioxide-rich blood from the body by superior and inferior vena cava. The left atrium gets oxygen-rich blood from the lungs by the pulmonary veins. The diastolic phase ends by both the atria contracting and adding extra blood into the ventricles.
Hence, In the given image, 1 is the pulmonary artery and 2 is the pulmonary vein.
Note:
-Systolic phase is the time when the contraction of the ventricles takes place and pushes the blood into the aorta and pulmonary artery.
-The cardiac cycle is of 7 parts which are P wave (atrial deposition) then second phase, the third phase, and fourth phases are of systolic phase and fifth phase, sixth phase, and seventh phase are of diastolic phase which repeats with P wave.
-Sound of heartbeat is represented by the Lubb and Dub sound. Lubb sound is formed by the closing of atrioventricular valves and the closing of semilunar valves at the root of the pulmonary artery and aorta produces Dub sound.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




