
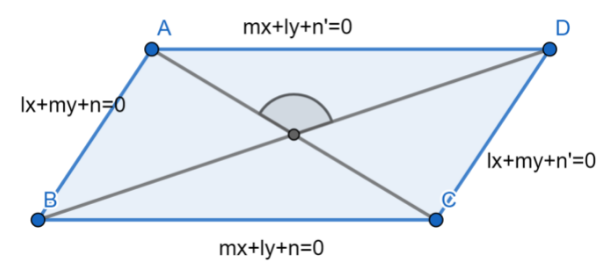
The diagonals of the parallelogram whose sides are $lx+my+n=0$ , $lx+my+n'=0$ , $mx+ly+n=0$ , $mx+ly+n'=0$ include an angle:
1)$\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
2) $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$
3) $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$
4) None of these
Answer
506.7k+ views
Hint: Here in this question we have been asked to find the angle between the diagonals of the parallelogram whose sides are $lx+my+n=0$ , $lx+my+n'=0$ , $mx+ly+n=0$ , $mx+ly+n'=0$ . For answering this question we will conclude the type of parallelogram is rectangle, square or rhombus.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now considering from the question we have been asked to find the angle between the diagonals of the parallelogram whose sides are $lx+my+n=0$ , $lx+my+n'=0$ , $mx+ly+n=0$ , $mx+ly+n'=0$ .
Now we will find the type of parallelogram it is rectangle, square or rhombus.
We know that in a rhombus the length of all sides is equal and the angle between the diagonals is a right angle. The angle between the adjacent sides is not a right angle.
We know that the slope of the line $ax+by+c=0$ is $\dfrac{-a}{b}$ .
From the basic concepts we know that the distance between two parallel lines $ax+by+c=0$ and $ax+by+c'=0$ is given as $\dfrac{\left| c-c' \right|}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}$ .
Hence the distance between the opposite sides in the given parallelogram is $\dfrac{\left| n-n' \right|}{\sqrt{{{l}^{2}}+{{m}^{2}}}}$ .
The product of slopes of the adjacent will be $\dfrac{-l}{m}\times \dfrac{-m}{l}=1$ .
Therefore we can conclude that the given parallelogram is rhombus so the angle between the diagonals is $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ .
Hence we will mark the option “1” as correct.
Note: We know that in a square the length of all sides is equal and the angle between the diagonals is a right angle and the angle between the adjacent sides is a right angle. We know that in a rectangle the length of all sides is not equal and the angle between the diagonals is not a right angle and the angle between the adjacent sides is a right angle.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now considering from the question we have been asked to find the angle between the diagonals of the parallelogram whose sides are $lx+my+n=0$ , $lx+my+n'=0$ , $mx+ly+n=0$ , $mx+ly+n'=0$ .
Now we will find the type of parallelogram it is rectangle, square or rhombus.
We know that in a rhombus the length of all sides is equal and the angle between the diagonals is a right angle. The angle between the adjacent sides is not a right angle.

We know that the slope of the line $ax+by+c=0$ is $\dfrac{-a}{b}$ .
From the basic concepts we know that the distance between two parallel lines $ax+by+c=0$ and $ax+by+c'=0$ is given as $\dfrac{\left| c-c' \right|}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}$ .
Hence the distance between the opposite sides in the given parallelogram is $\dfrac{\left| n-n' \right|}{\sqrt{{{l}^{2}}+{{m}^{2}}}}$ .
The product of slopes of the adjacent will be $\dfrac{-l}{m}\times \dfrac{-m}{l}=1$ .
Therefore we can conclude that the given parallelogram is rhombus so the angle between the diagonals is $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ .
Hence we will mark the option “1” as correct.
Note: We know that in a square the length of all sides is equal and the angle between the diagonals is a right angle and the angle between the adjacent sides is a right angle. We know that in a rectangle the length of all sides is not equal and the angle between the diagonals is not a right angle and the angle between the adjacent sides is a right angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




