
The diagonal of a rectangular field is 16 metres more than the shorter side. If the longer side is 14 metres more than the shortest side, then find the lengths of the sides of the field.

Answer
614.1k+ views
Hint:Here, we will proceed by expressing the diagonal and the length of the longer side in terms of the length of the shorter side according to the problem statement and then applying Pythagoras Theorem in order to get the lengths of the sides of the rectangular field.
Complete step-by-step answer:
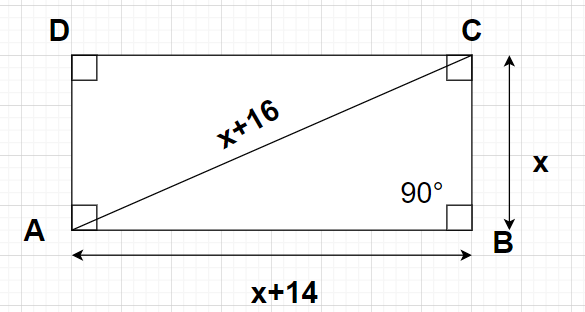
Let ABCD be a rectangle with AB = CD and BC = AD where sides AB and CD are the longest sides and sides BC and AD are the shortest sides. Here, the diagonals of the rectangle are AC and BD.
Let us suppose the length of the shorter side is x metres.
i.e., Shorter side = BC = AD = x metres
Given, the diagonal of the rectangle ABCD (take any one of the two diagonals) is 16 metres more than the shorter side
i.e., Diagonal = Shorter side + 16
Considering the diagonal AC in the above equation, we have
$ \Rightarrow $AC = (x+16) metres
Also, given that the longest side is 14 metres more than the shorter side
i.e., Longer side = Shorter side + 14
$ \Rightarrow $AB = CD = (x+14) metres
According to the properties of the rectangle, interior angles made at the vertices of a rectangle will always be right angles
So, $\angle {\text{B}} = {90^0}$ and hence, $\vartriangle $ABC is a right angled triangle
By Pythagoras Theorem in any right angled triangle, we have
${\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)^2}$
By using the above formula in $\vartriangle $ABC, we get
\[
{\left( {{\text{AC}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{BC}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{AB}}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {x + 16} \right)^2} = {\left( x \right)^2} + {\left( {x + 14} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + 256 + 32x = {x^2} + {x^2} + 196 + 28x \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + 256 + 32x = 2{x^2} + 196 + 28x \\
\Rightarrow 2{x^2} + 196 + 28x - \left( {{x^2} + 256 + 32x} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 2{x^2} + 196 + 28x - {x^2} - 256 - 32x = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} - 4x - 60 = 0 \\
\]
By solving the above quadratic equation by splitting the middle terms method, we have
\[
\Rightarrow {x^2} + 6x - 10x - 60 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow x\left( {x + 6} \right) - 10\left( {x + 6} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {x + 6} \right)\left( {x - 10} \right) = 0 \\
\]
Either \[
x + 6 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow x = - 6 \\
\] or \[
x - 10 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow x = 10 \\
\]
Since, the length of the side of any rectangle can never be negative.
So, x = -6 is neglected
Length of the shorter side = BC = AD = 10 metres
Length of the longer side = AB = CD = x+14 = 10+14 = 24 metres
Therefore, the lengths of the given rectangular field are 24 metres and 10 metres.
Note- In any right angled triangle, the side opposite to the right angle is known as hypotenuse, the side opposite to the considered angle is known as perpendicular and the remaining side is known as base. In this particular problem, in the right angled triangle ABC, AC is the hypotenuse, BC is the perpendicular and AB is the base, from this concept we can solve these types of questions.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let ABCD be a rectangle with AB = CD and BC = AD where sides AB and CD are the longest sides and sides BC and AD are the shortest sides. Here, the diagonals of the rectangle are AC and BD.
Let us suppose the length of the shorter side is x metres.
i.e., Shorter side = BC = AD = x metres
Given, the diagonal of the rectangle ABCD (take any one of the two diagonals) is 16 metres more than the shorter side
i.e., Diagonal = Shorter side + 16
Considering the diagonal AC in the above equation, we have
$ \Rightarrow $AC = (x+16) metres
Also, given that the longest side is 14 metres more than the shorter side
i.e., Longer side = Shorter side + 14
$ \Rightarrow $AB = CD = (x+14) metres
According to the properties of the rectangle, interior angles made at the vertices of a rectangle will always be right angles
So, $\angle {\text{B}} = {90^0}$ and hence, $\vartriangle $ABC is a right angled triangle
By Pythagoras Theorem in any right angled triangle, we have
${\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)^2}$
By using the above formula in $\vartriangle $ABC, we get
\[
{\left( {{\text{AC}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{BC}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{AB}}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {x + 16} \right)^2} = {\left( x \right)^2} + {\left( {x + 14} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + 256 + 32x = {x^2} + {x^2} + 196 + 28x \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + 256 + 32x = 2{x^2} + 196 + 28x \\
\Rightarrow 2{x^2} + 196 + 28x - \left( {{x^2} + 256 + 32x} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 2{x^2} + 196 + 28x - {x^2} - 256 - 32x = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} - 4x - 60 = 0 \\
\]
By solving the above quadratic equation by splitting the middle terms method, we have
\[
\Rightarrow {x^2} + 6x - 10x - 60 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow x\left( {x + 6} \right) - 10\left( {x + 6} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {x + 6} \right)\left( {x - 10} \right) = 0 \\
\]
Either \[
x + 6 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow x = - 6 \\
\] or \[
x - 10 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow x = 10 \\
\]
Since, the length of the side of any rectangle can never be negative.
So, x = -6 is neglected
Length of the shorter side = BC = AD = 10 metres
Length of the longer side = AB = CD = x+14 = 10+14 = 24 metres
Therefore, the lengths of the given rectangular field are 24 metres and 10 metres.
Note- In any right angled triangle, the side opposite to the right angle is known as hypotenuse, the side opposite to the considered angle is known as perpendicular and the remaining side is known as base. In this particular problem, in the right angled triangle ABC, AC is the hypotenuse, BC is the perpendicular and AB is the base, from this concept we can solve these types of questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What type of cell is found in the Seminiferous tub class 10 biology CBSE

What are the public facilities provided by the government? Also explain each facility




