
The dehydrohalogenation of neopentyl bromide with alcoholic KOH mainly gives
A) 2-methyl-1-butene
B) 2-methyl-2-butene
C) 2, 2-dimethyl-1-butene
D) 2-butene
Answer
371.1k+ views
Hint: The dehydrohalogenation reaction is a type of elimination reaction. In this reaction a carbocation is formed as an intermediate which further reacts to give an alkene.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
When an alkyl bromide is treated with an alcoholic base then an elimination reaction takes place.
In this reaction at first step the halogen atom that is bromine atom is removed from the alkyl halide that is neopentyl bromide to form a carbocation intermediate that is neopentyl carbocation in reaction with an alcoholic base that is potassium hydroxide.
In the next step one methyl group is shifted to the next carbon atom due to unavailability of beta hydrogen. Now the newly formed carbocation contains beta hydrogen and the beta hydrogen is easily removed and forms the desired product that is 2-methyl-2-butene. In this reaction hydrogen bromide is removed as a side product.
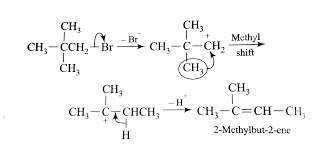
Thus the dehydrohalogenation of neopentyl bromide with alcoholic KOH mainly gives 2-methyl-2-butene as a major product.
Thus the correct option is B.
Note: In general E1 elimination reaction no shifting of any group takes place. If no beta hydrogen is present in the produced intermediate that is the carbocation then shifting of a group takes place to generate beta hydrogen which helps to produce the desired product.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
When an alkyl bromide is treated with an alcoholic base then an elimination reaction takes place.
In this reaction at first step the halogen atom that is bromine atom is removed from the alkyl halide that is neopentyl bromide to form a carbocation intermediate that is neopentyl carbocation in reaction with an alcoholic base that is potassium hydroxide.
In the next step one methyl group is shifted to the next carbon atom due to unavailability of beta hydrogen. Now the newly formed carbocation contains beta hydrogen and the beta hydrogen is easily removed and forms the desired product that is 2-methyl-2-butene. In this reaction hydrogen bromide is removed as a side product.

Thus the dehydrohalogenation of neopentyl bromide with alcoholic KOH mainly gives 2-methyl-2-butene as a major product.
Thus the correct option is B.
Note: In general E1 elimination reaction no shifting of any group takes place. If no beta hydrogen is present in the produced intermediate that is the carbocation then shifting of a group takes place to generate beta hydrogen which helps to produce the desired product.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

What are gulf countries and why they are called Gulf class 8 social science CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Name the states through which the Tropic of Cancer class 8 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE




