
The decreasing order of $pK_a$ value of the following is:
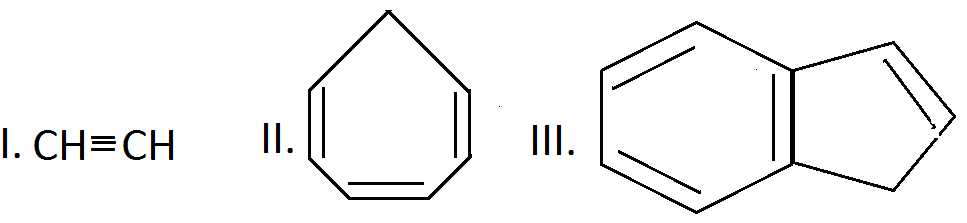
A.$III > I > II$
B.$II > I > III$
C.$I > III > II$
D.$I > II = III$

Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The measure for a compound to define its tendency to donate protons is known as $K_a$ value and the constant which describes the binding of protons is known as $pK_a$ . both of these constants are defined at the equilibrium.
Complete step by step answer:
To predict whether the acid will donate or withdraw protons, some constants such as $K_a, pK_a$ and $K_b, pK_b$ . The constants related to acids are $K_a, pK_a$ and the constants related to base are $Kb, pKb$. At equilibrium the acid constant is defined for an acid dissociation reaction, the acid dissociation constant is represented as ${K_a}$ . It represents the strength of an acid and the power of its dissociation in solvent. But the $pK_a$ value is something different, it tells how tightly a proton is bound with the he acid. If the $pK_a$ value is lower then we can say that the binding of proton and the bronsted acid is not very strong and hence it is easy to donate protons. So we can say that if the $pK_a$ value is lower, acid is more acidic and if the $pK_a$ value is low then the acidic strength of acid is very low.
So, $pK_a$ value is inversely proportional to the acidic strength of a compound.
Now we will observe the order of acidic strength of these given compounds and the reverse of it will be the order of the $pK_a$ values.
And we all know that, the compound having more stable conjugate base will be more acidic, so we will see their conjugate bases which are as follows:
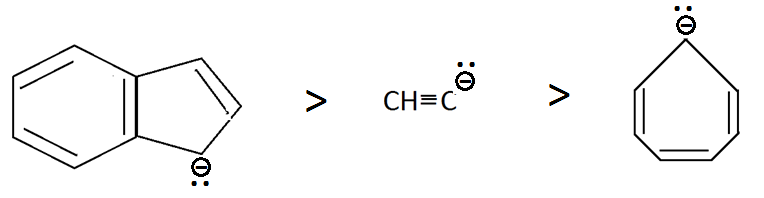
Compound $III$ has aromatic stability due to resonance, compound $II$ has negative charge on $sp$ carbon atom and the first compound is anti aromatic so the order stability will be the same as shown above.
Therefore the order of acidic strength will be as follows:
$III > I > II$
And the order reverse to it will be the order of $pK_a$ values, therefore the order of $pK_a$ values, will be as follows:
$II > I > III$
Hence option (B) is correct.
Note: As we have discussed above that, the smaller the value of $K_a$ , the larger the value of $pK_a$ and vice versa. But they have a unique relation between them mathematically also for numerical problems.
The relation is as follows: ${pK_a = - lo}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}{K_a}$
Complete step by step answer:
To predict whether the acid will donate or withdraw protons, some constants such as $K_a, pK_a$ and $K_b, pK_b$ . The constants related to acids are $K_a, pK_a$ and the constants related to base are $Kb, pKb$. At equilibrium the acid constant is defined for an acid dissociation reaction, the acid dissociation constant is represented as ${K_a}$ . It represents the strength of an acid and the power of its dissociation in solvent. But the $pK_a$ value is something different, it tells how tightly a proton is bound with the he acid. If the $pK_a$ value is lower then we can say that the binding of proton and the bronsted acid is not very strong and hence it is easy to donate protons. So we can say that if the $pK_a$ value is lower, acid is more acidic and if the $pK_a$ value is low then the acidic strength of acid is very low.
So, $pK_a$ value is inversely proportional to the acidic strength of a compound.
Now we will observe the order of acidic strength of these given compounds and the reverse of it will be the order of the $pK_a$ values.
And we all know that, the compound having more stable conjugate base will be more acidic, so we will see their conjugate bases which are as follows:
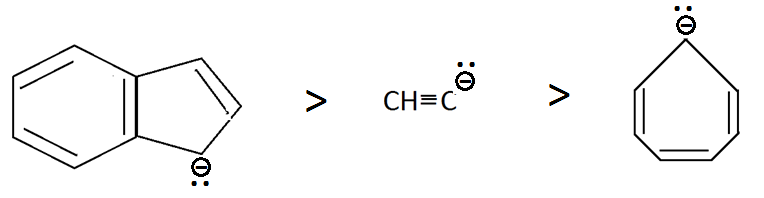
Compound $III$ has aromatic stability due to resonance, compound $II$ has negative charge on $sp$ carbon atom and the first compound is anti aromatic so the order stability will be the same as shown above.
Therefore the order of acidic strength will be as follows:
$III > I > II$
And the order reverse to it will be the order of $pK_a$ values, therefore the order of $pK_a$ values, will be as follows:
$II > I > III$
Hence option (B) is correct.
Note: As we have discussed above that, the smaller the value of $K_a$ , the larger the value of $pK_a$ and vice versa. But they have a unique relation between them mathematically also for numerical problems.
The relation is as follows: ${pK_a = - lo}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}{K_a}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




