
The cylindrical tube of a spray pump has radius R, one end of which has n fine holes, each of radius r. If the speed of the liquid in the tube is V, the speed of the ejection of the liquid through the holes is:
A. $\dfrac{{{V^2}R}}{{nR}}$
B. $\dfrac{{{V^2}R}}{{{n^2}{R^2}}}$
C. $\dfrac{{V{R^2}}}{{n{R^2}}}$
D. $\dfrac{{V{R^2}}}{{{n^3}{R^2}}}$
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: The discharge through the tube remains the same irrespective of the cross-section. The rate of volume flow of water entering the tube is equal to the rate of volume flow of water coming out of the tube.
Complete step by step answer:
Refer to the figure below of the tube with cross sectional area A.
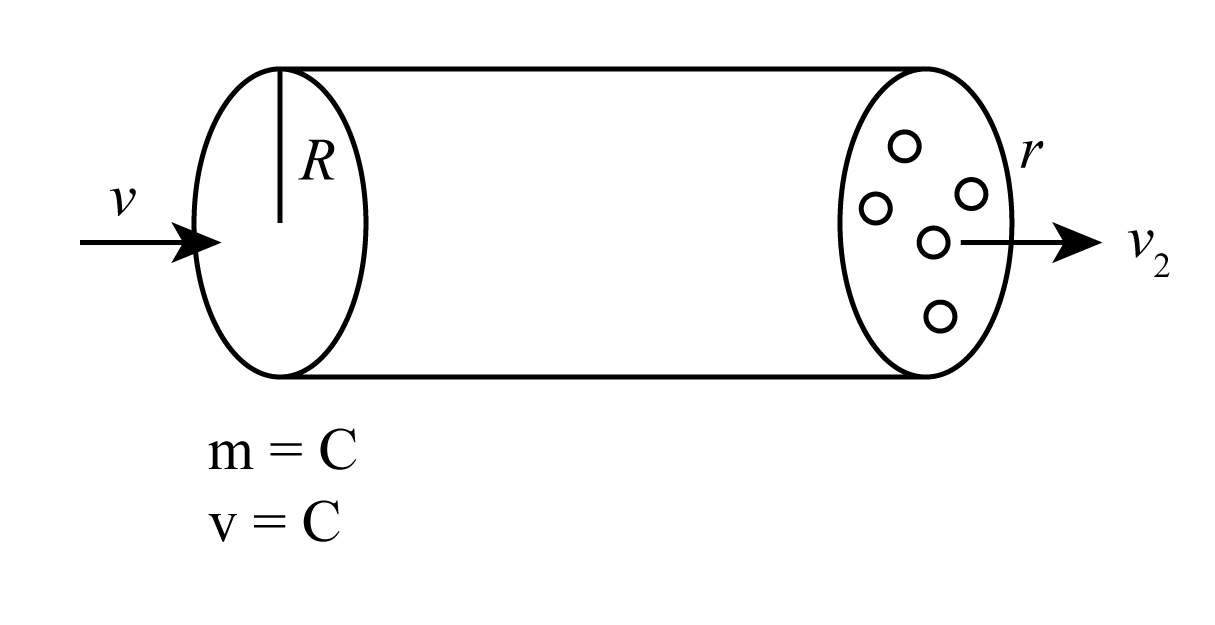
The radius of the cylindrical tube of the spray pump is R.
The speed of the liquid inside the tube is V.
We all know that the discharge is always constant, hence the equation of continuity can be applied to the flow of fluid through a cylindrical tube. Therefore, we can say that result becomes
\[
{A_1}{V_1} = {A_2}{V_2} \\
\pi {R^2}V = n\left( {\pi {r^2}v} \right) \\
\]
We are using here 1 as the subscript for entry side and 2 as the subscript for the delivery side and $A$ is the area and $V$ is the velocity which is further modified by the subscripts used.
As we see in the above relation, $R$ is the radius of the tube, $V$ is the speed of the liquid in the tube, $r$ is the radius of fine holes, $v$ is the velocity of liquid through the fine holes, $n$ are the number of holes.
When we further solve the above relation it becomes,
$v = \dfrac{{V{R^2}}}{{n{r^2}}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Therefore we can say that the velocity of ejection of liquid through the fine hole is $\dfrac{{V{R^2}}}{{n{r^2}}}$.
Note:
When we use the equation of continuity, then basically we are assuming the conservation of mass. We can say that the total mass entered inside the system is equal to the total mass exit out of the tube. In this context, we assume that the fluid is incompressible by which we mean that its density is not changing. Also we take into assumption that the flow is the steady state flow which means that the mass is not accumulating inside the system.
Complete step by step answer:
Refer to the figure below of the tube with cross sectional area A.

The radius of the cylindrical tube of the spray pump is R.
The speed of the liquid inside the tube is V.
We all know that the discharge is always constant, hence the equation of continuity can be applied to the flow of fluid through a cylindrical tube. Therefore, we can say that result becomes
\[
{A_1}{V_1} = {A_2}{V_2} \\
\pi {R^2}V = n\left( {\pi {r^2}v} \right) \\
\]
We are using here 1 as the subscript for entry side and 2 as the subscript for the delivery side and $A$ is the area and $V$ is the velocity which is further modified by the subscripts used.
As we see in the above relation, $R$ is the radius of the tube, $V$ is the speed of the liquid in the tube, $r$ is the radius of fine holes, $v$ is the velocity of liquid through the fine holes, $n$ are the number of holes.
When we further solve the above relation it becomes,
$v = \dfrac{{V{R^2}}}{{n{r^2}}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Therefore we can say that the velocity of ejection of liquid through the fine hole is $\dfrac{{V{R^2}}}{{n{r^2}}}$.
Note:
When we use the equation of continuity, then basically we are assuming the conservation of mass. We can say that the total mass entered inside the system is equal to the total mass exit out of the tube. In this context, we assume that the fluid is incompressible by which we mean that its density is not changing. Also we take into assumption that the flow is the steady state flow which means that the mass is not accumulating inside the system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




