
The curve represented by \[x=a\left( \sinh \theta +\cosh \theta \right)\] and \[y=b\left( -\sinh \theta +\cosh \theta \right)\] is
A. a hyperbola
B. a parabola
C. an ellipse
D. a circle.
Answer
506.1k+ views
Hint: In this problem we have to find the type of curve using the given equation. We can first write the given equation and divide a on both sides of the first equation and b on both sides of the second equation. We can then multiply the two new equations and simplify them. We will get a trigonometric identity, we can substitute the correct value of it and we will get a final equation which will represent the exact curve.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we are given two equations,
\[x=a\left( \sinh \theta +\cosh \theta \right)\]……. (1)
\[y=b\left( -\sinh \theta +\cosh \theta \right)\]……… (2)
We can now write the equation (1) as,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{a}=\left( \sinh \theta +\cosh \theta \right)\]……. (3)
We can now write the equation (2) as,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{b}=\left( -\sinh \theta +\cosh \theta \right)\]…….. (4)
We can now multiply equation (3) and (4), we get
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{a}\times \dfrac{y}{b}=\left( \sinh \theta +\cosh \theta \right)\times \left( -\sinh \theta +\cosh \theta \right)\]
We can now simplify the above step, we get
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{xy}{ab}={{\cosh }^{2}}\theta -{{\sinh }^{2}}\theta \]
We know that \[{{\cosh }^{2}}\theta -{{\sinh }^{2}}\theta =1\], we can now substitute it in the above step, we get
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{xy}{ab}=1\]
We can now multiply ab on both sides in the above step, we get
\[\Rightarrow xy=ab\]
Hence, it is a rectangular hyperbola.
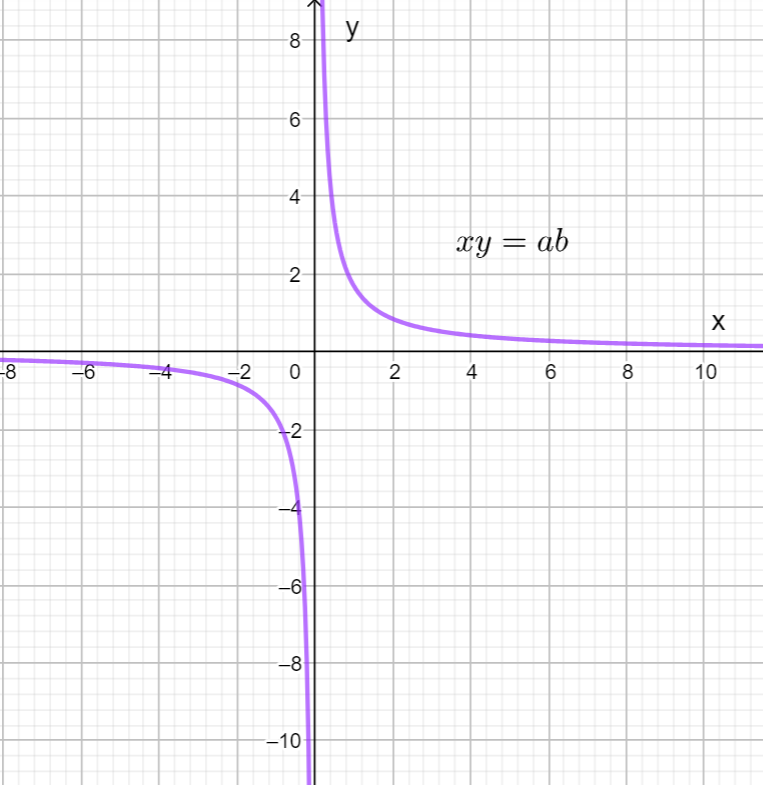
Therefore, the answer is option A. a hyperbola.
Note: We should always remember some of the trigonometric formulas and identities such as \[{{\cosh }^{2}}\theta -{{\sinh }^{2}}\theta =1\], we should also remember that the formula of a rectangular hyperbola is \[xy=ab\]. We should concentrate while multiplying the terms using the FOIL method.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we are given two equations,
\[x=a\left( \sinh \theta +\cosh \theta \right)\]……. (1)
\[y=b\left( -\sinh \theta +\cosh \theta \right)\]……… (2)
We can now write the equation (1) as,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{a}=\left( \sinh \theta +\cosh \theta \right)\]……. (3)
We can now write the equation (2) as,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{b}=\left( -\sinh \theta +\cosh \theta \right)\]…….. (4)
We can now multiply equation (3) and (4), we get
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{a}\times \dfrac{y}{b}=\left( \sinh \theta +\cosh \theta \right)\times \left( -\sinh \theta +\cosh \theta \right)\]
We can now simplify the above step, we get
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{xy}{ab}={{\cosh }^{2}}\theta -{{\sinh }^{2}}\theta \]
We know that \[{{\cosh }^{2}}\theta -{{\sinh }^{2}}\theta =1\], we can now substitute it in the above step, we get
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{xy}{ab}=1\]
We can now multiply ab on both sides in the above step, we get
\[\Rightarrow xy=ab\]
Hence, it is a rectangular hyperbola.

Therefore, the answer is option A. a hyperbola.
Note: We should always remember some of the trigonometric formulas and identities such as \[{{\cosh }^{2}}\theta -{{\sinh }^{2}}\theta =1\], we should also remember that the formula of a rectangular hyperbola is \[xy=ab\]. We should concentrate while multiplying the terms using the FOIL method.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




