
The current through the 10 $\Omega$ resistor shown in figure is
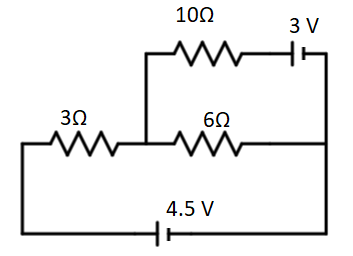
(A) 0.1 A
(B) 0.2 A
(C) 0.3 A
(D) zero

Answer
537.3k+ views
Hint: The Kirchhoff’s voltage law and current law can be applied here to determine the current through the given resistor. We have two loops and 3 equations in total to obtain the value of the total two missing variables here.
Formula used:
The Kirchhoff’s voltage law states that the product of current and resistance in a loop is equal to the emf in the loop or,
$\Sigma IR = 0$,
Similarly, Kirchhoff’s current law states that the sum of all currents through the node is zero:
$\Sigma I = 0$
Complete answer:
First we apply the Kirchhoff’s current law at the node where the current division is taking place i.e. point connecting 3, 6 and 10 $\Omega$ resistance.
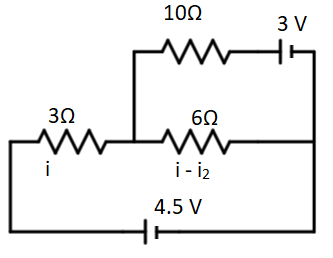
Let the current entering from the bigger loop be i (marked in the diagram),
$i = i_1 + i_2$
the current through our resistance will be i$_2$, therefore, the current in the 6 $\Omega$ resistance will be i - i$_2$.
Now, we consider the small loop on the upper side, applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law, we obtain:
$3 V = 3 i_2 + 6 ( i - i_2)$ .
Simplification of this gives us:
$3 = 6 i - 3 i_2$
We use i from here for the purpose of substitutions,
$i = \dfrac{1 + i_2}{2}$.
Now applying the Voltage law to the bigger loop, we get:
$4.5 V = 3 i + 6 ( i - i_2)$ .
$\implies 4.5 V = 9 i - 6 i_2$
Substituting the value of i here, we get:
$4.5 V = 9 \dfrac{ (1 + 2 i_2)}{2} - 6 i_2 $
$\implies i_2 = 0$
As we can see,
The correct answer is option (D) zero.
Note:
In applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law, one can start with one circuit element at a time and can go across the loop in the direction of current or opposite to it. The resistance polarities have to be marked according to the direction of current. The direction of the loop can be selected by us to be either clockwise or anticlockwise. If we go in the direction of the loop we travel from + to -, we mark that element positive and we mark negative when we go in the opposite direction.
Formula used:
The Kirchhoff’s voltage law states that the product of current and resistance in a loop is equal to the emf in the loop or,
$\Sigma IR = 0$,
Similarly, Kirchhoff’s current law states that the sum of all currents through the node is zero:
$\Sigma I = 0$
Complete answer:
First we apply the Kirchhoff’s current law at the node where the current division is taking place i.e. point connecting 3, 6 and 10 $\Omega$ resistance.

Let the current entering from the bigger loop be i (marked in the diagram),
$i = i_1 + i_2$
the current through our resistance will be i$_2$, therefore, the current in the 6 $\Omega$ resistance will be i - i$_2$.
Now, we consider the small loop on the upper side, applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law, we obtain:
$3 V = 3 i_2 + 6 ( i - i_2)$ .
Simplification of this gives us:
$3 = 6 i - 3 i_2$
We use i from here for the purpose of substitutions,
$i = \dfrac{1 + i_2}{2}$.
Now applying the Voltage law to the bigger loop, we get:
$4.5 V = 3 i + 6 ( i - i_2)$ .
$\implies 4.5 V = 9 i - 6 i_2$
Substituting the value of i here, we get:
$4.5 V = 9 \dfrac{ (1 + 2 i_2)}{2} - 6 i_2 $
$\implies i_2 = 0$
As we can see,
The correct answer is option (D) zero.
Note:
In applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law, one can start with one circuit element at a time and can go across the loop in the direction of current or opposite to it. The resistance polarities have to be marked according to the direction of current. The direction of the loop can be selected by us to be either clockwise or anticlockwise. If we go in the direction of the loop we travel from + to -, we mark that element positive and we mark negative when we go in the opposite direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




