
The correct option(s) regarding the complex ${[Co(en){(N{H_3})_3}({H_2}O)]^{3 + }}$ $(en = {H_2}N - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - N{H_2})$ is/are:
(The question has multiple correct options)
A. It has two geometrical isomers.
B. It will have three geometrical isomers if Bidentate $'en'$ is replaced by two cyanide ligands.
C. It is paramagnetic
D. It absorbs light at a longer wavelength as compared to ${[Co(en){(N{H_3})_4}]^{3 + }}$.
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: The geometrical isomers are the compounds which are found in heteroleptic complexes having different groups attached to the central metal atom and have different possible geometrical arrangements of the ligands. When two identical groups occupy adjacent positions, the isomer is called cis and when arranged opposite to one another, the isomer is called trans. This also has another type of configuration named as fac/mer isomerism which also comes under the category of geometrical isomerism.
Complete step by step answer: Let us discuss each of the options one by one.
-The structures of the two isomers of the complex are as follows:
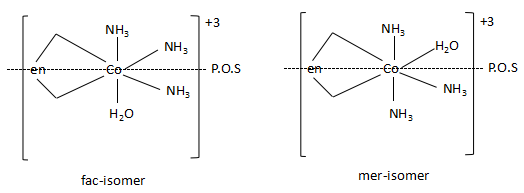
As the complex has two isomers namely, facial and meridional isomers, the statement is correct. The complex has two geometrical isomers. As there are planes of symmetry present in the two isomers, both the complexes are optically inactive.
-When the bidentate ligand, ethylene diamine, is replaced by two cyanide ions, the complex forms three geometrical isomers. They are as follows:
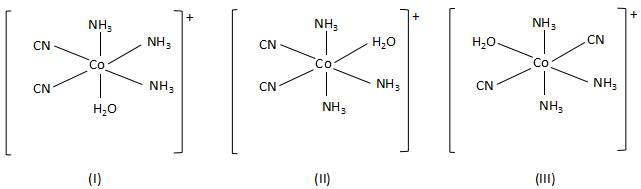
Thus, this statement is also true.
(iii) The magnetic nature of a central metal ion is decided by the presence of unpaired electrons in the orbitals and the surrounding ligands. If the ligands are strong fields, they will pair the electrons and thus the complex will be diamagnetic in nature. If there are unpaired electrons in the complex, it will act as paramagnetic.
In this case, the electronic configuration of cobalt in its ground state is:
$Co = [Ar]4{s^2}3{d^7}$
The electronic configuration of $C{o^{3 + }}$ ion will be:
$Co = [Ar]4{s^0}3{d^6}$
The surrounding ligands are strong field ligands in the complex. Thus, they will pair all the unpaired electrons and the complex will become diamagnetic. Due to this pairing, the hybridization of the complex will be ${d^2}s{p^3}$ and the complex will be a low spin complex.
Thus, this statement is wrong.
(iv) It absorbs light at a longer wavelength as compared to ${[Co(en){(N{H_3})_4}]^{3 + }}$. This statement is wrong because in the presence of a strong field ligand, the pairing energy increases and becomes more than that of the crystal field splitting energy. Thus, the wavelength decreases or becomes shorter as the energy gap between ${t_{2g}}$ and ${e_g}$ orbitals increases.
Thus, the correct options are:
A. It has two geometrical isomers.
B. It will have three geometrical isomers if Bidentate $'en'$ is replaced by two cyanide ligands.
Note: The elements of symmetry play a crucial role in deciding the geometry of the complexes in coordination chemistry. There are basically three elements of symmetry. They are planes of symmetry, center of symmetry and axis of symmetry. If any of these elements of symmetry are found in the complexes, they tend to become optically inactive and cannot rotate a plane polarized light.
Complete step by step answer: Let us discuss each of the options one by one.
-The structures of the two isomers of the complex are as follows:

As the complex has two isomers namely, facial and meridional isomers, the statement is correct. The complex has two geometrical isomers. As there are planes of symmetry present in the two isomers, both the complexes are optically inactive.
-When the bidentate ligand, ethylene diamine, is replaced by two cyanide ions, the complex forms three geometrical isomers. They are as follows:

Thus, this statement is also true.
(iii) The magnetic nature of a central metal ion is decided by the presence of unpaired electrons in the orbitals and the surrounding ligands. If the ligands are strong fields, they will pair the electrons and thus the complex will be diamagnetic in nature. If there are unpaired electrons in the complex, it will act as paramagnetic.
In this case, the electronic configuration of cobalt in its ground state is:
$Co = [Ar]4{s^2}3{d^7}$
The electronic configuration of $C{o^{3 + }}$ ion will be:
$Co = [Ar]4{s^0}3{d^6}$
The surrounding ligands are strong field ligands in the complex. Thus, they will pair all the unpaired electrons and the complex will become diamagnetic. Due to this pairing, the hybridization of the complex will be ${d^2}s{p^3}$ and the complex will be a low spin complex.
Thus, this statement is wrong.
(iv) It absorbs light at a longer wavelength as compared to ${[Co(en){(N{H_3})_4}]^{3 + }}$. This statement is wrong because in the presence of a strong field ligand, the pairing energy increases and becomes more than that of the crystal field splitting energy. Thus, the wavelength decreases or becomes shorter as the energy gap between ${t_{2g}}$ and ${e_g}$ orbitals increases.
Thus, the correct options are:
A. It has two geometrical isomers.
B. It will have three geometrical isomers if Bidentate $'en'$ is replaced by two cyanide ligands.
Note: The elements of symmetry play a crucial role in deciding the geometry of the complexes in coordination chemistry. There are basically three elements of symmetry. They are planes of symmetry, center of symmetry and axis of symmetry. If any of these elements of symmetry are found in the complexes, they tend to become optically inactive and cannot rotate a plane polarized light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




