
The correct IUPAC name of tartaric acid is:
(A) 1, 4-dicarboxy-2, 3-dihydroxyethane
(B) α, α-dihydroxybutane-1, 4-dioic acid
(C) 1, 4-dihydroxybutane-2, 3-dioic acid
(D) 2, 3-Dihydroxybutane-1, 4-dioic acid
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint:IUPAC refers to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. The nomenclature which follows the rules set up by this union is called IUPAC nomenclature and chemical compounds are named accordingly.
Complete step by step answer:
The complete IUPAC name of an organic compound consists of:
Secondary prefix + Primary prefix + Word root + Primary suffix + Secondary suffix
For example:

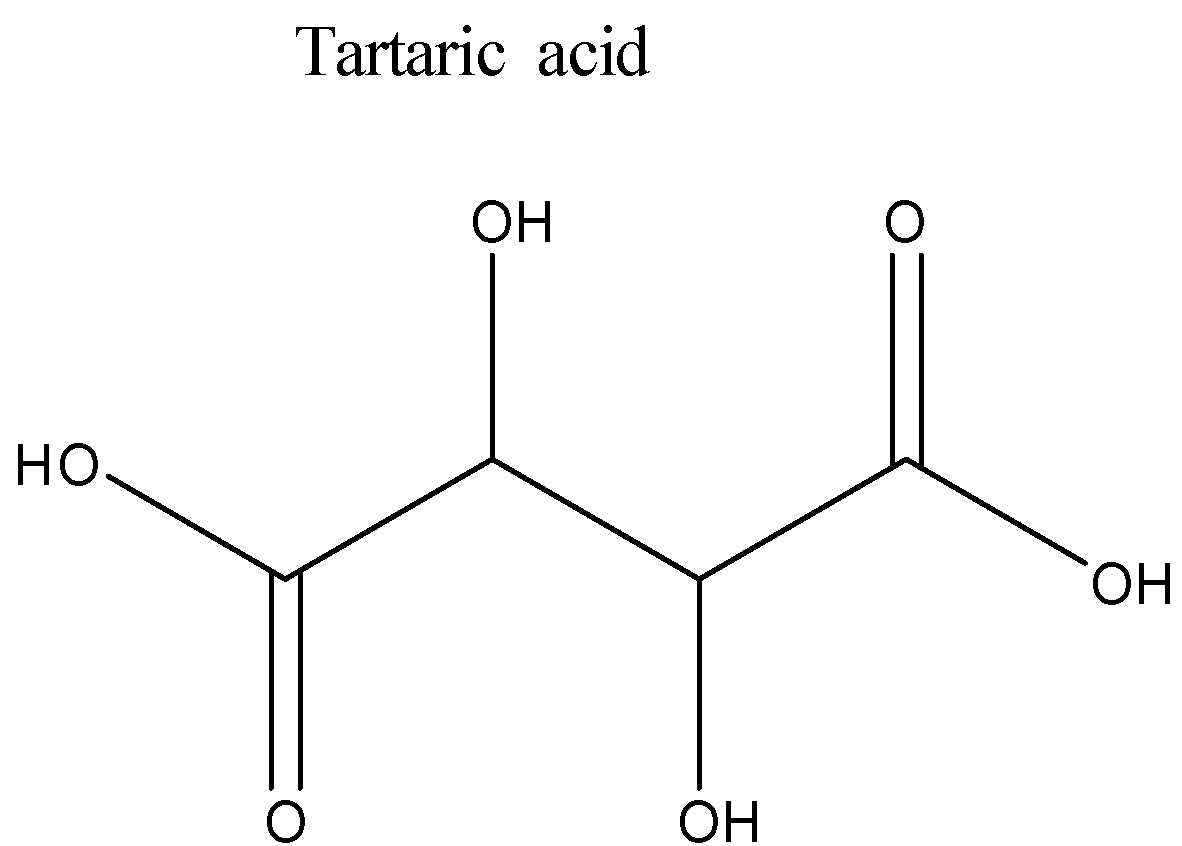
This is an aliphatic compound (with no branching) consisting of hydroxyl and carboxylic acid functional groups. For naming this compound certain IUPAC rules must be followed:
-number the carbon atoms starting with the carboxylic group (since this group is present where the chain is terminating).
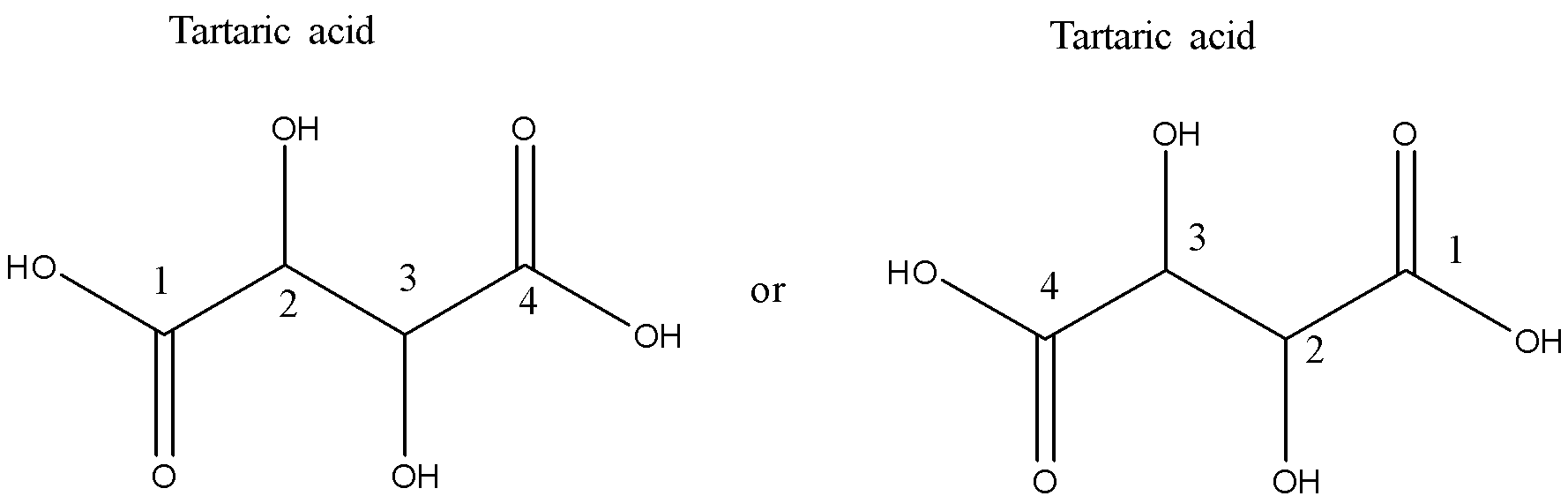
-There are two types of functional groups present in tartaric acid: the hydroxyl group and the carboxylic acid group. We need to decide the principal functional group. Carboxylic acid group is given preference over the hydroxyl functional group and therefore the hydroxyl functional group will be treated as a substituent. Since there are two hydroxyl groups, therefore ‘2, 3-Dihydroxy’ will be the secondary prefix.
- Since this compound is not cyclic, there will be no primary prefix.
-The total number of carbon atoms present in the chain is four. Therefore the word root will be ‘but’.
-This is a saturated hydrocarbon. There are no double or triple bonds present between the carbon atoms. Therefore, the primary suffix will be ‘ane’.
-Tartaric acid contains two carboxylic acid groups; therefore the secondary suffix will be ‘1, 4-dioic acid’.
Therefore the complete IUPAC name of tartaric acid will be (D) 2, 3-Dihydroxybutane-1, 4-dioic acid.
Note:
Tartaric acid actually has stereo centers due to which it will show stereochemical activity. The actual IUPAC name of tartaric acid will also consist of R/S nomenclature if it shows chirality.
Complete step by step answer:
The complete IUPAC name of an organic compound consists of:
Secondary prefix + Primary prefix + Word root + Primary suffix + Secondary suffix
For example:


This is an aliphatic compound (with no branching) consisting of hydroxyl and carboxylic acid functional groups. For naming this compound certain IUPAC rules must be followed:
-number the carbon atoms starting with the carboxylic group (since this group is present where the chain is terminating).

-There are two types of functional groups present in tartaric acid: the hydroxyl group and the carboxylic acid group. We need to decide the principal functional group. Carboxylic acid group is given preference over the hydroxyl functional group and therefore the hydroxyl functional group will be treated as a substituent. Since there are two hydroxyl groups, therefore ‘2, 3-Dihydroxy’ will be the secondary prefix.
- Since this compound is not cyclic, there will be no primary prefix.
-The total number of carbon atoms present in the chain is four. Therefore the word root will be ‘but’.
-This is a saturated hydrocarbon. There are no double or triple bonds present between the carbon atoms. Therefore, the primary suffix will be ‘ane’.
-Tartaric acid contains two carboxylic acid groups; therefore the secondary suffix will be ‘1, 4-dioic acid’.
Therefore the complete IUPAC name of tartaric acid will be (D) 2, 3-Dihydroxybutane-1, 4-dioic acid.
Note:
Tartaric acid actually has stereo centers due to which it will show stereochemical activity. The actual IUPAC name of tartaric acid will also consist of R/S nomenclature if it shows chirality.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




