
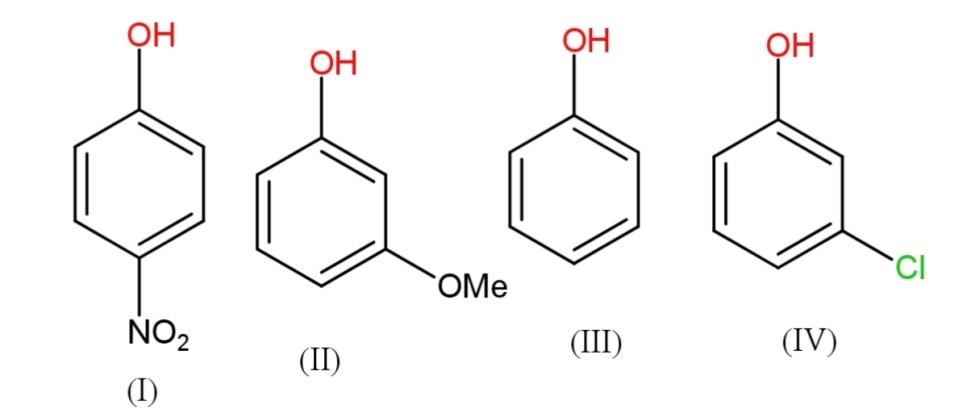
The correct increasing order of reactivity for the following molecules towards electrophilic aromatic substitution is:
A.$I < IV < II < III$
B. $I < IV < III < II$
C. $I < III < II < IV$
D. $I < III < IV < II$

Answer
516.6k+ views
Hint: An electrophile is an electron deficient species and readily reacts with electron dense molecules. Electrophilic aromatic substitution involves an electrophile removing a substituted group of atoms and taking its place. The electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions occur where there is greater electron density.
Complete answer:
An electrophilic aromatic substitution is a substitution reaction where the electrophile attaches on the reacting compound removing the already substituted group. An electrophile is the electron loving species that carry a neutral or a positive charge and are considered electron deficient. Therefore electrophilic substitution reaction occurs when there is more electron density on the reacting compounds.
The factor that affects the electron density on compounds is the inductive effect. The $-I$ effect or the negative inductive effect is responsible for withdrawing electrons from any compound as they consist of electronegative atoms that withdraw the electrons. This reduces the electron density. While, a$+I$effect or positive inductive effect is responsible for donating electrons and increases the electron density on the molecule.
Some $-I$ groups are $N{{O}_{2}},C{{l}^{-}},COOH,B{{r}^{-}}$,etc. while $+I$ groups are methyl, ethyl and other alkyl and alkoxy groups. Thus, $-I$groups will have less reactivity in electrophilic aromatic substitution, therefore the increasing order will have nitrophenol < meta - chlorophenol < phenol < methoxy phenol.
Hence the increasing order of reactivity towards electrophilic aromatic substitution is $ I < IV < III < II$.
So option B is correct.
Note:
The order of $-I $or negative inductive effect is $N{{O}_{2}} > Cl$, therefore nitrophenol has the least reactivity that chloro phenol in electrophilic aromatic substitution. The positive inductive effect is permanent. The negative inductive effect contains molecules with electronegativity difference therefore they create a negative and positive charge on the molecule affecting the electron density.
Complete answer:
An electrophilic aromatic substitution is a substitution reaction where the electrophile attaches on the reacting compound removing the already substituted group. An electrophile is the electron loving species that carry a neutral or a positive charge and are considered electron deficient. Therefore electrophilic substitution reaction occurs when there is more electron density on the reacting compounds.
The factor that affects the electron density on compounds is the inductive effect. The $-I$ effect or the negative inductive effect is responsible for withdrawing electrons from any compound as they consist of electronegative atoms that withdraw the electrons. This reduces the electron density. While, a$+I$effect or positive inductive effect is responsible for donating electrons and increases the electron density on the molecule.
Some $-I$ groups are $N{{O}_{2}},C{{l}^{-}},COOH,B{{r}^{-}}$,etc. while $+I$ groups are methyl, ethyl and other alkyl and alkoxy groups. Thus, $-I$groups will have less reactivity in electrophilic aromatic substitution, therefore the increasing order will have nitrophenol < meta - chlorophenol < phenol < methoxy phenol.
Hence the increasing order of reactivity towards electrophilic aromatic substitution is $ I < IV < III < II$.
So option B is correct.
Note:
The order of $-I $or negative inductive effect is $N{{O}_{2}} > Cl$, therefore nitrophenol has the least reactivity that chloro phenol in electrophilic aromatic substitution. The positive inductive effect is permanent. The negative inductive effect contains molecules with electronegativity difference therefore they create a negative and positive charge on the molecule affecting the electron density.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




