
The correct graph regarding v vs KE (incident)
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
521.7k+ views
Hint: The photoelectric effect occurs as light shines on a metal and causes electrons to be expelled from the metal's surface. Photoemission is another name for this method, and photoelectrons are the electrons that are ejected from the metal. Photoelectrons behave like other electrons in terms of action and properties. The prefix photo- literally indicates that incident light has ejected electrons from a metal surface.
Complete answer: Physicists expected that increasing light intensity would increase the kinetic energy of released photoelectrons, while increasing frequency would increase measured current, based on the wave model of light.
Experiments revealed that raising the light frequency increased photoelectrons' kinetic energy, thus increasing the light intensity increased current.
Physicists expected that increasing light intensity would increase the kinetic energy of released photoelectrons, while increasing frequency would increase measured current, based on the wave model of light.
Experiments found that increasing the light frequency increased the photoelectrons' kinetic energy, while increasing the light intensity increased the current, contrary to expectations.
Einstein suggested that light acted as a stream of particles called photons with an energy of E=hv based on these results.
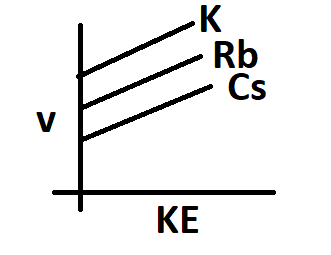
The frequency of incident radiation increases in the order of K > Rb > Cs for a given kinetic energy. The work function of metals also increases in the same order.
The minimum energy needed to remove one electron from a metal is known as the work function (WF) of the metal. Clearly, one of the basic electrical properties of bare and coated metallic surfaces is the WF.
Since alkali metals have a low work feature, electrons are less bound to the atoms. Alkali metals are easier to separate electrons from than other metals.
Hence option A is correct.
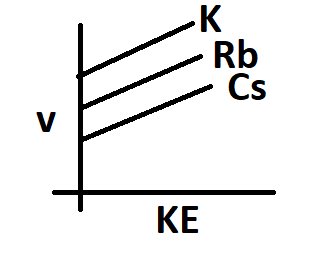
For K=48kJ/mol
Rb=47kJ/mol
Cs=46kJ/mol
Note:
The minimum amount of energy needed to extract an electron to infinity from the surface of a given solid is known as the work function of the substance. In an atomic scale, "immediately" means that the final electron location is far from the surface, but still near enough to the solid to be affected by atmospheric electric fields in the vacuum. The job function is a property of the material's surface rather than a property of the bulk material.
Complete answer: Physicists expected that increasing light intensity would increase the kinetic energy of released photoelectrons, while increasing frequency would increase measured current, based on the wave model of light.
Experiments revealed that raising the light frequency increased photoelectrons' kinetic energy, thus increasing the light intensity increased current.
Physicists expected that increasing light intensity would increase the kinetic energy of released photoelectrons, while increasing frequency would increase measured current, based on the wave model of light.
Experiments found that increasing the light frequency increased the photoelectrons' kinetic energy, while increasing the light intensity increased the current, contrary to expectations.
Einstein suggested that light acted as a stream of particles called photons with an energy of E=hv based on these results.
The frequency of incident radiation increases in the order of K > Rb > Cs for a given kinetic energy. The work function of metals also increases in the same order.
The minimum energy needed to remove one electron from a metal is known as the work function (WF) of the metal. Clearly, one of the basic electrical properties of bare and coated metallic surfaces is the WF.
Since alkali metals have a low work feature, electrons are less bound to the atoms. Alkali metals are easier to separate electrons from than other metals.
Hence option A is correct.

For K=48kJ/mol
Rb=47kJ/mol
Cs=46kJ/mol
Note:
The minimum amount of energy needed to extract an electron to infinity from the surface of a given solid is known as the work function of the substance. In an atomic scale, "immediately" means that the final electron location is far from the surface, but still near enough to the solid to be affected by atmospheric electric fields in the vacuum. The job function is a property of the material's surface rather than a property of the bulk material.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




