
The correct decreasing order of $p{{K}_{b}}$ is:
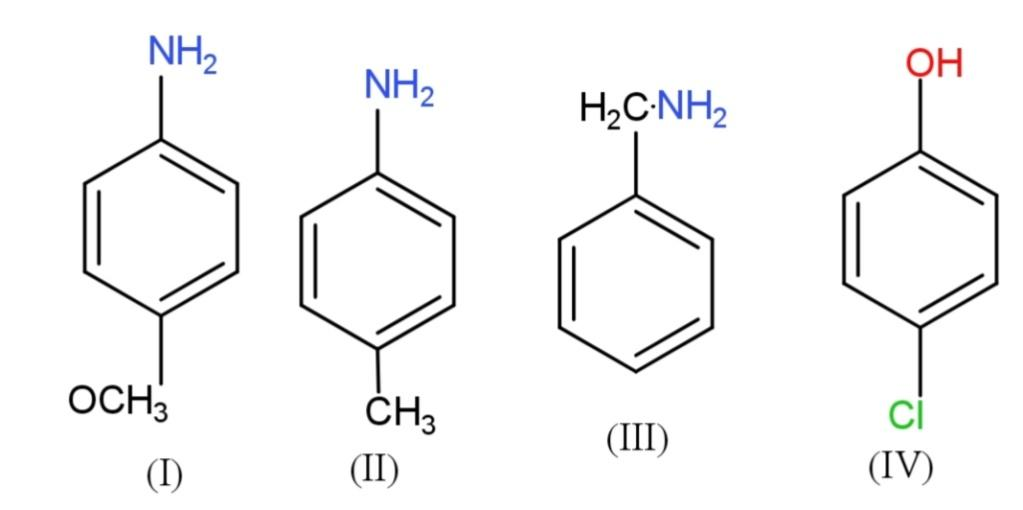
A. $I > II > III > IV$
B. $III > IV > II > I$
C. $II > III > IV > I$
D.$ IV > II > I > III$

Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: Dissociation is the ability to liberate the respective ions as that in a molecule. $p{{K}_{b}}$ is called the base dissociation constant. It tells us the extent of dissociation of a base. This means it tells us the strength of any basic substance. The basicity defines the strength of a base, which is the ability to replace the hydrogen atoms from an acid.
Complete answer:
The strength of any base, which is its basic character and the ability to replace the hydrogen atoms is identified by the dissociation of any basic compound. The dissociation is studied through $p{{K}_{b}}$, called as the base dissociation constant. Larger the value of $p{{K}_{b}}$, stronger is the base.
Now, we have given aromatic compounds with substituted groups, we have to find the decreasing order of $p{{K}_{b}}$, which will also be the decreasing order of their basicity. The basicity of any compound is affected by the inductive effect. The electron withdrawing$\left( -I \right)$groups, increase the acidity, as they are electronegative so, attracts shared pairs of electrons towards themselves that easily removes the hydrogen ions. So, the electron donating $\left( +I \right)$ groups will increase the basicity.
The $-I$ groups are $N{{O}_{2}},C{{l}^{-}},COOH,B{{r}^{-}}$,etc. while $+I$ groups are methyl, ethyl and other alkyl and alkoxy groups. So, more the $+I$ effect, more will be the basicity, therefore the order of decreasing basicity will be $IV > II > I > III$.
Hence, the decreasing order of $p{{K}_{b}}$ is $IV > II > I > III$.
So, option D is correct.
Note:
As $p{{K}_{b}}$, the strength of acids is determined by $p{{K}_{a}}$, the dissociation constants of acids, which tells the ability of an acid to donate hydrogen ions in any solution. The$-I$ effect increases the acidity by easily donating the hydrogen which is the proton as$-\Iota $ groups attract electron pairs toward themselves very strongly creating polarity that is a partial positive and negative character in a bond.
Complete answer:
The strength of any base, which is its basic character and the ability to replace the hydrogen atoms is identified by the dissociation of any basic compound. The dissociation is studied through $p{{K}_{b}}$, called as the base dissociation constant. Larger the value of $p{{K}_{b}}$, stronger is the base.
Now, we have given aromatic compounds with substituted groups, we have to find the decreasing order of $p{{K}_{b}}$, which will also be the decreasing order of their basicity. The basicity of any compound is affected by the inductive effect. The electron withdrawing$\left( -I \right)$groups, increase the acidity, as they are electronegative so, attracts shared pairs of electrons towards themselves that easily removes the hydrogen ions. So, the electron donating $\left( +I \right)$ groups will increase the basicity.
The $-I$ groups are $N{{O}_{2}},C{{l}^{-}},COOH,B{{r}^{-}}$,etc. while $+I$ groups are methyl, ethyl and other alkyl and alkoxy groups. So, more the $+I$ effect, more will be the basicity, therefore the order of decreasing basicity will be $IV > II > I > III$.
Hence, the decreasing order of $p{{K}_{b}}$ is $IV > II > I > III$.
So, option D is correct.
Note:
As $p{{K}_{b}}$, the strength of acids is determined by $p{{K}_{a}}$, the dissociation constants of acids, which tells the ability of an acid to donate hydrogen ions in any solution. The$-I$ effect increases the acidity by easily donating the hydrogen which is the proton as$-\Iota $ groups attract electron pairs toward themselves very strongly creating polarity that is a partial positive and negative character in a bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




