
The coordination numbers of Co and Al in $[Co(Cl){{(en)}_{2}}]Cl$ and ${{K}_{3}}[Al{{({{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}})}_{3}}]$ respectively are:
(en = ethnane-1,2 diamine)
A. 3 and 3
B. 6 and 6
C. 5 and 6
D. 5 and 3
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:. The en ligand( ethane 1-2 diamine) is a chelating ligand. So, instead of 1, it occupies 2 bonds with the central metal atom of the coordination compound. Whereas, other compounds which are non-chelating occupy 1 bond with the central metal atom.
Complete step by step answer:
In order to solve the question, let us find out what chelating ligands are. But before that, let us learn about coordination spheres. In coordination chemistry, the primary coordination sphere refers to the array of molecules and ions which are directly attached to the central metal atom of the sphere. The second coordination sphere consists of molecules and ions that are attached in various ways to the primary coordination sphere. Coordination sphere is the basic part of coordination chemistry which deals with the structure of the compounds and their constitution. The coordination sphere can also be related to the atmosphere of the earth, a surrounding that encloses the whole structure.
In a coordination compound, there is a central metal atom. Now there are other atoms attached to this central atom. These attached atoms/groups of atoms are called ligands. Ligands are an active part of the coordination compound and do not get dissolved into ions like salts do. Generally, ligands bind with one bond. But there are special ligands which occupy a space of 2 or more. These special ligands are called chelating ligands. Ethane 1,2 diamine and ${{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}$ (oxalate) are chelating ligands.
Now, let us look at the structure of the two compounds given in the question:
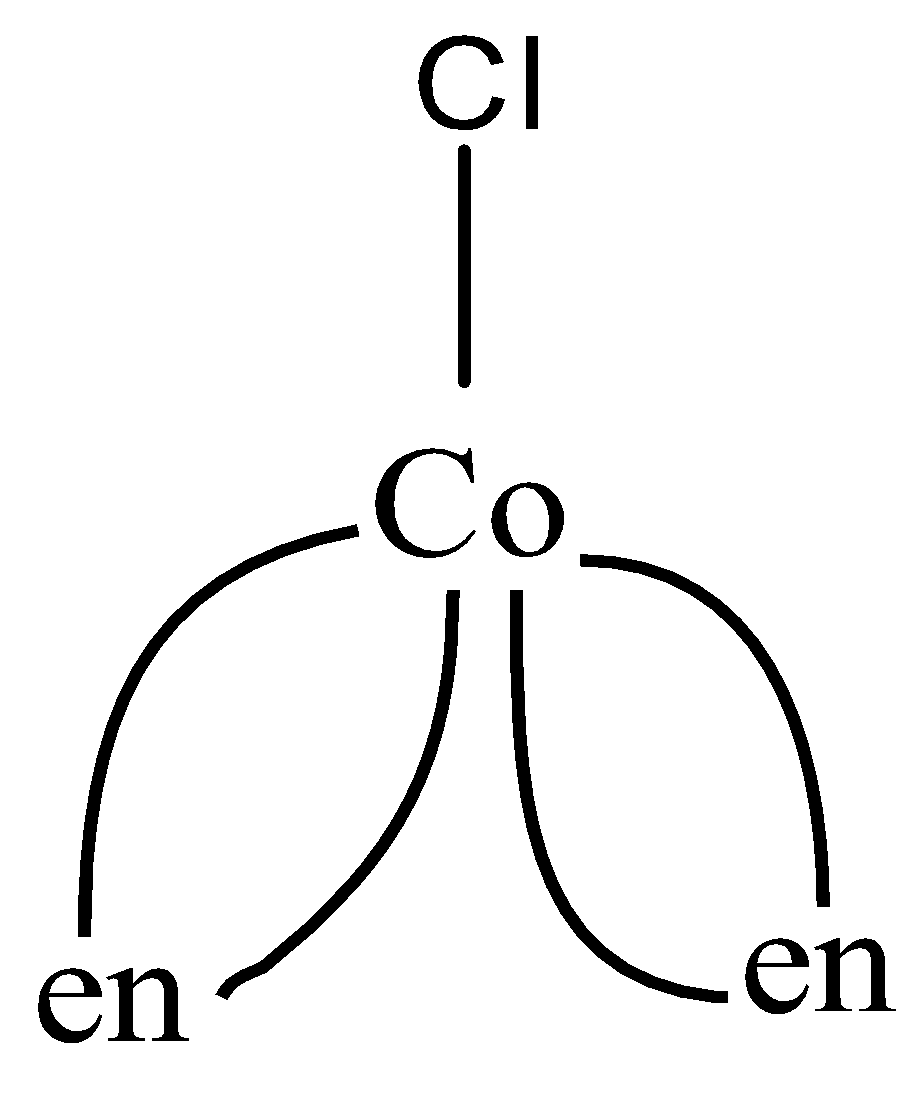
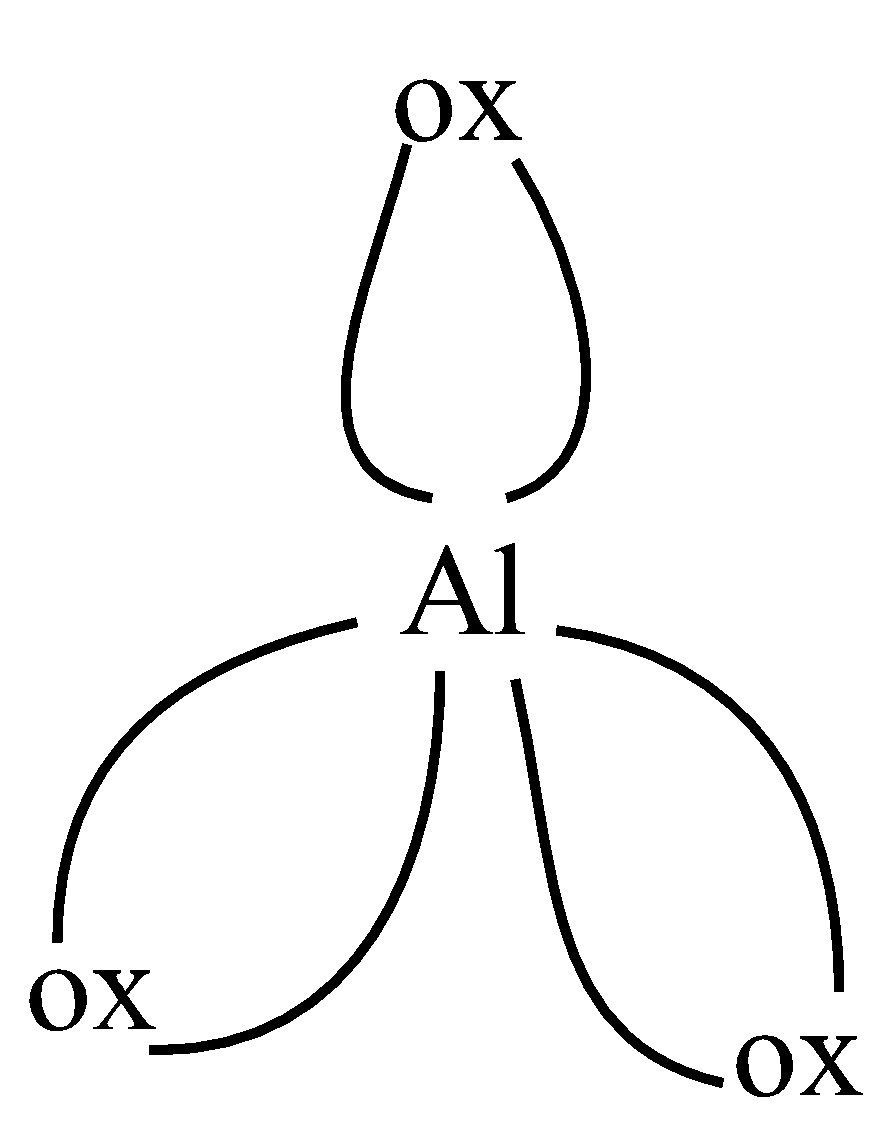
As we can see, in the first figure, coordination number is 5, as 5 bonds are formed and 6 in the second figure, as 6 bonds are formed. So the coordination numbers are 5,6 respectively,
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Generally, it is observed that the coordination compounds which have chelating ligands attached to them are more stable than normal ligands. It is due to a phenomenon called the “chelating effect”. More the number of chelating ligands implies more stability of the coordination compound.
Complete step by step answer:
In order to solve the question, let us find out what chelating ligands are. But before that, let us learn about coordination spheres. In coordination chemistry, the primary coordination sphere refers to the array of molecules and ions which are directly attached to the central metal atom of the sphere. The second coordination sphere consists of molecules and ions that are attached in various ways to the primary coordination sphere. Coordination sphere is the basic part of coordination chemistry which deals with the structure of the compounds and their constitution. The coordination sphere can also be related to the atmosphere of the earth, a surrounding that encloses the whole structure.
In a coordination compound, there is a central metal atom. Now there are other atoms attached to this central atom. These attached atoms/groups of atoms are called ligands. Ligands are an active part of the coordination compound and do not get dissolved into ions like salts do. Generally, ligands bind with one bond. But there are special ligands which occupy a space of 2 or more. These special ligands are called chelating ligands. Ethane 1,2 diamine and ${{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}$ (oxalate) are chelating ligands.
Now, let us look at the structure of the two compounds given in the question:


As we can see, in the first figure, coordination number is 5, as 5 bonds are formed and 6 in the second figure, as 6 bonds are formed. So the coordination numbers are 5,6 respectively,
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Generally, it is observed that the coordination compounds which have chelating ligands attached to them are more stable than normal ligands. It is due to a phenomenon called the “chelating effect”. More the number of chelating ligands implies more stability of the coordination compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




